Frequent persons on Canada's street signs
countries
463 names / 12255 streets
Queen Victoria
 334
Victoria was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days—which was longer than those of any of her...
334
Victoria was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days—which was longer than those of any of her...
Mary, mother of Jesus
 278
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under various titles such as virgin or queen, many of...
278
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under various titles such as virgin or queen, many of...
Saint Joseph
 258
Joseph was a 1st-century Jewish man of Nazareth who, according to the canonical Gospels, was married to Mary, the mother of Jesus, and was the legal father of Jesus.
258
Joseph was a 1st-century Jewish man of Nazareth who, according to the canonical Gospels, was married to Mary, the mother of Jesus, and was the legal father of Jesus.
John Graves Simcoe
 237
John Graves Simcoe was a British Army general and the first lieutenant governor of Upper Canada from 1791 until 1796 in southern Ontario and the watersheds of Georgian Bay and Lake Superior. He...
237
John Graves Simcoe was a British Army general and the first lieutenant governor of Upper Canada from 1791 until 1796 in southern Ontario and the watersheds of Georgian Bay and Lake Superior. He...
William IV
 212
William IV was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 26 June 1830 until his death in 1837. The third son of George III, William succeeded his elder brother...
212
William IV was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 26 June 1830 until his death in 1837. The third son of George III, William succeeded his elder brother...
Saint Lawrence
 210
Saint Lawrence or Laurence was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the persecution of the Christians that the Roman Emperor Valerian ordered in 258.
210
Saint Lawrence or Laurence was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the persecution of the Christians that the Roman Emperor Valerian ordered in 258.
Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
 210
Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha was the husband of Queen Victoria. As such, he was consort of the British monarch from their marriage on 10 February 1840, until his death in 1861. He received...
210
Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha was the husband of Queen Victoria. As such, he was consort of the British monarch from their marriage on 10 February 1840, until his death in 1861. He received...
Saint Peter
 209
Saint Peter, also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ and one of the first leaders of the early Christian Church. He...
209
Saint Peter, also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ and one of the first leaders of the early Christian Church. He...
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington
 186
Field Marshal Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, was an Anglo-Irish statesman, soldier, and Tory politician who was one of the leading military and political figures of 19th-century Britain,...
186
Field Marshal Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, was an Anglo-Irish statesman, soldier, and Tory politician who was one of the leading military and political figures of 19th-century Britain,...
Elizabeth II
 186
Elizabeth II was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states over the course of her lifetime...
186
Elizabeth II was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states over the course of her lifetime...
Alexander Campbell (Canadian senator)
 185
Sir Alexander Campbell was an Upper Canadian statesman and a father of Canadian Confederation.
185
Sir Alexander Campbell was an Upper Canadian statesman and a father of Canadian Confederation.
John the Apostle
 183
John the Apostle, also known as Saint John the Beloved and, in Eastern Orthodox Christianity, Saint John the Theologian, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament....
183
John the Apostle, also known as Saint John the Beloved and, in Eastern Orthodox Christianity, Saint John the Theologian, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament....
Woodrow Wilson
 169
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president...
169
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president...
Louis IX of France
 154
Louis IX, commonly revered as Saint Louis, was King of France from 1226 until his death in 1270. He is widely recognized as the most distinguished of the Direct Capetians. Following the death of his...
154
Louis IX, commonly revered as Saint Louis, was King of France from 1226 until his death in 1270. He is widely recognized as the most distinguished of the Direct Capetians. Following the death of his...
Simon Fraser (explorer)
 148
Simon Fraser was a Canadian explorer and fur trader who charted much of what is now the Canadian province of British Columbia. He also built the first European settlement in British Columbia.
148
Simon Fraser was a Canadian explorer and fur trader who charted much of what is now the Canadian province of British Columbia. He also built the first European settlement in British Columbia.
Jacques Cartier
 146
Jacques Cartier was a French-Breton maritime explorer for France. Jacques Cartier was the first European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River,...
146
Jacques Cartier was a French-Breton maritime explorer for France. Jacques Cartier was the first European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River,...
Saint George
 138
Saint George, also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition, he was a soldier in the Roman army. Of Cappadocian Greek origin,...
138
Saint George, also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition, he was a soldier in the Roman army. Of Cappadocian Greek origin,...
Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson
 136
Vice-Admiral Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, 1st Duke of Bronte was a British flag officer in the Royal Navy. His inspirational leadership, grasp of strategy and unconventional tactics brought...
136
Vice-Admiral Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, 1st Duke of Bronte was a British flag officer in the Royal Navy. His inspirational leadership, grasp of strategy and unconventional tactics brought...
Wilfrid Laurier
 136
Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier, was a Canadian lawyer, statesman, and politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Canada from 1896 to 1911. The first French Canadian prime minister, his...
136
Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier, was a Canadian lawyer, statesman, and politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Canada from 1896 to 1911. The first French Canadian prime minister, his...
Paul the Apostle
 132
Paul, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is...
132
Paul, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is...
Samuel de Champlain
 131
Samuel de Champlain was a French explorer, navigator, cartographer, draftsman, soldier, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He made between 21 and 29 trips across the Atlantic Ocean,...
131
Samuel de Champlain was a French explorer, navigator, cartographer, draftsman, soldier, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He made between 21 and 29 trips across the Atlantic Ocean,...
John F. Kennedy
 129
John Fitzgerald Kennedy, often referred to as JFK, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the youngest...
129
John Fitzgerald Kennedy, often referred to as JFK, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the youngest...
Thomas Bruce, 7th Earl of Elgin
 128
Thomas Bruce, 7th Earl of Elgin and 11th Earl of Kincardine,, often known as Lord Elgin, was a British nobleman, diplomat, and collector, known primarily for the controversial procurement of marble...
128
Thomas Bruce, 7th Earl of Elgin and 11th Earl of Kincardine,, often known as Lord Elgin, was a British nobleman, diplomat, and collector, known primarily for the controversial procurement of marble...
James Douglas (governor)
 123
Sir James Douglas, was a Canadian fur trader and politician who became the first Governor of the Colony of British Columbia. He is often credited as "The Father of British Columbia". He was...
123
Sir James Douglas, was a Canadian fur trader and politician who became the first Governor of the Colony of British Columbia. He is often credited as "The Father of British Columbia". He was...
Saint Anne
 120
According to apocrypha, as well as Christian and Islamic tradition, Saint Anne was the mother of Mary, the wife of Joachim and the maternal grandmother of Jesus. Mary's mother is not named in the...
120
According to apocrypha, as well as Christian and Islamic tradition, Saint Anne was the mother of Mary, the wife of Joachim and the maternal grandmother of Jesus. Mary's mother is not named in the...
Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany
 113
Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany was the second son of George III, King of the United Kingdom and Hanover, and his consort Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz. A soldier by profession, from...
113
Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany was the second son of George III, King of the United Kingdom and Hanover, and his consort Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz. A soldier by profession, from...
Edward VII
 111
Edward VII was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
111
Edward VII was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
Winston Churchill
 105
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again...
105
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again...
Edward Smith-Stanley, 14th Earl of Derby
 103
Edward George Geoffrey Smith-Stanley, 14th Earl of Derby,, known as Lord Stanley from 1834 to 1851, was a British statesman and Conservative politician who served three times as Prime Minister of the...
103
Edward George Geoffrey Smith-Stanley, 14th Earl of Derby,, known as Lord Stanley from 1834 to 1851, was a British statesman and Conservative politician who served three times as Prime Minister of the...
Frederick Hamilton-Temple-Blackwood, 1st Marquess of Dufferin and Ava
 102
Frederick Temple Hamilton-Temple-Blackwood, 1st Marquess of Dufferin and Ava,, was a British public servant and prominent member of Victorian society. In his youth he was a popular figure in the...
102
Frederick Temple Hamilton-Temple-Blackwood, 1st Marquess of Dufferin and Ava,, was a British public servant and prominent member of Victorian society. In his youth he was a popular figure in the...
André Bessette
 98
André Bessette, C.S.C., commonly known as Brother André and since his canonization as Saint André of Montreal, was a lay brother of the Congregation of Holy Cross and a significant figure of the...
98
André Bessette, C.S.C., commonly known as Brother André and since his canonization as Saint André of Montreal, was a lay brother of the Congregation of Holy Cross and a significant figure of the...
John the Baptist
 93
John the Baptist was a Jewish preacher active in the area of the Jordan River in the early 1st century AD. He is also known as Saint John the Forerunner in Eastern Orthodoxy, John the Immerser in...
93
John the Baptist was a Jewish preacher active in the area of the Jordan River in the early 1st century AD. He is also known as Saint John the Forerunner in Eastern Orthodoxy, John the Immerser in...
Peter Russell
 92
Peter Russell may refer to:Patricia "Peter" Russell (1910–2004), third wife of Bertrand Russell
Peter Edward Lionel Russell (1913–2006) British historian
Peter H. Russell, Canadian political...
92
Peter Russell may refer to:Patricia "Peter" Russell (1910–2004), third wife of Bertrand Russell
Peter Edward Lionel Russell (1913–2006) British historian
Peter H. Russell, Canadian political...
Félix Leclerc
 90
Félix Leclerc, was a French-Canadian singer-songwriter, poet, writer, actor and Québécois political activist. He was made an Officer of the Order of Canada on December 20, 1968. Leclerc was...
90
Félix Leclerc, was a French-Canadian singer-songwriter, poet, writer, actor and Québécois political activist. He was made an Officer of the Order of Canada on December 20, 1968. Leclerc was...
Wilfrid Pelletier
 90
Joseph Louis Wilfrid Pelletier, was a Canadian conductor, pianist, composer, and arts administrator. He was instrumental in establishing the Montreal Symphony Orchestra, serving as the orchestra's...
90
Joseph Louis Wilfrid Pelletier, was a Canadian conductor, pianist, composer, and arts administrator. He was instrumental in establishing the Montreal Symphony Orchestra, serving as the orchestra's...
Émile Bouchard
 80
Joseph Émile Alcide Bouchard was a Canadian ice hockey player who played defence with the Montreal Canadiens in the National Hockey League from 1941 to 1956. He is a member of the Hockey Hall of...
80
Joseph Émile Alcide Bouchard was a Canadian ice hockey player who played defence with the Montreal Canadiens in the National Hockey League from 1941 to 1956. He is a member of the Hockey Hall of...
Marc-Aurèle Fortin
 73
Marc-Aurèle Fortin was a Québécois painter, known best for paintings that convey the charm of small-town Quebec.
73
Marc-Aurèle Fortin was a Québécois painter, known best for paintings that convey the charm of small-town Quebec.
Benjamin Franklin
 71
Benjamin Franklin was an American polymath, a leading writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Among the most influential intellectuals of his...
71
Benjamin Franklin was an American polymath, a leading writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Among the most influential intellectuals of his...
Renaude Lapointe
 71
Louise Marguerite Renaude Lapointe, was a Canadian journalist and a Senator. She was among the first Canadian women to work as a professional journalist and the first French-Canadian woman to preside...
71
Louise Marguerite Renaude Lapointe, was a Canadian journalist and a Senator. She was among the first Canadian women to work as a professional journalist and the first French-Canadian woman to preside...
Pierre-Évariste Leblanc
 71
Sir Pierre-Évariste Leblanc, was born in Saint-Martin.
71
Sir Pierre-Évariste Leblanc, was born in Saint-Martin.
Michael (archangel)
 70
Michael, also called Saint Michael the Archangel, Archangel Michael and Saint Michael the Taxiarch is an archangel in Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baha'i faith. The earliest surviving...
70
Michael, also called Saint Michael the Archangel, Archangel Michael and Saint Michael the Taxiarch is an archangel in Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baha'i faith. The earliest surviving...
Louis Hébert
 69
Louis Hébert is widely considered the first European apothecary in the region that would later become Canada, as well as the first European to farm in said region. He was born around 1575 at 129 de...
69
Louis Hébert is widely considered the first European apothecary in the region that would later become Canada, as well as the first European to farm in said region. He was born around 1575 at 129 de...
Honoré Mercier
 68
Honoré Mercier was a Canadian lawyer, journalist and politician in Quebec. He was the ninth premier of Quebec from January 27, 1887, to December 21, 1891, as leader of the Parti National or Quebec...
68
Honoré Mercier was a Canadian lawyer, journalist and politician in Quebec. He was the ninth premier of Quebec from January 27, 1887, to December 21, 1891, as leader of the Parti National or Quebec...
Neil Armstrong
 68
Neil Alden Armstrong was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer who in 1969 became the first person to walk on the Moon. He was also a naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor.
68
Neil Alden Armstrong was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer who in 1969 became the first person to walk on the Moon. He was also a naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor.
Georges Vanier
 66
Georges-Philias Vanier was a Canadian military officer and diplomat who served as governor general of Canada, the first Quebecer and second Canadian-born person to hold the position.
66
Georges-Philias Vanier was a Canadian military officer and diplomat who served as governor general of Canada, the first Quebecer and second Canadian-born person to hold the position.
Thomas the Apostle
 66
Thomas the Apostle, also known as Didymus, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Thomas is commonly known as "Doubting Thomas" because he initially doubted the...
66
Thomas the Apostle, also known as Didymus, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Thomas is commonly known as "Doubting Thomas" because he initially doubted the...
Pierre Boucher
 66
Pierre Boucher de Boucherville was a French settler, soldier, officer, naturalist, official, governor, and ennobled aristocrat in Nouvelle-France or New France.
66
Pierre Boucher de Boucherville was a French settler, soldier, officer, naturalist, official, governor, and ennobled aristocrat in Nouvelle-France or New France.
Andrew the Apostle
 65
Andrew the Apostle, also called Saint Andrew, was an apostle of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was a fisherman and one of the Twelve Apostles chosen by Jesus. The title First-Called stems...
65
Andrew the Apostle, also called Saint Andrew, was an apostle of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was a fisherman and one of the Twelve Apostles chosen by Jesus. The title First-Called stems...
René Lévesque
 65
René Lévesque was a Canadian politician and journalist who served as the 23rd premier of Quebec from 1976 to 1985. He was the first Québécois political leader since Confederation to seek, through a...
65
René Lévesque was a Canadian politician and journalist who served as the 23rd premier of Quebec from 1976 to 1985. He was the first Québécois political leader since Confederation to seek, through a...
Bernard Montgomery
 64
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein,, nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and...
64
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein,, nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and...
Antoine Labelle
 62
François-Xavier-Antoine Labelle was a Roman Catholic priest and the person principally responsible for the settlement of the Laurentians. He is also referred to as "Curé Labelle" and sometimes, the...
62
François-Xavier-Antoine Labelle was a Roman Catholic priest and the person principally responsible for the settlement of the Laurentians. He is also referred to as "Curé Labelle" and sometimes, the...
Denis of Paris
 61
Denis of Paris was a 3rd-century Christian martyr and saint. According to his hagiographies, he was bishop of Paris in the third century and, together with his companions Rusticus and Eleutherius,...
61
Denis of Paris was a 3rd-century Christian martyr and saint. According to his hagiographies, he was bishop of Paris in the third century and, together with his companions Rusticus and Eleutherius,...
Ozias Leduc
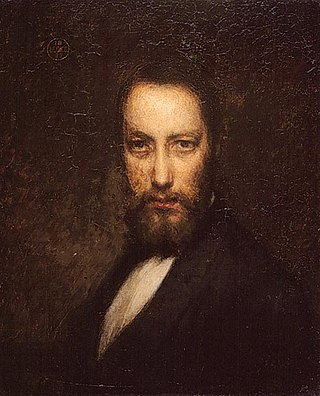 60
Ozias Leduc is one of Quebec's early painters. He was born in Saint-Hilaire-de-Rouville. Leduc produced many portraits and landscapes.
60
Ozias Leduc is one of Quebec's early painters. He was born in Saint-Hilaire-de-Rouville. Leduc produced many portraits and landscapes.
Étienne Parent
 59
Étienne Parent was a Canadian journalist, politician and government official. A French-Canadian nationalist, he wrote extensively on political theory and governance during the 1820s and 1830s in...
59
Étienne Parent was a Canadian journalist, politician and government official. A French-Canadian nationalist, he wrote extensively on political theory and governance during the 1820s and 1830s in...
Jean Paul Lemieux
 57
Jean Paul Lemieux, was one of the foremost twentieth century painters in Canada. He worked in several different styles, as represented by his five artistic periods.
57
Jean Paul Lemieux, was one of the foremost twentieth century painters in Canada. He worked in several different styles, as represented by his five artistic periods.
Isaac Newton
 56
Sir Isaac Newton was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author who was described in his time as a natural philosopher. He was a key...
56
Sir Isaac Newton was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author who was described in his time as a natural philosopher. He was a key...
Jean-Jacques Bertrand
 55
Jean-Jacques Bertrand was the 21st premier of Quebec, from October 2, 1968, to May 12, 1970. He led the Union Nationale party.
55
Jean-Jacques Bertrand was the 21st premier of Quebec, from October 2, 1968, to May 12, 1970. He led the Union Nationale party.
Thérèse of Lisieux
 54
Therese of Lisieux, also known as Saint Therese of the Child Jesus and the Holy Face, was a French Discalced Carmelite who is widely venerated in modern times. She is popularly known in English as...
54
Therese of Lisieux, also known as Saint Therese of the Child Jesus and the Holy Face, was a French Discalced Carmelite who is widely venerated in modern times. She is popularly known in English as...
Louis-Joseph Papineau
 54
Louis-Joseph Papineau, born in Montreal, Quebec, was a politician, lawyer, and the landlord of the seigneurie de la Petite-Nation. He was the leader of the reformist Patriote movement before the...
54
Louis-Joseph Papineau, born in Montreal, Quebec, was a politician, lawyer, and the landlord of the seigneurie de la Petite-Nation. He was the leader of the reformist Patriote movement before the...
Abraham Lincoln
 53
Abraham Lincoln was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman, who served as the 16th president of the United States, from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the United States...
53
Abraham Lincoln was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman, who served as the 16th president of the United States, from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the United States...
Saint Patrick
 52
Saint Patrick was a fifth-century Romano-British Christian missionary and bishop in Ireland. Known as the "Apostle of Ireland", he is the primary patron saint of Ireland, the other patron saints...
52
Saint Patrick was a fifth-century Romano-British Christian missionary and bishop in Ireland. Known as the "Apostle of Ireland", he is the primary patron saint of Ireland, the other patron saints...
Pierre Laporte
 51
Pierre Laporte was a Canadian lawyer, journalist and politician. He was deputy premier of the province of Quebec when he was kidnapped and murdered by members of the Front de libération du Québec...
51
Pierre Laporte was a Canadian lawyer, journalist and politician. He was deputy premier of the province of Quebec when he was kidnapped and murdered by members of the Front de libération du Québec...
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
 51
Jean-Jacques Rousseau was a Genevan philosopher (philosophe), writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects...
51
Jean-Jacques Rousseau was a Genevan philosopher (philosophe), writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects...
Clement of Rome
 50
Clement of Rome, also known as Pope Clement I, was the bishop of Rome in the late first century AD. He is listed by Irenaeus and Tertullian as the bishop of Rome, holding office from 88 AD to his...
50
Clement of Rome, also known as Pope Clement I, was the bishop of Rome in the late first century AD. He is listed by Irenaeus and Tertullian as the bishop of Rome, holding office from 88 AD to his...
Pierre-Stanislas Bédard
 50
Pierre-Stanislas Bédard was a lawyer, judge, journalist and political figure in Lower Canada.
50
Pierre-Stanislas Bédard was a lawyer, judge, journalist and political figure in Lower Canada.
Philip the Apostle
 49
Philip the Apostle was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Later Christian traditions describe Philip as the apostle who preached in Greece, Syria, and Asia-Minor.
49
Philip the Apostle was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Later Christian traditions describe Philip as the apostle who preached in Greece, Syria, and Asia-Minor.
Marie-Victorin Kirouac
 48
Brother Marie-Victorin, F.S.C., was a Canadian member of Brothers of the Christian Schools and a noted botanist in Quebec, Canada. He is known as the father of the Botanical Garden of Montreal.
48
Brother Marie-Victorin, F.S.C., was a Canadian member of Brothers of the Christian Schools and a noted botanist in Quebec, Canada. He is known as the father of the Botanical Garden of Montreal.
Catherine of Alexandria
 47
Catherine of Alexandria, also spelled Katherine is, according to tradition, a Christian saint and virgin, who was martyred in the early fourth century at the hands of the emperor Maxentius. According...
47
Catherine of Alexandria, also spelled Katherine is, according to tradition, a Christian saint and virgin, who was martyred in the early fourth century at the hands of the emperor Maxentius. According...
Isidore of Seville
 46
Isidore of Seville was a Hispano-Roman scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of the ancient...
46
Isidore of Seville was a Hispano-Roman scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of the ancient...
Napoleon
 44
Napoleon Bonaparte, later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French emperor and military commander who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the...
44
Napoleon Bonaparte, later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French emperor and military commander who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the...
James the Great
 41
James the Great was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was the second of the apostles to die, and the first to be martyred. Saint James is the patron saint of...
41
James the Great was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was the second of the apostles to die, and the first to be martyred. Saint James is the patron saint of...
Calixa Lavallée
 41
Calixa Lavallée was a Canadian musician and Union Army band musician during the American Civil War. He was born in the Province of Canada. He is best known for composing the music for "O Canada",...
41
Calixa Lavallée was a Canadian musician and Union Army band musician during the American Civil War. He was born in the Province of Canada. He is best known for composing the music for "O Canada",...
Matthew the Apostle
 40
Matthew the Apostle is named in the New Testament as one of the twelve apostles of Jesus. According to Christian traditions, he was also one of the four Evangelists as author of the Gospel of...
40
Matthew the Apostle is named in the New Testament as one of the twelve apostles of Jesus. According to Christian traditions, he was also one of the four Evangelists as author of the Gospel of...
William Chapman (poet)
 39
George William Albert Chapman, né George William Alphred, was a Canadian poet.
39
George William Albert Chapman, né George William Alphred, was a Canadian poet.
Jean Lesage
 39
Jean Lesage was a Canadian lawyer and politician from Quebec. He served as the 19th premier of Quebec from July 5, 1960, to June 16, 1966. Alongside Georges-Émile Lapalme, René Lévesque and others,...
39
Jean Lesage was a Canadian lawyer and politician from Quebec. He served as the 19th premier of Quebec from July 5, 1960, to June 16, 1966. Alongside Georges-Émile Lapalme, René Lévesque and others,...
Saint Cecilia
 39
Saint Cecilia, also spelled Cecelia, was a Roman virgin martyr and is venerated in Catholic, Orthodox, Anglican, and some Lutheran churches, such as the Church of Sweden. She became the patroness of...
39
Saint Cecilia, also spelled Cecelia, was a Roman virgin martyr and is venerated in Catholic, Orthodox, Anglican, and some Lutheran churches, such as the Church of Sweden. She became the patroness of...
Jean Marchand
 39
Jean Marchand was a French Canadian public figure, trade unionist and politician in Quebec, Canada.
39
Jean Marchand was a French Canadian public figure, trade unionist and politician in Quebec, Canada.
Félix-Antoine Savard
 38
Félix-Antoine Savard, was a Canadian priest, academic, poet, novelist and folklorist.
38
Félix-Antoine Savard, was a Canadian priest, academic, poet, novelist and folklorist.
Augustine of Hippo
 37
Augustine of Hippo, also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings influenced the...
37
Augustine of Hippo, also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings influenced the...
James Buchanan
 37
James Buchanan Jr. was an American lawyer, diplomat, and politician. He served as the 15th president of the United States from 1857 to 1861, as the secretary of State from 1845 to 1849, and...
37
James Buchanan Jr. was an American lawyer, diplomat, and politician. He served as the 15th president of the United States from 1857 to 1861, as the secretary of State from 1845 to 1849, and...
Alfred DesRochers
 37
Alfred DesRochers est un poète québécois.
37
Alfred DesRochers est un poète québécois.
Damase Potvin
 36
Damase Potvin was a writer and journalist born in Bagotville. He is the son of Charles Potvin and Julie Hudon.
36
Damase Potvin was a writer and journalist born in Bagotville. He is the son of Charles Potvin and Julie Hudon.
Alexandre Dumas
 36
Alexandre Dumas, also known as Alexandre Dumas père, was a French novelist and playwright.
36
Alexandre Dumas, also known as Alexandre Dumas père, was a French novelist and playwright.
Fernand Dumont
 36
Fernand Dumont was a Canadian sociologist, philosopher, theologian, and poet from Quebec. A longtime professor at Université Laval, he won the Governor General's Award for French-language non-fiction...
36
Fernand Dumont was a Canadian sociologist, philosopher, theologian, and poet from Quebec. A longtime professor at Université Laval, he won the Governor General's Award for French-language non-fiction...
Ernest Cormier
 36
Ernest Cormier OC was a Canadian engineer and architect. He spent much of his career in the Montreal area, designing notable examples of Art Deco architecture, including the Université de Montréal...
36
Ernest Cormier OC was a Canadian engineer and architect. He spent much of his career in the Montreal area, designing notable examples of Art Deco architecture, including the Université de Montréal...
Francis Xavier
 35
Francis Xavier, SJ, venerated as Saint Francis Xavier, was a Spanish Catholic missionary and saint who co-founded the Society of Jesus and, as a representative of the Portuguese Empire, led the first...
35
Francis Xavier, SJ, venerated as Saint Francis Xavier, was a Spanish Catholic missionary and saint who co-founded the Society of Jesus and, as a representative of the Portuguese Empire, led the first...
George Washington
 35
George Washington was an American Founding Father, military officer, and politician who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Second Continental...
35
George Washington was an American Founding Father, military officer, and politician who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Second Continental...
Antonio Barrette
 34
Antonio J. Barrette was a Quebec politician born in Joliette, Quebec, Canada, who became the 18th Premier of Quebec.
34
Antonio J. Barrette was a Quebec politician born in Joliette, Quebec, Canada, who became the 18th Premier of Quebec.
André Mathieu
 33
André Mathieu was a Canadian pianist and composer.
33
André Mathieu was a Canadian pianist and composer.
Nérée Beauchemin
 33
Charles-Nérée Beauchemin was a French Canadian regionalist poet and physician from Yamachiche, near Trois-Rivières, Quebec. He was part of Quebec's Le Terroir school of poetry.
33
Charles-Nérée Beauchemin was a French Canadian regionalist poet and physician from Yamachiche, near Trois-Rivières, Quebec. He was part of Quebec's Le Terroir school of poetry.
Jean de Brébeuf
 32
Jean de Brébeuf, SJ was a French Jesuit missionary who travelled to New France (Canada) in 1625. There he worked primarily with the Huron for the rest of his life, except for a few years in France...
32
Jean de Brébeuf, SJ was a French Jesuit missionary who travelled to New France (Canada) in 1625. There he worked primarily with the Huron for the rest of his life, except for a few years in France...
Jacques Marquette
 31
Jacques Marquette, S.J., sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded...
31
Jacques Marquette, S.J., sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded...
Seneca the Younger
 31
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Younger, usually known mononymously as Seneca, was a Stoic philosopher of Ancient Rome, a statesman, dramatist, and in one work, satirist, from the post-Augustan age of...
31
Lucius Annaeus Seneca the Younger, usually known mononymously as Seneca, was a Stoic philosopher of Ancient Rome, a statesman, dramatist, and in one work, satirist, from the post-Augustan age of...
James Clerk Maxwell
 31
James Clerk Maxwell was a Scottish physicist with broad interests who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity,...
31
James Clerk Maxwell was a Scottish physicist with broad interests who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity,...
Joseph-Adolphe Chapleau
 31
Sir Joseph-Adolphe Chapleau, born in Sainte-Thérèse, Quebec, was a French-Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 7th Lieutenant Governor of Quebec from 1892 to 1898.
31
Sir Joseph-Adolphe Chapleau, born in Sainte-Thérèse, Quebec, was a French-Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 7th Lieutenant Governor of Quebec from 1892 to 1898.
Antoine Gérin-Lajoie
 31
Antoine Gérin-Lajoie was a Québécois Canadian lawyer, poet and novelist.
31
Antoine Gérin-Lajoie was a Québécois Canadian lawyer, poet and novelist.
Lomer Gouin
 31
Sir Jean Lomer Gouin, was a Canadian politician. He served as 13th premier of Quebec, as a Cabinet minister in the federal government of Canada, and as the 15th lieutenant governor of Quebec.
31
Sir Jean Lomer Gouin, was a Canadian politician. He served as 13th premier of Quebec, as a Cabinet minister in the federal government of Canada, and as the 15th lieutenant governor of Quebec.
André Prévost (composer)
 31
André Prévost, was a Canadian composer and music educator. He was awarded the Canadian Music Council Medal in 1977 and in 1985 he was made an Officer of the Order of Canada. He also received the...
31
André Prévost, was a Canadian composer and music educator. He was awarded the Canadian Music Council Medal in 1977 and in 1985 he was made an Officer of the Order of Canada. He also received the...
Mark the Evangelist
 31
Mark the Evangelist also known as John Mark or Saint Mark, is the person who is traditionally ascribed to be the author of the Gospel of Mark. Modern Bible scholars have concluded that the Gospel of...
31
Mark the Evangelist also known as John Mark or Saint Mark, is the person who is traditionally ascribed to be the author of the Gospel of Mark. Modern Bible scholars have concluded that the Gospel of...
Olivar Asselin
 30
Olivar Asselin was a writer and journalist in Quebec, Canada. He was a prominent nationalist, pamphleteer and polemist.
30
Olivar Asselin was a writer and journalist in Quebec, Canada. He was a prominent nationalist, pamphleteer and polemist.
Louise Carrier
 30
Louise Carrier was a Canadian artist, known for her body of work including portraits, and for her commissions for the decoration of churches.
30
Louise Carrier was a Canadian artist, known for her body of work including portraits, and for her commissions for the decoration of churches.
Benedict of Nursia
 30
Benedict of Nursia, often known as Saint Benedict, was an Italian Christian monk, writer, and theologian. He is venerated in the Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodox...
30
Benedict of Nursia, often known as Saint Benedict, was an Italian Christian monk, writer, and theologian. He is venerated in the Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodox...
Yves Thériault
 30
Yves Thériault, OC was a Canadian author.
30
Yves Thériault, OC was a Canadian author.
Roméo Vachon
 29
Joseph Pierre Roméo Vachon, né le 29 juin 1898 à Sainte-Marie-de-Beauce, au Québec, et mort le 17 décembre 1954 à Ottawa, est un pionnier québécois de l'aviation. Il est le plus connu des membres de...
29
Joseph Pierre Roméo Vachon, né le 29 juin 1898 à Sainte-Marie-de-Beauce, au Québec, et mort le 17 décembre 1954 à Ottawa, est un pionnier québécois de l'aviation. Il est le plus connu des membres de...
Vincent Massey
 29
Charles Vincent Massey was a Canadian diplomat who served as Governor General of Canada, the 18th since Confederation. Massey was the first governor general of Canada who was born in Canada.
29
Charles Vincent Massey was a Canadian diplomat who served as Governor General of Canada, the 18th since Confederation. Massey was the first governor general of Canada who was born in Canada.
Lord Byron
 29
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron was a British poet and peer. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest of English poets. Among his...
29
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron was a British poet and peer. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest of English poets. Among his...
Frédéric Chopin
 29
Frédéric François Chopin was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist of the Romantic period, who wrote primarily for solo piano. He has maintained worldwide renown as a leading musician of his era,...
29
Frédéric François Chopin was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist of the Romantic period, who wrote primarily for solo piano. He has maintained worldwide renown as a leading musician of his era,...
Christopher Columbus
 29
Christopher Columbus was an Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed four Spanish-based voyages across the Atlantic Ocean sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs, opening...
29
Christopher Columbus was an Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed four Spanish-based voyages across the Atlantic Ocean sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs, opening...
Robert Bourassa
 29
Robert Bourassa was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 22nd premier of Quebec from 1970 to 1976 and from 1985 to 1994. A member of the Liberal Party of Quebec, he served a total of...
29
Robert Bourassa was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 22nd premier of Quebec from 1970 to 1976 and from 1985 to 1994. A member of the Liberal Party of Quebec, he served a total of...
Joan of Arc
 29
Joan of Arc is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the coronation of Charles VII of France during the...
29
Joan of Arc is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the coronation of Charles VII of France during the...
Gabriel
 29
In the Abrahamic religions, Gabriel is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament, the Quran and the Kitáb-i-Aqdas. Many...
29
In the Abrahamic religions, Gabriel is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament, the Quran and the Kitáb-i-Aqdas. Many...
Jean Talon
 28
Jean Talon, Count d'Orsainville was a French colonial administrator who served as the first Intendant of New France. Talon was appointed by King Louis XIV and his minister, Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to...
28
Jean Talon, Count d'Orsainville was a French colonial administrator who served as the first Intendant of New France. Talon was appointed by King Louis XIV and his minister, Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to...
Louis Riel
 27
Louis Riel was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of Canada and its...
27
Louis Riel was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of Canada and its...
Saint David
 27
David was a Welsh Christian prelate who served as Bishop of Mynyw during the 6th century. He is the patron saint of Wales.
27
David was a Welsh Christian prelate who served as Bishop of Mynyw during the 6th century. He is the patron saint of Wales.
Louis-Nazaire Bégin
 27
Louis-Nazaire Bégin was a Canadian cardinal of the Catholic Church. Begin held a doctorate in Sacred Theology from the Pontifical Gregorian University in Rome and was later appointed Archbishop of...
27
Louis-Nazaire Bégin was a Canadian cardinal of the Catholic Church. Begin held a doctorate in Sacred Theology from the Pontifical Gregorian University in Rome and was later appointed Archbishop of...
Jeanne Mance
 27
Jeanne Mance was a French nurse and settler of New France. She arrived in New France two years after the Ursuline nuns came to Quebec. Among the founders of Montreal in 1642, she established its...
27
Jeanne Mance was a French nurse and settler of New France. She arrived in New France two years after the Ursuline nuns came to Quebec. Among the founders of Montreal in 1642, she established its...
Lionel Groulx
 26
Lionel Groulx was a Canadian Roman Catholic priest, historian, professor, public intellectual and Quebec nationalist.
26
Lionel Groulx was a Canadian Roman Catholic priest, historian, professor, public intellectual and Quebec nationalist.
Roland
 26
Roland was a Frankish military leader under Charlemagne who became one of the principal figures in the literary cycle known as the Matter of France. The historical Roland was military governor of the...
26
Roland was a Frankish military leader under Charlemagne who became one of the principal figures in the literary cycle known as the Matter of France. The historical Roland was military governor of the...
Adélard Godbout
 26
Joseph-Adélard Godbout was a Canadian agronomist and politician. He served as the 15th premier of Quebec briefly in 1936, and again from 1939 to 1944. He served as leader of the Parti Libéral du...
26
Joseph-Adélard Godbout was a Canadian agronomist and politician. He served as the 15th premier of Quebec briefly in 1936, and again from 1939 to 1944. He served as leader of the Parti Libéral du...
Saint Maurice
 25
Maurice was an Egyptian military leader who headed the legendary Theban Legion of Rome in the 3rd century, and is one of the favourite and most widely venerated saints of that martyred group. He is...
25
Maurice was an Egyptian military leader who headed the legendary Theban Legion of Rome in the 3rd century, and is one of the favourite and most widely venerated saints of that martyred group. He is...
Léon Trépanier
 25
Léon Trépanier OBE, was a Quebec journalist, historian and politician. He was president of the Saint-Jean-Baptiste Society of Montreal from 1925 to 1929.
25
Léon Trépanier OBE, was a Quebec journalist, historian and politician. He was president of the Saint-Jean-Baptiste Society of Montreal from 1925 to 1929.
Franklin D. Roosevelt
 24
Franklin Delano Roosevelt, commonly known by his initials FDR, was an American statesman and politician who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. He was...
24
Franklin Delano Roosevelt, commonly known by his initials FDR, was an American statesman and politician who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. He was...
Prince Rupert of the Rhine
 24
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, was an English-German army officer, admiral, scientist, and colonial governor. He first rose to prominence as a Royalist cavalry commander during the...
24
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, was an English-German army officer, admiral, scientist, and colonial governor. He first rose to prominence as a Royalist cavalry commander during the...
Blaise Pascal
 24
Blaise Pascal was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic writer.
24
Blaise Pascal was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic writer.
Jean Dallaire
 24
Jean-Philippe Dallaire was one of the leading artists working figuratively in the 1960s in Canada. He is known for his festive scenes peopled by macabre characters.
24
Jean-Philippe Dallaire was one of the leading artists working figuratively in the 1960s in Canada. He is known for his festive scenes peopled by macabre characters.
Marguerite Bourgeoys
 24
Marguerite Bourgeoys, CND, was a French religious sister and founder of the Congregation of Notre Dame of Montreal in the colony of New France, now part of Québec, Canada.
24
Marguerite Bourgeoys, CND, was a French religious sister and founder of the Congregation of Notre Dame of Montreal in the colony of New France, now part of Québec, Canada.
Émile Nelligan
Albert Dumouchel
 24
Albert Dumouchel was a Canadian printmaker, painter and teacher. A multi-talented individual, Dumouchel also was a photographer and gifted musician. His work as an artist ranged from abstract to...
24
Albert Dumouchel was a Canadian printmaker, painter and teacher. A multi-talented individual, Dumouchel also was a photographer and gifted musician. His work as an artist ranged from abstract to...
Alfred Laliberté
 24
Alfred Laliberté was a French-Canadian sculptor and painter based in Montreal. His output includes more than 900 sculptures in bronze, marble, wood, and plaster. Many of his sculptures depict...
24
Alfred Laliberté was a French-Canadian sculptor and painter based in Montreal. His output includes more than 900 sculptures in bronze, marble, wood, and plaster. Many of his sculptures depict...
Thomas Jefferson
 23
Thomas Jefferson was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary...
23
Thomas Jefferson was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary...
Albertus Magnus
 23
Albertus Magnus, also known as Saint Albert the Great, Albert of Swabia
or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop, considered one of the greatest medieval...
23
Albertus Magnus, also known as Saint Albert the Great, Albert of Swabia
or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop, considered one of the greatest medieval...
Saint Nicholas
 23
Saint Nicholas of Myra, also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greek descent from the maritime city of Patara in Anatolia during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the...
23
Saint Nicholas of Myra, also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greek descent from the maritime city of Patara in Anatolia during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the...
Saint Stephen
 23
Stephen is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first martyr of Christianity. According to the Acts of the Apostles, he was a deacon in the early church at Jerusalem who angered members of...
23
Stephen is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first martyr of Christianity. According to the Acts of the Apostles, he was a deacon in the early church at Jerusalem who angered members of...
Hubertus
 22
Hubertus or Hubert was a Christian saint who became the first bishop of Liège in 708 A.D. He is the patron saint of hunters, mathematicians, opticians and metalworkers. Known as the "Apostle of the...
22
Hubertus or Hubert was a Christian saint who became the first bishop of Liège in 708 A.D. He is the patron saint of hunters, mathematicians, opticians and metalworkers. Known as the "Apostle of the...
Thomas D'Arcy McGee
 22
Thomas D'Arcy McGee was an Irish-Canadian politician, Catholic spokesman, journalist, poet, and a Father of Canadian Confederation. The young McGee was an Irish Catholic who opposed British rule in...
22
Thomas D'Arcy McGee was an Irish-Canadian politician, Catholic spokesman, journalist, poet, and a Father of Canadian Confederation. The young McGee was an Irish Catholic who opposed British rule in...
Saint Timothy
 22
Timothy or Timothy of Ephesus was an early Christian evangelist and the first Christian bishop of Ephesus, who tradition relates died around the year AD 97.
22
Timothy or Timothy of Ephesus was an early Christian evangelist and the first Christian bishop of Ephesus, who tradition relates died around the year AD 97.
Louis Pasteur
 22
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist, pharmacist, and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation, and pasteurization, the last of which was...
22
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist, pharmacist, and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation, and pasteurization, the last of which was...
Ignace Bourget
 22
Ignace Bourget was a Canadian Roman Catholic priest who held the title of Bishop of Montreal from 1840 to 1876. Born in Lévis, Quebec, in 1799, Bourget entered the clergy at an early age, undertook...
22
Ignace Bourget was a Canadian Roman Catholic priest who held the title of Bishop of Montreal from 1840 to 1876. Born in Lévis, Quebec, in 1799, Bourget entered the clergy at an early age, undertook...
Saint Roch
 22
Roch, also called Rock in English, was a Majorcan Catholic confessor whose death is commemorated on 16 August and 9 September in Italy; he was especially invoked against the plague. He has the...
22
Roch, also called Rock in English, was a Majorcan Catholic confessor whose death is commemorated on 16 August and 9 September in Italy; he was especially invoked against the plague. He has the...
Joseph-Armand Bombardier
 22
Joseph-Armand Bombardier was a Canadian inventor and businessman who was the founder of Bombardier. His most famous invention was a snowmobile.
22
Joseph-Armand Bombardier was a Canadian inventor and businessman who was the founder of Bombardier. His most famous invention was a snowmobile.
Ludger Duvernay
 22
Ludger Duvernay, born in Verchères, Quebec, was a printer by profession and published a number of newspapers including the Gazette des Trois-Rivières, the first newspaper in Lower Canada outside of...
22
Ludger Duvernay, born in Verchères, Quebec, was a printer by profession and published a number of newspapers including the Gazette des Trois-Rivières, the first newspaper in Lower Canada outside of...
Camille Marcoux
 22
Camille Marcoux (né à Tête-à-la-Baleine en 1930, mort à Blanc-Sablon le 13 septembre 1973, fut le premier médecin originaire de la Basse Côte-Nord du Québec. Il étudia la médecine à Sherbrooke avant...
22
Camille Marcoux (né à Tête-à-la-Baleine en 1930, mort à Blanc-Sablon le 13 septembre 1973, fut le premier médecin originaire de la Basse Côte-Nord du Québec. Il étudia la médecine à Sherbrooke avant...
Napoléon-Alexandre Labrie
 22
Napoléon-Alexandre Labrie, eudiste, né à Godbout le 5 août 1893 et mort à Québec le 16 mai 1973, est un homme d'Église québécois, évêque-fondateur du diocèse catholique de Baie-Comeau entre 1945 et...
22
Napoléon-Alexandre Labrie, eudiste, né à Godbout le 5 août 1893 et mort à Québec le 16 mai 1973, est un homme d'Église québécois, évêque-fondateur du diocèse catholique de Baie-Comeau entre 1945 et...
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
 21
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition resulted in more than 800 works representing virtually...
21
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition resulted in more than 800 works representing virtually...
Norman Bethune
 21
Henry Norman Bethune was a Canadian thoracic surgeon, early advocate of socialized medicine, and member of the Communist Party of Canada. Bethune came to international prominence first for his...
21
Henry Norman Bethune was a Canadian thoracic surgeon, early advocate of socialized medicine, and member of the Communist Party of Canada. Bethune came to international prominence first for his...
Louis Jolliet
 21
Louis Jolliet was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to...
21
Louis Jolliet was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to...
Ella Fitzgerald
 20
Ella Jane Fitzgerald was an American jazz singer, sometimes referred to as the "First Lady of Song", "Queen of Jazz", and "Lady Ella". She was noted for her purity of tone, impeccable diction,...
20
Ella Jane Fitzgerald was an American jazz singer, sometimes referred to as the "First Lady of Song", "Queen of Jazz", and "Lady Ella". She was noted for her purity of tone, impeccable diction,...
Thomas Chapais
 20
Sir Joseph Amable Thomas Chapais was a French Canadian author, editor, historian, journalist, professor, and politician.
20
Sir Joseph Amable Thomas Chapais was a French Canadian author, editor, historian, journalist, professor, and politician.
Paul Comtois
 20
Paul Comtois was a Canadian politician.
20
Paul Comtois was a Canadian politician.
Victor Hugo
 19
Victor-Marie Hugo, vicomte Hugo, sometimes nicknamed the Ocean Man, was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of...
19
Victor-Marie Hugo, vicomte Hugo, sometimes nicknamed the Ocean Man, was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of...
Jean Nicolet
 19
Jean Nicolet (Nicollet), Sieur de Belleborne was a French coureur des bois noted for exploring Lake Michigan, Mackinac Island, Green Bay, and being the first European to set foot in what is now the...
19
Jean Nicolet (Nicollet), Sieur de Belleborne was a French coureur des bois noted for exploring Lake Michigan, Mackinac Island, Green Bay, and being the first European to set foot in what is now the...
Charles Garnier (architect)
 19
Jean-Louis Charles Garnier was a French architect, perhaps best known as the architect of the Palais Garnier and the Opéra de Monte-Carlo.
19
Jean-Louis Charles Garnier was a French architect, perhaps best known as the architect of the Palais Garnier and the Opéra de Monte-Carlo.
Jean-Paul Riopelle
 19
Jean-Paul Riopelle, was a Canadian painter and sculptor from Quebec. He had one of the longest and most important international careers of the sixteen signatories of the Refus Global, the 1948...
19
Jean-Paul Riopelle, was a Canadian painter and sculptor from Quebec. He had one of the longest and most important international careers of the sixteen signatories of the Refus Global, the 1948...
Thérèse Casgrain
 19
Marie Thérèse Casgrain, ., née Forget was a French Canadian feminist, reformer, politician and senator. She was a leader in the fight for women's right to vote in the province of Quebec, as well as...
19
Marie Thérèse Casgrain, ., née Forget was a French Canadian feminist, reformer, politician and senator. She was a leader in the fight for women's right to vote in the province of Quebec, as well as...
Isidore Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire
 19
Isidore Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire was a French zoologist and an authority on deviation from normal structure. In 1854 he coined the term éthologie (ethology).
19
Isidore Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire was a French zoologist and an authority on deviation from normal structure. In 1854 he coined the term éthologie (ethology).
Rodolphe Duguay
 19
Rodolphe Duguay est un peintre, dessinateur, graveur et illustrateur québécois. Il est un pionnier de la gravure sur bois au Canada. Il privilégie le procédé de la gravure en relief.
19
Rodolphe Duguay est un peintre, dessinateur, graveur et illustrateur québécois. Il est un pionnier de la gravure sur bois au Canada. Il privilégie le procédé de la gravure en relief.
Marie-Marguerite d'Youville
 18
Marguerite d'Youville, SGM was a French Canadian widow who founded the Sisters of Charity of Montreal, commonly known as the "Grey Nuns". She was canonized by Pope John Paul II in 1990, becoming the...
18
Marguerite d'Youville, SGM was a French Canadian widow who founded the Sisters of Charity of Montreal, commonly known as the "Grey Nuns". She was canonized by Pope John Paul II in 1990, becoming the...
Paul-Émile Borduas
Henri Bourassa
 17
Joseph-Napoléon-Henri Bourassa was a French Canadian political leader and publisher. In 1899, Bourassa was outspoken against the British government's request for Canada to send a militia to fight for...
17
Joseph-Napoléon-Henri Bourassa was a French Canadian political leader and publisher. In 1899, Bourassa was outspoken against the British government's request for Canada to send a militia to fight for...
Octave Crémazie
 17
Octave Crémazie was a French Canadian poet and bookseller born in Quebec City. Recognized both during and after his lifetime for his patriotic verse and his significant role in the cultural...
17
Octave Crémazie was a French Canadian poet and bookseller born in Quebec City. Recognized both during and after his lifetime for his patriotic verse and his significant role in the cultural...
John Kenneth Galbraith
 17
John Kenneth Galbraith, also known as Ken Galbraith, was a Canadian-American economist, diplomat, public official, and intellectual. His books on economic topics were bestsellers from the 1950s...
17
John Kenneth Galbraith, also known as Ken Galbraith, was a Canadian-American economist, diplomat, public official, and intellectual. His books on economic topics were bestsellers from the 1950s...
Alfred Nobel
 17
Alfred Bernhard Nobel was a Swedish chemist, inventor, engineer and businessman. He is known for inventing dynamite as well as having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prize. He also made...
17
Alfred Bernhard Nobel was a Swedish chemist, inventor, engineer and businessman. He is known for inventing dynamite as well as having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prize. He also made...
Laure Gaudreault
 17
Laure Gaudreault was a Canadian teacher, trade unionist, and journalist. She worked to improve working conditions and wages, and later, retirement rights, for rural women teachers.
17
Laure Gaudreault was a Canadian teacher, trade unionist, and journalist. She worked to improve working conditions and wages, and later, retirement rights, for rural women teachers.
Saint Remigius
 17
Remigius was the Bishop of Reims and "Apostle of the Franks". On 25 December 496, he baptised Clovis I, King of the Franks. The baptism, leading to about 3000 additional converts, was an important...
17
Remigius was the Bishop of Reims and "Apostle of the Franks". On 25 December 496, he baptised Clovis I, King of the Franks. The baptism, leading to about 3000 additional converts, was an important...
Mary Magdalene
 16
Mary Magdalene was a woman who, according to the four canonical gospels, traveled with Jesus as one of his followers and was a witness to his crucifixion and resurrection. She is mentioned by name...
16
Mary Magdalene was a woman who, according to the four canonical gospels, traveled with Jesus as one of his followers and was a witness to his crucifixion and resurrection. She is mentioned by name...
Richard Nixon
 16
Richard Milhous Nixon was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California...
16
Richard Milhous Nixon was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California...
James Watt
 16
James Watt was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was fundamental to the...
16
James Watt was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was fundamental to the...
Gérard D. Levesque
 16
Gérard D. Levesque was a longtime Quebec politician and Cabinet minister, who twice served as interim leader of the Quebec Liberal Party.
16
Gérard D. Levesque was a longtime Quebec politician and Cabinet minister, who twice served as interim leader of the Quebec Liberal Party.
Henry Dunant
 16
Henry Dunant, also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, social activist, and co-founder of the Red Cross. His humanitarian efforts won him the first Nobel Peace Prize in 1901.
16
Henry Dunant, also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, social activist, and co-founder of the Red Cross. His humanitarian efforts won him the first Nobel Peace Prize in 1901.
Madeleine de Verchères
 16
Marie-Madeleine Jarret, known as Madeleine de Verchères was a woman of New France credited with repelling a raid on Fort Verchères when she was 14 years old.
16
Marie-Madeleine Jarret, known as Madeleine de Verchères was a woman of New France credited with repelling a raid on Fort Verchères when she was 14 years old.
Saint Aimé
 16
Saint Amatus, also called St. Aimé or Aimé of Sion, was a Benedictine monk.
16
Saint Amatus, also called St. Aimé or Aimé of Sion, was a Benedictine monk.
Alexius of Rome
 16
Saint Alexius of Rome or Alexius of Edessa, also Alexis, was a fourth-century Greek monk who lived in anonymity and is known for his dedication to Christ. Two versions of his life exist, one in...
16
Saint Alexius of Rome or Alexius of Edessa, also Alexis, was a fourth-century Greek monk who lived in anonymity and is known for his dedication to Christ. Two versions of his life exist, one in...
Georges-Alexandre Courchesne
 16
Georges-Alexandre Courchesne, était un ecclésiastique québécois, évêque de Rimouski de 1928 à 1946. Il est élevé au rang de premier archevêque de Rimouski lors de sa création en 1946, un poste qu'il...
16
Georges-Alexandre Courchesne, était un ecclésiastique québécois, évêque de Rimouski de 1928 à 1946. Il est élevé au rang de premier archevêque de Rimouski lors de sa création en 1946, un poste qu'il...
Louis-Joseph Francœur
 16
Louis-Joseph Francœur was a French violinist, composer, and administrator of the Opéra de Paris.
16
Louis-Joseph Francœur was a French violinist, composer, and administrator of the Opéra de Paris.
Maurice Ravel
 15
Joseph Maurice Ravel was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the...
15
Joseph Maurice Ravel was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the...
Lord Kelvin
 15
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. He was the professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53...
15
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. He was the professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53...
William Faulkner
 15
William Cuthbert Faulkner was an American writer known for his novels and short stories set in the fictional Yoknapatawpha County, based on Lafayette County, Mississippi, where Faulkner spent most of...
15
William Cuthbert Faulkner was an American writer known for his novels and short stories set in the fictional Yoknapatawpha County, based on Lafayette County, Mississippi, where Faulkner spent most of...
Brigid of Kildare
 15
Saint Brigid of Kildare or Saint Brigid of Ireland is the patroness saint of Ireland, and one of its three national saints along with Patrick and Columba. According to medieval Irish hagiographies,...
15
Saint Brigid of Kildare or Saint Brigid of Ireland is the patroness saint of Ireland, and one of its three national saints along with Patrick and Columba. According to medieval Irish hagiographies,...
Claude Jutra
 15
Claude Jutra was a Canadian actor, film director, and screenwriter.
15
Claude Jutra was a Canadian actor, film director, and screenwriter.
Olivier Guimond
 15
Olivier Guimond was a Canadian actor and humorist. He is the father of voice actor Richard Darbois.
15
Olivier Guimond was a Canadian actor and humorist. He is the father of voice actor Richard Darbois.
Armand Frappier
 15
Armand Frappier was a physician, microbiologist, and expert on tuberculosis from Quebec, Canada.
15
Armand Frappier was a physician, microbiologist, and expert on tuberculosis from Quebec, Canada.
Cardinal Richelieu
 15
Armand Jean du Plessis, 1st Duke of Richelieu, known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a French statesman and prelate of the Catholic Church. He became known as l'Éminence rouge, or "the Red Eminence", a...
15
Armand Jean du Plessis, 1st Duke of Richelieu, known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a French statesman and prelate of the Catholic Church. He became known as l'Éminence rouge, or "the Red Eminence", a...
Alfred Pellan
 15
Alfred Pellan was an important figure in twentieth-century Canadian painting.
15
Alfred Pellan was an important figure in twentieth-century Canadian painting.
Saint Christopher
 15
Saint Christopher is venerated by several Christian denominations as a martyr killed in the reign of the 3rd-century Roman emperor Decius, or alternatively under the emperor Maximinus Daia. There...
15
Saint Christopher is venerated by several Christian denominations as a martyr killed in the reign of the 3rd-century Roman emperor Decius, or alternatively under the emperor Maximinus Daia. There...
Adam Dollard des Ormeaux
 14
Adam Dollard des Ormeaux is an iconic figure in the history of New France. Arriving in the colony in 1658, Dollard was appointed the position of garrison commander of the fort of Ville-Marie. In the...
14
Adam Dollard des Ormeaux is an iconic figure in the history of New France. Arriving in the colony in 1658, Dollard was appointed the position of garrison commander of the fort of Ville-Marie. In the...
Guglielmo Marconi
 14
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi was an Italian inventor and electrical engineer, known for his creation of a practical radio wave–based wireless telegraph system. This led to...
14
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi was an Italian inventor and electrical engineer, known for his creation of a practical radio wave–based wireless telegraph system. This led to...
Antonio Vivaldi
 14
Antonio Lucio Vivaldi was an Italian composer, virtuoso violinist and impresario of Baroque music. Along with Johann Sebastian Bach and George Frideric Handel, Vivaldi ranks amongst the greatest...
14
Antonio Lucio Vivaldi was an Italian composer, virtuoso violinist and impresario of Baroque music. Along with Johann Sebastian Bach and George Frideric Handel, Vivaldi ranks amongst the greatest...
Genevieve
 14
Genevieve was a consecrated virgin, and is the patron saint of Paris in the Catholic and Orthodox traditions. Her feast day is on 3 January.
14
Genevieve was a consecrated virgin, and is the patron saint of Paris in the Catholic and Orthodox traditions. Her feast day is on 3 January.
Pierre Mercure
 14
Pierre Mercure was a Québécois composer, TV producer, bassoonist, and administrator.
14
Pierre Mercure was a Québécois composer, TV producer, bassoonist, and administrator.
Édouard Montpetit
 13
Édouard Montpetit was a Quebec lawyer, economist and academic.
13
Édouard Montpetit was a Quebec lawyer, economist and academic.
Bernadette Soubirous
 13
Bernadette Soubirous, also known as Bernadette of Lourdes, was the firstborn daughter of a miller from Lourdes, in the department of Hautes-Pyrénées in France, and is best known for experiencing...
13
Bernadette Soubirous, also known as Bernadette of Lourdes, was the firstborn daughter of a miller from Lourdes, in the department of Hautes-Pyrénées in France, and is best known for experiencing...
Louis-François Richer Laflèche
 13
Louis-François Laflèche was a Catholic bishop of the diocese of Trois-Rivières, in the province of Quebec, Canada.
13
Louis-François Laflèche was a Catholic bishop of the diocese of Trois-Rivières, in the province of Quebec, Canada.
Pope Pius XII
 13
Pope Pius XII was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 2 March 1939 until his death in October 1958. Before his election to the papacy, he served as secretary of...
13
Pope Pius XII was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 2 March 1939 until his death in October 1958. Before his election to the papacy, he served as secretary of...
Elzéar of Sabran
 13
Elzéar of Sabran, TOSF, Baron of Ansouis, Count of Ariano, was born in the castle of Saint-Jean-de-Robians, near Cabrières-d'Aigues in Provence, southern France, in 1285. He died in Paris, France, on...
13
Elzéar of Sabran, TOSF, Baron of Ansouis, Count of Ariano, was born in the castle of Saint-Jean-de-Robians, near Cabrières-d'Aigues in Provence, southern France, in 1285. He died in Paris, France, on...
Michel Foucault
 13
Paul-Michel Foucault was a French philosopher, historian of ideas, writer, political activist, and literary critic. Foucault's theories primarily address the relationships between power and...
13
Paul-Michel Foucault was a French philosopher, historian of ideas, writer, political activist, and literary critic. Foucault's theories primarily address the relationships between power and...
Marius Barbeau
 13
Charles Marius Barbeau,, also known as C. Marius Barbeau, or more commonly simply Marius Barbeau, was a Canadian ethnographer and folklorist who is today considered a founder of Canadian...
13
Charles Marius Barbeau,, also known as C. Marius Barbeau, or more commonly simply Marius Barbeau, was a Canadian ethnographer and folklorist who is today considered a founder of Canadian...
William Shakespeare
 12
William Shakespeare was an English playwright, poet, and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called...
12
William Shakespeare was an English playwright, poet, and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called...
John Keats
 12
John Keats was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, along with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of...
12
John Keats was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, along with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of...
Cuthbert
 12
Cuthbert of Lindisfarne was an Anglo-Saxon saint of the early Northumbrian church in the Celtic tradition. He was a monk, bishop and hermit, associated with the monasteries of Melrose and Lindisfarne...
12
Cuthbert of Lindisfarne was an Anglo-Saxon saint of the early Northumbrian church in the Celtic tradition. He was a monk, bishop and hermit, associated with the monasteries of Melrose and Lindisfarne...
Fernand Seguin
 12
Fernand Seguin, was a Canadian biochemist, professor and host of science programs on radio and television.
12
Fernand Seguin, was a Canadian biochemist, professor and host of science programs on radio and television.
Giuseppe Verdi
 12
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi was an Italian composer best known for his operas. He was born near Busseto to a provincial family of moderate means, receiving a musical education with the help of...
12
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi was an Italian composer best known for his operas. He was born near Busseto to a provincial family of moderate means, receiving a musical education with the help of...
Paul Verlaine
 12
Paul-Marie Verlaine was a French poet associated with the Symbolist movement and the Decadent movement. He is considered one of the greatest representatives of the fin de siècle in international and...
12
Paul-Marie Verlaine was a French poet associated with the Symbolist movement and the Decadent movement. He is considered one of the greatest representatives of the fin de siècle in international and...
Germaine Guèvremont
 12
Germaine Guèvremont, born Grignon was a Canadian writer, who was a prominent figure in Quebec literature.
12
Germaine Guèvremont, born Grignon was a Canadian writer, who was a prominent figure in Quebec literature.
Molière
 12
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin, known by his stage name Molière, was a French playwright, actor, and poet, widely regarded as one of the great writers in the French language and world literature. His extant...
12
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin, known by his stage name Molière, was a French playwright, actor, and poet, widely regarded as one of the great writers in the French language and world literature. His extant...
Petrus Peregrinus de Maricourt
 12
Petrus Peregrinus de Maricourt (Latin), Pierre Pelerin de Maricourt (French), or Peter Peregrinus of Maricourt, was a French mathematician, physicist, and writer who conducted experiments on...
12
Petrus Peregrinus de Maricourt (Latin), Pierre Pelerin de Maricourt (French), or Peter Peregrinus of Maricourt, was a French mathematician, physicist, and writer who conducted experiments on...
Charles Baudelaire
 12
Charles Pierre Baudelaire was a French poet who also worked as an essayist, art critic and translator. His poems are described as exhibiting mastery of rhyme and rhythm, containing an exoticism...
12
Charles Pierre Baudelaire was a French poet who also worked as an essayist, art critic and translator. His poems are described as exhibiting mastery of rhyme and rhythm, containing an exoticism...
Gabrielle Roy
 12
Gabrielle Roy was a Canadian author from St. Boniface, Manitoba and one of the major figures in French Canadian literature.
12
Gabrielle Roy was a Canadian author from St. Boniface, Manitoba and one of the major figures in French Canadian literature.
Maria Chapdelaine
 12
Maria Chapdelaine is a romance novel written in 1913 by the Breton writer Louis Hémon, who was then residing in Quebec. Aimed at young French and Quebecois people, the book had been included in...
12
Maria Chapdelaine is a romance novel written in 1913 by the Breton writer Louis Hémon, who was then residing in Quebec. Aimed at young French and Quebecois people, the book had been included in...
René Goupil
 12
René Goupil, S.J., was a French Jesuit lay missionary who became a lay brother of the Society of Jesus shortly before his death. He was the first of the eight North American Martyrs of the Roman...
12
René Goupil, S.J., was a French Jesuit lay missionary who became a lay brother of the Society of Jesus shortly before his death. He was the first of the eight North American Martyrs of the Roman...
Charles Albanel
 12
Charles Albanel, born in Ardes or Auvergne, was a French missionary explorer in Canada, and a Jesuit priest.
12
Charles Albanel, born in Ardes or Auvergne, was a French missionary explorer in Canada, and a Jesuit priest.
Magdelaine Laframboise
 12
Magdelaine La Framboise (1780–1846), born Marguerite-Magdelaine Marcot, was one of the most successful fur traders in the Northwest Territory of the United States, in the area of present-day western...
12
Magdelaine La Framboise (1780–1846), born Marguerite-Magdelaine Marcot, was one of the most successful fur traders in the Northwest Territory of the United States, in the area of present-day western...
Raoul Jobin
 12
Raoul Jobin, was a French-Canadian operatic tenor, particularly associated with the French repertory.
12
Raoul Jobin, was a French-Canadian operatic tenor, particularly associated with the French repertory.
Marie Curie
 12
Maria Salomea Skłodowska-Curie, known simply as Marie Curie, was a Polish and naturalised-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first woman to...
12
Maria Salomea Skłodowska-Curie, known simply as Marie Curie, was a Polish and naturalised-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first woman to...
Angela of Foligno
 12
Angela of Foligno was an Italian Franciscan tertiary who became known as a mystic from her extensive writings about her mystical revelations. Due to the respect those writings engendered in the...
12
Angela of Foligno was an Italian Franciscan tertiary who became known as a mystic from her extensive writings about her mystical revelations. Due to the respect those writings engendered in the...
John de Beauchesne
 12
John de Beauchesne, also known as John de Beau Chesne, Jean de Beauchesne and Jehan de Beauchesne was a French Huguenot writing master and calligrapher. He relocated to London around 1565, in the...
12
John de Beauchesne, also known as John de Beau Chesne, Jean de Beauchesne and Jehan de Beauchesne was a French Huguenot writing master and calligrapher. He relocated to London around 1565, in the...
Pope John XXIII
 12
Pope John XXIII was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 28 October 1958 until his death in June 1963.
12
Pope John XXIII was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 28 October 1958 until his death in June 1963.
Antoine Lavoisier
 12
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier, also Antoine Lavoisier after the French Revolution, was a French nobleman and chemist who was central to the 18th-century chemical revolution and who had a large...
12
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier, also Antoine Lavoisier after the French Revolution, was a French nobleman and chemist who was central to the 18th-century chemical revolution and who had a large...
Louis Hémon
 12
Louis Hémon, was a French writer, best known for his novel Maria Chapdelaine.
12
Louis Hémon, was a French writer, best known for his novel Maria Chapdelaine.
Marie Rollet
 11
Marie Rollet was a French woman and early settler in Quebec. Her second husband, Louis Hébert, was apothecary to Samuel Champlain's expeditions to Acadia and Quebec on 1606 and 1610–13. When she and...
11
Marie Rollet was a French woman and early settler in Quebec. Her second husband, Louis Hébert, was apothecary to Samuel Champlain's expeditions to Acadia and Quebec on 1606 and 1610–13. When she and...
Leonardo da Vinci
 11
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame...
11
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame...
Charles Darwin
 11
Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a...
11
Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a...
Marie Antoinette
 11
Marie Antoinette was the last queen of France prior to the French Revolution. She was born an archduchess of Austria, and was the penultimate child and youngest daughter of Empress Maria Theresa and...
11
Marie Antoinette was the last queen of France prior to the French Revolution. She was born an archduchess of Austria, and was the penultimate child and youngest daughter of Empress Maria Theresa and...
Pablo Picasso
 11
Pablo Ruiz Picasso was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist, and theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th century,...
11
Pablo Ruiz Picasso was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist, and theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th century,...
Charlemagne
 11
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and Emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding all these titles until his death in 814. Charlemagne succeeded in...
11
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and Emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding all these titles until his death in 814. Charlemagne succeeded in...
Claude-Henri Grignon
 11
Claude-Henri Grignon, OC, FRSC was a French-Canadian novelist, journalist and politician, best known for his 1933 novel Un Homme et son péché.
11
Claude-Henri Grignon, OC, FRSC was a French-Canadian novelist, journalist and politician, best known for his 1933 novel Un Homme et son péché.
Jude the Apostle
 11
Jude was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. He is generally identified as Thaddeus and is also variously called Judas Thaddaeus, Jude Thaddaeus, Jude of James, or...
11
Jude was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. He is generally identified as Thaddeus and is also variously called Judas Thaddaeus, Jude Thaddaeus, Jude of James, or...
Cyril of Alexandria
 11
Cyril of Alexandria was the Patriarch of Alexandria from 412 to 444. He was enthroned when the city was at the height of its influence and power within the Roman Empire. Cyril wrote extensively and...
11
Cyril of Alexandria was the Patriarch of Alexandria from 412 to 444. He was enthroned when the city was at the height of its influence and power within the Roman Empire. Cyril wrote extensively and...
André Laurendeau
 11
Joseph-Edmond-André Laurendeau was a journalist, politician, co-chair of the Royal Commission on Bilingualism and Biculturalism, and playwright in Quebec, Canada. He is usually referred to as André...
11
Joseph-Edmond-André Laurendeau was a journalist, politician, co-chair of the Royal Commission on Bilingualism and Biculturalism, and playwright in Quebec, Canada. He is usually referred to as André...
Charles de Gaulle
 10
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle was a French army officer and statesman who led the Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French...
10
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle was a French army officer and statesman who led the Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French...
Thomas Gainsborough
 10
Thomas Gainsborough was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists of...
10
Thomas Gainsborough was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists of...
Helen McNicoll
 10
Helen Galloway McNicoll was a Canadian impressionist painter. She was one of the most notable women artists in Canada in the early twentieth century and achieved considerable success during her...
10
Helen Galloway McNicoll was a Canadian impressionist painter. She was one of the most notable women artists in Canada in the early twentieth century and achieved considerable success during her...
Rembrandt
 10
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker, and draughtsman. He is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in the...
10
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker, and draughtsman. He is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in the...
Paul Gauguin
 10
Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin was a French painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, and writer, whose work has been primarily associated with the Post-Impressionist and Symbolist movements. He was also...
10
Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin was a French painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, and writer, whose work has been primarily associated with the Post-Impressionist and Symbolist movements. He was also...
Stanislaus Kostka
 10
Stanisław Kostka S.J. was a Polish novice of the Society of Jesus. He is venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Stanislaus Kostka.
10
Stanisław Kostka S.J. was a Polish novice of the Society of Jesus. He is venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Stanislaus Kostka.
Joachim
 10
Joachim was, according to Christianity, the husband of Saint Anne, the father of Mary, mother of Jesus, and the maternal grandfather of Jesus.
10
Joachim was, according to Christianity, the husband of Saint Anne, the father of Mary, mother of Jesus, and the maternal grandfather of Jesus.
Agatha of Sicily
 10
Agatha of Sicily is a Christian saint. Her feast is on 5 February. Agatha was born in Catania, part of the Roman Province of Sicily, and was martyred c. 251. She is one of several virgin martyrs who...
10
Agatha of Sicily is a Christian saint. Her feast is on 5 February. Agatha was born in Catania, part of the Roman Province of Sicily, and was martyred c. 251. She is one of several virgin martyrs who...
Jean de La Fontaine
 10
Jean de La Fontaine was a French fabulist and one of the most widely read French poets of the 17th century. He is known above all for his Fables, which provided a model for subsequent fabulists...
10
Jean de La Fontaine was a French fabulist and one of the most widely read French poets of the 17th century. He is known above all for his Fables, which provided a model for subsequent fabulists...
René Émard
 10
René Émard was a Liberal party member of the House of Commons of Canada. He was born in Châteauguay, Quebec and worked as a unionist. He served during the Second World War in the Régiment de...
10
René Émard was a Liberal party member of the House of Commons of Canada. He was born in Châteauguay, Quebec and worked as a unionist. He served during the Second World War in the Régiment de...
Sophia of Rome
 10
Saint Sophia of Rome is venerated as a Christian martyr.
She is identified in hagiographical tradition with the figure of Sophia of Milan, the mother of Saints Faith, Hope and Charity, whose...
10
Saint Sophia of Rome is venerated as a Christian martyr.
She is identified in hagiographical tradition with the figure of Sophia of Milan, the mother of Saints Faith, Hope and Charity, whose...
Arthur Buies
 10
Arthur Buies est un journaliste et essayiste québécois. Adolescent dissipé, orphelin de mère et dont le père refait sa vie en Guyane, le jeune Buies est renvoyé de deux établissements scolaires avant...
10
Arthur Buies est un journaliste et essayiste québécois. Adolescent dissipé, orphelin de mère et dont le père refait sa vie en Guyane, le jeune Buies est renvoyé de deux établissements scolaires avant...
Jerome
 10
Jerome, also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian priest, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome.
10
Jerome, also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian priest, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome.
Cyricus and Julitta
Anne Hébert
 10
Anne Hébert, was a Canadian author and poet. She won Canada's top literary honor, the Governor General's Award, three times, twice for fiction and once for poetry.
10
Anne Hébert, was a Canadian author and poet. She won Canada's top literary honor, the Governor General's Award, three times, twice for fiction and once for poetry.
Honoré de Balzac
 10
Honoré de Balzac was a French novelist and playwright. The novel sequence La Comédie humaine, which presents a panorama of post-Napoleonic French life, is generally viewed as his magnum opus.
10
Honoré de Balzac was a French novelist and playwright. The novel sequence La Comédie humaine, which presents a panorama of post-Napoleonic French life, is generally viewed as his magnum opus.
Homer
 9
Homer was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the most revered...
9
Homer was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the most revered...
Charles Lindbergh
 9
Charles Augustus Lindbergh was an American aviator and military officer. On May 20–21, 1927, he made the first nonstop flight from New York City to Paris, a distance of 3,600 miles (5,800 km), flying...
9
Charles Augustus Lindbergh was an American aviator and military officer. On May 20–21, 1927, he made the first nonstop flight from New York City to Paris, a distance of 3,600 miles (5,800 km), flying...
Ernest Hemingway
 9
Ernest Miller Hemingway was an American novelist, short-story writer and journalist. Best known for an economical, understated style that significantly influenced later 20th-century writers, he is...
9
Ernest Miller Hemingway was an American novelist, short-story writer and journalist. Best known for an economical, understated style that significantly influenced later 20th-century writers, he is...
Douglas MacArthur
 9
Douglas MacArthur was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He served with distinction in World War...
9
Douglas MacArthur was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He served with distinction in World War...
Johann Sebastian Bach
 9
Johann Sebastian Bach was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his prolific authorship of music across a variety of instruments and forms, including; orchestral...
9
Johann Sebastian Bach was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his prolific authorship of music across a variety of instruments and forms, including; orchestral...
François de Laval
 9
Francis-Xavier de Montmorency-Laval, commonly referred to as François de Laval, was a French prelate of the Catholic Church. Consecrated a bishop in 1658, he led the Apostolic Vicariate of New France...
9
Francis-Xavier de Montmorency-Laval, commonly referred to as François de Laval, was a French prelate of the Catholic Church. Consecrated a bishop in 1658, he led the Apostolic Vicariate of New France...
Roger Lemelin
 9
Roger Lemelin, was a Quebec novelist, television writer and essayist.
9
Roger Lemelin, was a Quebec novelist, television writer and essayist.
Simone de Beauvoir
 9
Simone Lucie Ernestine Marie Bertrand de Beauvoir was a French existentialist philosopher, writer, social theorist, and feminist activist. Though she did not consider herself a philosopher, nor was...
9
Simone Lucie Ernestine Marie Bertrand de Beauvoir was a French existentialist philosopher, writer, social theorist, and feminist activist. Though she did not consider herself a philosopher, nor was...
Marcellin Berthelot
 9
Pierre Eugène Marcellin Berthelot was a French chemist and Republican politician noted for the Thomsen–Berthelot principle of thermochemistry. He synthesized many organic compounds from inorganic...
9
Pierre Eugène Marcellin Berthelot was a French chemist and Republican politician noted for the Thomsen–Berthelot principle of thermochemistry. He synthesized many organic compounds from inorganic...
Arthur Fecteau
 9
Arthur Fecteau, né le 10 août 1910 à Sainte-Marie et mort le 14 novembre 1987 à Dothan en Alabama, est un pilote, entrepreneur et pionnier de l'aviation civile au Québec. Il est propriétaire et...
9
Arthur Fecteau, né le 10 août 1910 à Sainte-Marie et mort le 14 novembre 1987 à Dothan en Alabama, est un pilote, entrepreneur et pionnier de l'aviation civile au Québec. Il est propriétaire et...
Pope Pius X
 9
Pope Pius X was head of the Catholic Church from 4 August 1903 to his death in August 1914. Pius X is known for vigorously opposing modernist interpretations of Catholic doctrine, and for promoting...
9
Pope Pius X was head of the Catholic Church from 4 August 1903 to his death in August 1914. Pius X is known for vigorously opposing modernist interpretations of Catholic doctrine, and for promoting...
John Francis Regis
 9
Jean-François Régis, SJ, commonly known as Saint John Francis Regis and Saint Regis, was a French priest of the Society of Jesus, recognized as a saint by the Catholic Church in 1737. A tireless...
9
Jean-François Régis, SJ, commonly known as Saint John Francis Regis and Saint Regis, was a French priest of the Society of Jesus, recognized as a saint by the Catholic Church in 1737. A tireless...
Alexis Contant
 9
Joseph Pierre Alexis Contant was a Canadian composer, organist, pianist, and music educator. Trained as a pianist, he became one of the first Canadians to compose large-scale choral and orchestral...
9
Joseph Pierre Alexis Contant was a Canadian composer, organist, pianist, and music educator. Trained as a pianist, he became one of the first Canadians to compose large-scale choral and orchestral...
Anthony of Padua
 9
Anthony of Padua, OFM or Anthony of Lisbon was a Portuguese Catholic priest and friar of the Franciscan Order.
9
Anthony of Padua, OFM or Anthony of Lisbon was a Portuguese Catholic priest and friar of the Franciscan Order.
Charles Dickens
 8
Charles John Huffam Dickens was an English novelist and social critic who created some of the world's best-known fictional characters, and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the...
8
Charles John Huffam Dickens was an English novelist and social critic who created some of the world's best-known fictional characters, and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the...
Claude Monet
 8
Oscar-Claude Monet was a French painter and founder of impressionist painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his...
8
Oscar-Claude Monet was a French painter and founder of impressionist painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his...
Lucille Teasdale-Corti
 8
Lucille Teasdale-Corti was a Canadian physician and pediatric surgeon, who worked in Uganda from 1961 until her death in 1996. Despite considerable hardship, including civil war and the AIDS...
8
Lucille Teasdale-Corti was a Canadian physician and pediatric surgeon, who worked in Uganda from 1961 until her death in 1996. Despite considerable hardship, including civil war and the AIDS...
Johannes Brahms
 8
Johannes Brahms was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid-Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes...
8
Johannes Brahms was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid-Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes...
Saint Ursula
 8
Ursula was a Romano-British virgin and martyr possibly of royal origin. She is venerated as a saint in the Roman Catholic Church and the Anglican Communion. Her feast day in the pre-1970 General...
8
Ursula was a Romano-British virgin and martyr possibly of royal origin. She is venerated as a saint in the Roman Catholic Church and the Anglican Communion. Her feast day in the pre-1970 General...
Marc-Aurèle de Foy Suzor-Coté
 8
Marc-Aurèle de Foy Suzor-Coté was a French Canadian painter and sculptor. He was one of the first native-born Canadian artists whose works were directly influenced by French Impressionism and...
8
Marc-Aurèle de Foy Suzor-Coté was a French Canadian painter and sculptor. He was one of the first native-born Canadian artists whose works were directly influenced by French Impressionism and...
Joseph Robidoux IV
 8
Joseph Robidoux IV (1783–1868), was an American fur trader credited as the founder of St. Joseph, Missouri, which developed around his Blacksnake Hills Trading Post. His buildings in St. Joseph,...
8
Joseph Robidoux IV (1783–1868), was an American fur trader credited as the founder of St. Joseph, Missouri, which developed around his Blacksnake Hills Trading Post. His buildings in St. Joseph,...
René Descartes
 8
René Descartes was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathematics was paramount to his method of...
8
René Descartes was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathematics was paramount to his method of...
Alfred de Musset
 8
Alfred Louis Charles de Musset-Pathay was a French dramatist, poet, and novelist. Along with his poetry, he is known for writing the autobiographical novel La Confession d'un enfant du siècle.
8
Alfred Louis Charles de Musset-Pathay was a French dramatist, poet, and novelist. Along with his poetry, he is known for writing the autobiographical novel La Confession d'un enfant du siècle.
Léo Ayotte
 8
Léo Ayotte est un peintre québécois. Il a surtout peint la campagne québécoise, mais aussi des portraits, des nus et des natures mortes.
8
Léo Ayotte est un peintre québécois. Il a surtout peint la campagne québécoise, mais aussi des portraits, des nus et des natures mortes.
Philomena
 8
Philomena, also known as Saint Philomena or Philomena of Rome was a virgin martyr whose remains were discovered on May 24–25, 1802, in the Catacomb of Priscilla. Three tiles enclosing the tomb bore...
8
Philomena, also known as Saint Philomena or Philomena of Rome was a virgin martyr whose remains were discovered on May 24–25, 1802, in the Catacomb of Priscilla. Three tiles enclosing the tomb bore...
Hyacinthe Rigaud
 8
Jacint Rigau-Ros i Serra, known in French as Hyacinthe Rigaud, was a Spanish-French baroque painter most famous for his portraits of Louis XIV and other members of the French nobility.
8
Jacint Rigau-Ros i Serra, known in French as Hyacinthe Rigaud, was a Spanish-French baroque painter most famous for his portraits of Louis XIV and other members of the French nobility.
Antoine de Saint-Exupéry
 8
Antoine Marie Jean-Baptiste Roger, comte de Saint-Exupéry, known simply as Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, was a French writer, poet, journalist and aviator. He received several prestigious literary awards...
8
Antoine Marie Jean-Baptiste Roger, comte de Saint-Exupéry, known simply as Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, was a French writer, poet, journalist and aviator. He received several prestigious literary awards...
Jules Verne
 8
Jules Gabriel Verne was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the Voyages extraordinaires, a series of bestselling...
8
Jules Gabriel Verne was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the Voyages extraordinaires, a series of bestselling...
Honoratus of Amiens
 8
Saint Honoratus of Amiens was the seventh bishop of Amiens. His feast day is May 16.
8
Saint Honoratus of Amiens was the seventh bishop of Amiens. His feast day is May 16.
André Bourbeau
 8
André Bourbeau, was a Canadian politician. A member of the Quebec Liberal Party, Bourbeau served as member of the National Assembly of Quebec for Laporte serving from 1981 until 2003.
8
André Bourbeau, was a Canadian politician. A member of the Quebec Liberal Party, Bourbeau served as member of the National Assembly of Quebec for Laporte serving from 1981 until 2003.
Jean Guyon
 8
Jean Guyon du Buisson was the patriarch of one of the earliest families to settle on the North shore of New France's St. Lawrence River.
8
Jean Guyon du Buisson was the patriarch of one of the earliest families to settle on the North shore of New France's St. Lawrence River.
Pope Pius IX
 8
Pope Pius IX was head of the Catholic Church from 1846 to 1878. His reign of 32 years is the second longest of any pope in history, behind that of Saint Peter. He was notable for convoking the First...
8
Pope Pius IX was head of the Catholic Church from 1846 to 1878. His reign of 32 years is the second longest of any pope in history, behind that of Saint Peter. He was notable for convoking the First...
Bernard of Clairvaux
 8
Bernard of Clairvaux, O. Cist., venerated as Saint Bernard, was an abbot, mystic, co-founder of the Knights Templar, and a major leader in the reformation of the Benedictine Order through the nascent...
8
Bernard of Clairvaux, O. Cist., venerated as Saint Bernard, was an abbot, mystic, co-founder of the Knights Templar, and a major leader in the reformation of the Benedictine Order through the nascent...
Marcellin Champagnat
 8
Marcellin Joseph Benedict Champagnat, FMS was a French Catholic religious born in Le Rosey, village of Marlhes, near St. Etienne (Loire), France. He was the founder of the Marist Brothers, a...
8
Marcellin Joseph Benedict Champagnat, FMS was a French Catholic religious born in Le Rosey, village of Marlhes, near St. Etienne (Loire), France. He was the founder of the Marist Brothers, a...
Voltaire
 8
François-Marie Arouet, known by his nom de plume M. de Voltaire, was a French Enlightenment writer, philosopher (philosophe), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit and his criticism of...
8
François-Marie Arouet, known by his nom de plume M. de Voltaire, was a French Enlightenment writer, philosopher (philosophe), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit and his criticism of...
Éric K. Boulianne
 8
Éric K. Boulianne is a Canadian screenwriter and actor from Quebec. He is most noted as the writer of the film Before We Explode , for which he was a Prix Iris nominee for Best Screenplay at the 21st...
8
Éric K. Boulianne is a Canadian screenwriter and actor from Quebec. He is most noted as the writer of the film Before We Explode , for which he was a Prix Iris nominee for Best Screenplay at the 21st...
Henri Julien
 7
Henri Julien, baptised Octave-Henri Julien, was a Québécois artist and cartoonist noted for his work for the Canadian Illustrated News and for his political cartoons in the Montreal Daily Star. His...
7
Henri Julien, baptised Octave-Henri Julien, was a Québécois artist and cartoonist noted for his work for the Canadian Illustrated News and for his political cartoons in the Montreal Daily Star. His...
Ivanhoe
 7
Ivanhoe: A Romance by Walter Scott is a historical novel published in three volumes, in December 1819, as one of the Waverley novels. It marked a shift away from Scott's prior practice of setting...
7
Ivanhoe: A Romance by Walter Scott is a historical novel published in three volumes, in December 1819, as one of the Waverley novels. It marked a shift away from Scott's prior practice of setting...
Margaret Thatcher
 7
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher, was a British stateswoman and Conservative politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative...
7
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher, was a British stateswoman and Conservative politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative...
Simón Bolívar
 7
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar Palacios Ponte y Blanco was a Venezuelan military and political leader who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador,...
7
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar Palacios Ponte y Blanco was a Venezuelan military and political leader who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador,...
Giuseppe Garibaldi
 7
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi was an Italian general, patriot, revolutionary and republican. He contributed to Italian unification (Risorgimento) and the creation of the Kingdom of Italy. He is considered...
7
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi was an Italian general, patriot, revolutionary and republican. He contributed to Italian unification (Risorgimento) and the creation of the Kingdom of Italy. He is considered...
Lancelot
 7
Lancelot du Lac, also written as Launcelot and other variants, is a character in some versions of Arthurian legend where he is typically depicted as King Arthur's close companion and one of the...
7
Lancelot du Lac, also written as Launcelot and other variants, is a character in some versions of Arthurian legend where he is typically depicted as King Arthur's close companion and one of the...
Saint Boniface
 7
Boniface, OSB was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of Francia during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of the...
7
Boniface, OSB was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of Francia during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of the...
Franz Schubert
 7
Franz Peter Schubert was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short life, Schubert left behind a vast oeuvre, including more than 600 secular vocal works,...
7
Franz Peter Schubert was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short life, Schubert left behind a vast oeuvre, including more than 600 secular vocal works,...
Robert H. Goddard
 7
Robert Hutchings Goddard was an American engineer, professor, physicist, and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid-fueled rocket, which was successfully...
7
Robert Hutchings Goddard was an American engineer, professor, physicist, and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid-fueled rocket, which was successfully...
Percival
 7
Percival, alternatively called Peredur, is a figure in the legend of King Arthur, often appearing as one of the Knights of the Round Table. First mentioned by the French author Chrétien de Troyes in...
7
Percival, alternatively called Peredur, is a figure in the legend of King Arthur, often appearing as one of the Knights of the Round Table. First mentioned by the French author Chrétien de Troyes in...
Marie of the Incarnation (Ursuline)
 7
Marie of the Incarnation, OSU was a French Ursuline nun. As part of a group of nuns sent to New France (Quebec) to establish the Ursuline Order, Marie was crucial in the spread of Catholicism in New...
7
Marie of the Incarnation, OSU was a French Ursuline nun. As part of a group of nuns sent to New France (Quebec) to establish the Ursuline Order, Marie was crucial in the spread of Catholicism in New...
Jeanne Le Ber
 7
Jeanne Le Ber was a recluse in New France.
7
Jeanne Le Ber was a recluse in New France.
Pope Gregory I
 7
Pope Gregory I, commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great, was the 64th Bishop of Rome from 3 September 590 to his death. He is known for instituting the first recorded large-scale mission from Rome,...
7
Pope Gregory I, commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great, was the 64th Bishop of Rome from 3 September 590 to his death. He is known for instituting the first recorded large-scale mission from Rome,...
Georges Bizet
 7
Georges Bizet was a French composer of the Romantic era. Best known for his operas in a career cut short by his early death, Bizet achieved few successes before his final work, Carmen, which has...
7
Georges Bizet was a French composer of the Romantic era. Best known for his operas in a career cut short by his early death, Bizet achieved few successes before his final work, Carmen, which has...
François Mauriac
 7
François Charles Mauriac was a French novelist, dramatist, critic, poet, and journalist, a member of the Académie française, and laureate of the Nobel Prize in Literature (1952). He was awarded the...
7
François Charles Mauriac was a French novelist, dramatist, critic, poet, and journalist, a member of the Académie française, and laureate of the Nobel Prize in Literature (1952). He was awarded the...
Lucien Fugère
 7
Lucien Fugère was a French baritone, particularly associated with the French repertory and Mozart roles. He enjoyed an exceptionally long career, singing into his 80s.
7
Lucien Fugère was a French baritone, particularly associated with the French repertory and Mozart roles. He enjoyed an exceptionally long career, singing into his 80s.
Marcelle Ferron
 7
Marcelle Ferron, was a Canadian Québécoise painter and stained glass artist, was one of the original 16 signatories of Paul-Émile Borduas's Refus global manifesto, and a major figure in the Quebec...
7
Marcelle Ferron, was a Canadian Québécoise painter and stained glass artist, was one of the original 16 signatories of Paul-Émile Borduas's Refus global manifesto, and a major figure in the Quebec...
Clarence Gagnon
 7
Clarence Alphonse Gagnon, LL. D. was a French Canadian painter, draughtsman, engraver and illustrator. He is known for his landscape paintings of the Laurentians and the Charlevoix region of eastern...
7
Clarence Alphonse Gagnon, LL. D. was a French Canadian painter, draughtsman, engraver and illustrator. He is known for his landscape paintings of the Laurentians and the Charlevoix region of eastern...
Laure Conan
 7
Marie-Louise-Félicité Angers, better known by her pen name Laure Conan, was a French Canadian writer and journalist. She is regarded as one of the first French-Canadian female novelists and the...
7
Marie-Louise-Félicité Angers, better known by her pen name Laure Conan, was a French Canadian writer and journalist. She is regarded as one of the first French-Canadian female novelists and the...
Claude Péloquin
 7
Claude Péloquin was a Québécois poet, writer, singer, songwriter, screenwriter, and director.
7
Claude Péloquin was a Québécois poet, writer, singer, songwriter, screenwriter, and director.
Raphael
 7
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, now generally known in English as Raphael, was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition,...
7
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, now generally known in English as Raphael, was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition,...
Jean Désy
 7
Jean Désy was a Canadian diplomat.
7
Jean Désy was a Canadian diplomat.
Alphonse Daudet
 7
Alphonse Daudet was a French novelist. He was the husband of Julia Daudet and father of Edmée, Léon and Lucien Daudet.
7
Alphonse Daudet was a French novelist. He was the husband of Julia Daudet and father of Edmée, Léon and Lucien Daudet.
Arthur Rimbaud
 7
Jean Nicolas Arthur Rimbaud was a French poet known for his transgressive and surreal themes and for his influence on modern literature and arts, prefiguring surrealism. Born in Charleville, he...
7
Jean Nicolas Arthur Rimbaud was a French poet known for his transgressive and surreal themes and for his influence on modern literature and arts, prefiguring surrealism. Born in Charleville, he...
Albert Camus
 7
Albert Camus was a French philosopher, author, dramatist, journalist, world federalist, and political activist. He was the recipient of the 1957 Nobel Prize in Literature at the age of 44, the...
7
Albert Camus was a French philosopher, author, dramatist, journalist, world federalist, and political activist. He was the recipient of the 1957 Nobel Prize in Literature at the age of 44, the...
Albert Einstein
 7
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is widely held to be one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time. Best known for developing the theory of relativity,...
7
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is widely held to be one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time. Best known for developing the theory of relativity,...
Louis Cyr
 7
Louis Cyr was a French Canadian strongman with a career spanning the late 19th and early 20th centuries. His recorded feats, including lifting 500 pounds (227 kg) with one finger and backlifting...
7
Louis Cyr was a French Canadian strongman with a career spanning the late 19th and early 20th centuries. His recorded feats, including lifting 500 pounds (227 kg) with one finger and backlifting...
Columba
 7
Columba or Colmcille was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is today Scotland at the start of the Hiberno-Scottish mission. He founded the important...
7
Columba or Colmcille was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is today Scotland at the start of the Hiberno-Scottish mission. He founded the important...
Dante Alighieri
 6
Dante Alighieri, most likely baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante, was an Italian poet, writer, and philosopher. His Divine Comedy, originally called Comedìa...
6
Dante Alighieri, most likely baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante, was an Italian poet, writer, and philosopher. His Divine Comedy, originally called Comedìa...
Charlie Chaplin
 6
Sir Charles Spencer Chaplin was an English comic actor, filmmaker, and composer who rose to fame in the era of silent film. He became a worldwide icon through his screen persona, the Tramp, and is...
6
Sir Charles Spencer Chaplin was an English comic actor, filmmaker, and composer who rose to fame in the era of silent film. He became a worldwide icon through his screen persona, the Tramp, and is...
Gregor Mendel
 6
Gregor Johann Mendel OSA was an Austrian-Czech biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinian friar and abbot of St. Thomas' Abbey in Brno (Brünn), Margraviate of Moravia. Mendel was born in a...
6
Gregor Johann Mendel OSA was an Austrian-Czech biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinian friar and abbot of St. Thomas' Abbey in Brno (Brünn), Margraviate of Moravia. Mendel was born in a...
Tristan
 6
Tristan, also known as Tristram, Tristyn or Tristain and similar names, is the hero of the legend of Tristan and Iseult. In the legend, he is tasked with escorting the Irish princess Iseult to wed...
6
Tristan, also known as Tristram, Tristyn or Tristain and similar names, is the hero of the legend of Tristan and Iseult. In the legend, he is tasked with escorting the Irish princess Iseult to wed...
Achilles
 6
In Greek mythology, Achilles or Achilleus was a hero of the Trojan War who was known as being the greatest of all the Greek warriors. A central character in Homer's Iliad, he was the son of the...
6
In Greek mythology, Achilles or Achilleus was a hero of the Trojan War who was known as being the greatest of all the Greek warriors. A central character in Homer's Iliad, he was the son of the...
Frank Fitzsimmons
 6
Frank Edward Fitzsimmons was an American labor leader. He was acting president of the International Brotherhood of Teamsters from 1967 to 1971, and president from 1971 to 1981.
6
Frank Edward Fitzsimmons was an American labor leader. He was acting president of the International Brotherhood of Teamsters from 1967 to 1971, and president from 1971 to 1981.
John Lennon
 6
John Winston Ono Lennon was an English singer, songwriter and musician. He gained worldwide fame as the founder, co-songwriter, co-lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist of the Beatles. His work included...
6
John Winston Ono Lennon was an English singer, songwriter and musician. He gained worldwide fame as the founder, co-songwriter, co-lead vocalist and rhythm guitarist of the Beatles. His work included...
Ludwig van Beethoven
 6
Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music...
6
Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music...
Augustus
 6
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus, also known as Octavian, was the founder of the Roman Empire. He reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated...
6
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus, also known as Octavian, was the founder of the Roman Empire. He reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated...
Serge Garant
 6
Albert Antonio Serge Garant, was a Canadian composer, conductor, music critic, professor of music at the University of Montreal and radio host of Musique de notre siècle on Radio-Canada. In 1966, he...
6
Albert Antonio Serge Garant, was a Canadian composer, conductor, music critic, professor of music at the University of Montreal and radio host of Musique de notre siècle on Radio-Canada. In 1966, he...
Georges Clemenceau
 6
Georges Benjamin Clemenceau was a French statesman who served as Prime Minister of France from 1906 to 1909 and again from 1917 until 1920. A physician turned journalist, he played a central role in...
6
Georges Benjamin Clemenceau was a French statesman who served as Prime Minister of France from 1906 to 1909 and again from 1917 until 1920. A physician turned journalist, he played a central role in...
Pierre Bourgault
 6
Pierre Bourgault was a politician and essayist, as well as an actor and journalist, from Quebec, Canada. He is most famous as a public speaker who advocated sovereignty for Quebec from Canada.
6
Pierre Bourgault was a politician and essayist, as well as an actor and journalist, from Quebec, Canada. He is most famous as a public speaker who advocated sovereignty for Quebec from Canada.
Gilles Hocquart
 6
Gilles Hocquart was born in 1694, in Sainte-Croix, Mortagne-au-Perche to Jean-Hyacinthe Hocquart. From September, 1729 to August, 1748, Hocquart served as Intendant of New France. Hocquart put his...
6
Gilles Hocquart was born in 1694, in Sainte-Croix, Mortagne-au-Perche to Jean-Hyacinthe Hocquart. From September, 1729 to August, 1748, Hocquart served as Intendant of New France. Hocquart put his...
Rina Lasnier
 6
Rina Lasnier, was a Québécois Canadian poet. Born in St-Grégoire d'Iberville-Mont-Saint-Grégoire, Quebec, she attended Collège Marguerite Bourgeoys and the Université de Montréal. Although she was...
6
Rina Lasnier, was a Québécois Canadian poet. Born in St-Grégoire d'Iberville-Mont-Saint-Grégoire, Quebec, she attended Collège Marguerite Bourgeoys and the Université de Montréal. Although she was...
Paul Sauvé
 6
Joseph-Mignault-Paul Sauvé was a Canadian lawyer, World War II veteran, and politician. He was the 17th premier of Quebec in 1959 and 1960.
6
Joseph-Mignault-Paul Sauvé was a Canadian lawyer, World War II veteran, and politician. He was the 17th premier of Quebec in 1959 and 1960.
Francis of Assisi
 6
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, known as Francis of Assisi, was an Italian mystic, poet and Catholic friar who founded the religious order of the Franciscans. He was inspired to lead a Christian...
6
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, known as Francis of Assisi, was an Italian mystic, poet and Catholic friar who founded the religious order of the Franciscans. He was inspired to lead a Christian...
Hector Berlioz
 6
Louis-Hector Berlioz was a French Romantic composer and conductor. His output includes orchestral works such as the Symphonie fantastique and Harold in Italy, choral pieces including the Requiem and...
6
Louis-Hector Berlioz was a French Romantic composer and conductor. His output includes orchestral works such as the Symphonie fantastique and Harold in Italy, choral pieces including the Requiem and...
Martha
 6
Martha is a biblical figure described in the Gospels of Luke and John. Together with her siblings Lazarus and Mary of Bethany, she is described as living in the village of Bethany near Jerusalem. She...
6
Martha is a biblical figure described in the Gospels of Luke and John. Together with her siblings Lazarus and Mary of Bethany, she is described as living in the village of Bethany near Jerusalem. She...
Paul-Émile Léger
 6
Paul-Émile Léger was a Canadian cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as Archbishop of Montreal from 1950 to 1967, and was elevated to the cardinalate in 1953 by Pope Pius XII.
6
Paul-Émile Léger was a Canadian cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as Archbishop of Montreal from 1950 to 1967, and was elevated to the cardinalate in 1953 by Pope Pius XII.
Pope Paul VI
 6
Pope Paul VI was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 21 June 1963 to his death in August 1978. Succeeding John XXIII, he continued the Second Vatican Council,...
6
Pope Paul VI was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 21 June 1963 to his death in August 1978. Succeeding John XXIII, he continued the Second Vatican Council,...
René Pomerleau
 6
René Pomerleau, OC was a mycologist and plant pathologist whose specialty was fungi and lichens. He received a Bachelor of Agricultural Science from Laval University before an MS at the McGill...
6
René Pomerleau, OC was a mycologist and plant pathologist whose specialty was fungi and lichens. He received a Bachelor of Agricultural Science from Laval University before an MS at the McGill...
Saint Ours
 6
Saint Ursus of Toul, known in French as Saint Ours, was a 5th-century French bishop of Toul and a saint of the Roman Catholic Church with a locally venerated feast day celebrated on 1 March.
6
Saint Ursus of Toul, known in French as Saint Ours, was a 5th-century French bishop of Toul and a saint of the Roman Catholic Church with a locally venerated feast day celebrated on 1 March.
Nicolas Perrot
 6
Nicolas Perrot, a French explorer, fur trader, and diplomat, was one of the first European men to travel in the Upper Mississippi Valley, in what is now Wisconsin and Minnesota.
6
Nicolas Perrot, a French explorer, fur trader, and diplomat, was one of the first European men to travel in the Upper Mississippi Valley, in what is now Wisconsin and Minnesota.
Jean Paul
 6
Jean Paul was a German Romantic writer, best known for his humorous novels and stories.
6
Jean Paul was a German Romantic writer, best known for his humorous novels and stories.
Honoré Beaugrand
 6
Honoré Beaugrand was a French Canadian journalist, politician, author and folklorist, born in Berthier County, Quebec.
6
Honoré Beaugrand was a French Canadian journalist, politician, author and folklorist, born in Berthier County, Quebec.
Bernie Geoffrion
 6
Joseph Bernard André Geoffrion, nicknamed "Boom Boom", was a Canadian professional ice hockey player and coach. Generally considered one of the innovators of the slapshot, he was inducted into the...
6
Joseph Bernard André Geoffrion, nicknamed "Boom Boom", was a Canadian professional ice hockey player and coach. Generally considered one of the innovators of the slapshot, he was inducted into the...
Charles Daudelin
 6
Charles Daudelin, was a French Canadian pioneer in modern sculpture and painting. He worked in a wide variety of media, including painting, metal and ceramic sculpture, jewelry, and marionettes which...
6
Charles Daudelin, was a French Canadian pioneer in modern sculpture and painting. He worked in a wide variety of media, including painting, metal and ceramic sculpture, jewelry, and marionettes which...
Arthur of Glastonbury
Saint Eustace
 6
Saint Eustace is revered as a Christian martyr. According to legend, he was martyred in AD 118, at the command of emperor Hadrian. Eustace was a pagan Roman general, who converted to Christianity...
6
Saint Eustace is revered as a Christian martyr. According to legend, he was martyred in AD 118, at the command of emperor Hadrian. Eustace was a pagan Roman general, who converted to Christianity...
Gérard Morisset
 6
Gérard Morisset est un historien de l'art et écrivain québécois. Il est considéré comme le père de l'histoire de l'art au Québec.
6
Gérard Morisset est un historien de l'art et écrivain québécois. Il est considéré comme le père de l'histoire de l'art au Québec.
Jacques Landriault
 6
Jacques Landriault was a Canadian Prelate of Roman Catholic Church.
6
Jacques Landriault was a Canadian Prelate of Roman Catholic Church.
Gustave Flaubert
 6
Gustave Flaubert also known as Flambert, was a French novelist. He has been considered the leading exponent of literary realism in his country and abroad. According to the literary theorist Kornelije...
6
Gustave Flaubert also known as Flambert, was a French novelist. He has been considered the leading exponent of literary realism in his country and abroad. According to the literary theorist Kornelije...
François Rabelais
 6
François Rabelais was a French writer who has been called the first great French prose author. A humanist of the French Renaissance and Greek scholar, he attracted opposition from both John Calvin...
6
François Rabelais was a French writer who has been called the first great French prose author. A humanist of the French Renaissance and Greek scholar, he attracted opposition from both John Calvin...
Louis-Hippolyte Lafontaine
 6
Sir Louis-Hippolyte Ménard dit La Fontaine, 1st Baronet, KCMG was a Canadian politician who served as the first Premier of the United Province of Canada and the first head of a responsible government...
6
Sir Louis-Hippolyte Ménard dit La Fontaine, 1st Baronet, KCMG was a Canadian politician who served as the first Premier of the United Province of Canada and the first head of a responsible government...
Guy de Maupassant
 6
Henri René Albert Guy de Maupassant was a 19th-century French author, celebrated as a master of the short story, as well as a representative of the naturalist school, depicting human lives, destinies...
6
Henri René Albert Guy de Maupassant was a 19th-century French author, celebrated as a master of the short story, as well as a representative of the naturalist school, depicting human lives, destinies...
Hubert Aquin
 6
Hubert Aquin was a Quebec novelist, political activist, essayist, filmmaker and editor.
6
Hubert Aquin was a Quebec novelist, political activist, essayist, filmmaker and editor.
Lambert Closse
 6
Raphaël Lambert Closse (1618–1662) was a merchant when he disembarked at Ville-Marie, Nouvelle-France in 1647.
6
Raphaël Lambert Closse (1618–1662) was a merchant when he disembarked at Ville-Marie, Nouvelle-France in 1647.
Gilles Villeneuve
 6
Joseph Gilles Henri Villeneuve was a Canadian racing driver who spent six years in Formula One racing for Scuderia Ferrari, winning six Grands Prix and earning widespread acclaim for his performances.
6
Joseph Gilles Henri Villeneuve was a Canadian racing driver who spent six years in Formula One racing for Scuderia Ferrari, winning six Grands Prix and earning widespread acclaim for his performances.
Saint Alban
 5
Saint Alban is venerated as the first-recorded British Christian martyr, for which reason he is considered to be the British protomartyr. Along with fellow Saints Julius and Aaron, Alban is one of...
5
Saint Alban is venerated as the first-recorded British Christian martyr, for which reason he is considered to be the British protomartyr. Along with fellow Saints Julius and Aaron, Alban is one of...
Adam Dalgliesh
 5
Adam Dalgliesh is a fictional character who is the protagonist of fourteen mystery novels by P. D. James; the first being James's 1962 novel Cover Her Face. He also appears in the two novels...
5
Adam Dalgliesh is a fictional character who is the protagonist of fourteen mystery novels by P. D. James; the first being James's 1962 novel Cover Her Face. He also appears in the two novels...
Gioachino Rossini
 5
Gioachino Antonio Rossini was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces and some sacred music. He set new standards...
5
Gioachino Antonio Rossini was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces and some sacred music. He set new standards...
Michael Faraday
 5
Michael Faraday was a British scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction,...
5
Michael Faraday was a British scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction,...
Peter Paul Rubens
 5
Sir Peter Paul Rubens was a Flemish artist and diplomat. He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque tradition. Rubens's highly charged compositions reference erudite aspects...
5
Sir Peter Paul Rubens was a Flemish artist and diplomat. He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque tradition. Rubens's highly charged compositions reference erudite aspects...
Brian Beaucage
 5
Brian Leslie Beaucage, better known as "Bo" Beaucage, was a Canadian gangster, outlaw biker and convicted criminal best known as one of the leaders of the 1971 Kingston Penitentiary riot. His plea...
5
Brian Leslie Beaucage, better known as "Bo" Beaucage, was a Canadian gangster, outlaw biker and convicted criminal best known as one of the leaders of the 1971 Kingston Penitentiary riot. His plea...
Caradoc
 5
Caradoc Vreichvras was a semi-legendary ancestor to the kings of Gwent. He may have lived during the 5th or 6th century. He is remembered in the Matter of Britain as a Knight of the Round Table,...
5
Caradoc Vreichvras was a semi-legendary ancestor to the kings of Gwent. He may have lived during the 5th or 6th century. He is remembered in the Matter of Britain as a Knight of the Round Table,...
Hélène Boullé
 5
Hélène Boullé née en 1598 à Paris et décédée le 20 décembre 1654 à Meaux (France), est fondatrice des Ursulines de Meaux.
5
Hélène Boullé née en 1598 à Paris et décédée le 20 décembre 1654 à Meaux (France), est fondatrice des Ursulines de Meaux.
Maurice Duplessis
 5
Maurice Le Noblet Duplessis,, byname "Le Chef", was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 16th premier of Quebec. A conservative, nationalist, populist, anti-communist, anti-unionist and...
5
Maurice Le Noblet Duplessis,, byname "Le Chef", was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 16th premier of Quebec. A conservative, nationalist, populist, anti-communist, anti-unionist and...
Lambert of Maastricht
 5
Lambert of Maastricht, commonly referred to as Saint Lambert, was the bishop of Maastricht-Liège (Tongeren) from about 670 until his death. Lambert denounced Pepin's liaison with his mistress or...
5
Lambert of Maastricht, commonly referred to as Saint Lambert, was the bishop of Maastricht-Liège (Tongeren) from about 670 until his death. Lambert denounced Pepin's liaison with his mistress or...
Jacques Plante
 5
Joseph Jacques Omer Plante was a Canadian professional ice hockey goaltender. During a career lasting from 1947 to 1975, he was considered to be one of the most important innovators in hockey. He...
5
Joseph Jacques Omer Plante was a Canadian professional ice hockey goaltender. During a career lasting from 1947 to 1975, he was considered to be one of the most important innovators in hockey. He...
Norbert of Xanten
 5
Norbert of Xanten, O. Praem (Xanten-Magdeburg), also known as Norbert Gennep, was a bishop of the Catholic Church, founder of the Premonstratensian order of canons regular, and is venerated as a...
5
Norbert of Xanten, O. Praem (Xanten-Magdeburg), also known as Norbert Gennep, was a bishop of the Catholic Church, founder of the Premonstratensian order of canons regular, and is venerated as a...
Paschal Baylón
 5
Paschal Baylón was a Spanish Roman Catholic lay professed religious of the Order of Friars Minor. He served as a shepherd alongside his father in his childhood and adolescence, but desired to enter...
5
Paschal Baylón was a Spanish Roman Catholic lay professed religious of the Order of Friars Minor. He served as a shepherd alongside his father in his childhood and adolescence, but desired to enter...
Jules Léger
 5
Joseph Jules Léger was a Canadian diplomat and statesman who served as Governor General of Canada, the 21st since Canadian Confederation.
5
Joseph Jules Léger was a Canadian diplomat and statesman who served as Governor General of Canada, the 21st since Canadian Confederation.
Louis d'Ailleboust de Coulonge
 5
Louis d'Ailleboust de Coulonge was the French governor of New France from 1648 to 1651 and acting governor from 1657 to 1658. He caused to be built the house that is today known as the Duke of Kent...
5
Louis d'Ailleboust de Coulonge was the French governor of New France from 1648 to 1651 and acting governor from 1657 to 1658. He caused to be built the house that is today known as the Duke of Kent...
Benjamin Sulte
 5
Benjamin Sulte, baptized Olivier-Benjamin Vadeboncœur, was a Canadian journalist, writer, civil servant, and historian.
5
Benjamin Sulte, baptized Olivier-Benjamin Vadeboncœur, was a Canadian journalist, writer, civil servant, and historian.
Amandus
 5
Amandus, commonly called Saint Amand, was a bishop of Tongeren-Maastricht and one of the catholic missionaries of Flanders. He is venerated as a saint, particularly in France and Belgium.
5
Amandus, commonly called Saint Amand, was a bishop of Tongeren-Maastricht and one of the catholic missionaries of Flanders. He is venerated as a saint, particularly in France and Belgium.
Judith Jasmin
 5
Judith Jasmin was a journalist from Quebec. Born in Terrebonne, Quebec, Canada, she was the first woman from Quebec to become a grand reporter.
5
Judith Jasmin was a journalist from Quebec. Born in Terrebonne, Quebec, Canada, she was the first woman from Quebec to become a grand reporter.
Jules Massenet
 5
Jules Émile Frédéric Massenet was a French composer of the Romantic era best known for his operas, of which he wrote more than thirty. The two most frequently staged are Manon (1884) and Werther...
5
Jules Émile Frédéric Massenet was a French composer of the Romantic era best known for his operas, of which he wrote more than thirty. The two most frequently staged are Manon (1884) and Werther...
François-René de Chateaubriand
 5
François-René, vicomte de Chateaubriand was a French writer, politician, diplomat and historian who influenced French literature of the nineteenth century. Descended from an old aristocratic family...
5
François-René, vicomte de Chateaubriand was a French writer, politician, diplomat and historian who influenced French literature of the nineteenth century. Descended from an old aristocratic family...
Michel de Montaigne
 5
Michel Eyquem, Seigneur de Montaigne, commonly known as Michel de Montaigne, was one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance. He is known for popularizing the essay as a...
5
Michel Eyquem, Seigneur de Montaigne, commonly known as Michel de Montaigne, was one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance. He is known for popularizing the essay as a...
Guillaume Couture
 4
Guillaume Couture was a citizen of New France. During his life he was a lay missionary with the Jesuits, a survivor of torture, a member of an Iroquois council, a translator, a diplomat, a militia...
4
Guillaume Couture was a citizen of New France. During his life he was a lay missionary with the Jesuits, a survivor of torture, a member of an Iroquois council, a translator, a diplomat, a militia...
Johannes Kepler
 4
Johannes Kepler was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of...
4
Johannes Kepler was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of...
Julius Caesar
 4
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war,...
4
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war,...
Ferdinand Magellan
 4
Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the East Indies across the Pacific Ocean to open a maritime trade route, during which...
4
Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the East Indies across the Pacific Ocean to open a maritime trade route, during which...
Salvador Dalí
 4
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol, known as Salvador Dalí, was a Spanish surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the...
4
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol, known as Salvador Dalí, was a Spanish surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the...
George V
 4
George V was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
4
George V was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Henri Matisse
 4
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known...
4
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known...
Saint Giles
 4
Saint Giles, also known as Giles the Hermit, was a hermit or monk active in the lower Rhône most likely in the 7th century. Revered as a saint, his cult became widely diffused but his hagiography is...
4
Saint Giles, also known as Giles the Hermit, was a hermit or monk active in the lower Rhône most likely in the 7th century. Revered as a saint, his cult became widely diffused but his hagiography is...
Onésime Gagnon
 4
Onésime Gagnon was a Canadian politician who served as the 20th Lieutenant Governor of Québec.
4
Onésime Gagnon was a Canadian politician who served as the 20th Lieutenant Governor of Québec.
Marie Le Franc
 4
Marie Le Franc was a French-born writer who found much of her inspiration in Canada.
4
Marie Le Franc was a French-born writer who found much of her inspiration in Canada.
Alessandro Volta
 4
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta was an Italian physicist and chemist who was a pioneer of electricity and power and is credited as the inventor of the electric battery and the discoverer...
4
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta was an Italian physicist and chemist who was a pioneer of electricity and power and is credited as the inventor of the electric battery and the discoverer...
Raymond Lasnier
 4
Raymond Lasnier est un peintre important pour l'histoire de l'art de la Mauricie né le 28 février 1924 et décédé le 10 février 1968. Actif dans le domaine culturel mauricien, il fut membre de...
4
Raymond Lasnier est un peintre important pour l'histoire de l'art de la Mauricie né le 28 février 1924 et décédé le 10 février 1968. Actif dans le domaine culturel mauricien, il fut membre de...
Jean Bourdon
 4
Jean Bourdon was the first engineer-in-chief and land-surveyor in the colony of New France, and the first attorney-general of the Conseil Superieur.
4
Jean Bourdon was the first engineer-in-chief and land-surveyor in the colony of New France, and the first attorney-general of the Conseil Superieur.
Prosper of Aquitaine
 4
Prosper of Aquitaine, also called Prosper Tiro, was a Christian writer and disciple of Augustine of Hippo, and the first continuator of Jerome's Universal Chronicle.
4
Prosper of Aquitaine, also called Prosper Tiro, was a Christian writer and disciple of Augustine of Hippo, and the first continuator of Jerome's Universal Chronicle.
Jacques Ferron
 4
Jacques Ferron was a Canadian physician and author.
4
Jacques Ferron was a Canadian physician and author.
Mary Ellen Pleasant
 4
Mary Ellen Pleasant was an American entrepreneur, financier, real estate magnate and abolitionist. She was arguably the first self-made millionaire of African-American heritage, preceding Madam C. J....
4
Mary Ellen Pleasant was an American entrepreneur, financier, real estate magnate and abolitionist. She was arguably the first self-made millionaire of African-American heritage, preceding Madam C. J....
Wilfrid Hamel
 4
Wilfrid Hamel was a Canadian politician, serving as a member of the Legislative Assembly of Quebec and as Mayor of Quebec City.
4
Wilfrid Hamel was a Canadian politician, serving as a member of the Legislative Assembly of Quebec and as Mayor of Quebec City.
Joseph-Elzéar Bernier
 4
Joseph-Elzéar Bernier was a Canadian mariner from Quebec who led expeditions into the Canadian Arctic in the early 20th century.
4
Joseph-Elzéar Bernier was a Canadian mariner from Quebec who led expeditions into the Canadian Arctic in the early 20th century.
Louis Dantin
 4
Louis Dantin was the pen name of Eugène Seers, a Canadian writer and editor from Quebec. He is historically most noted as the original editor and publisher of the poetry of Émile Nelligan, although...
4
Louis Dantin was the pen name of Eugène Seers, a Canadian writer and editor from Quebec. He is historically most noted as the original editor and publisher of the poetry of Émile Nelligan, although...
George Sand
 4
Amantine Lucile Aurore Dupin de Francueil, best known by her pen name George Sand, was a French novelist, memoirist and journalist. One of the most popular writers in Europe in her lifetime, being...
4
Amantine Lucile Aurore Dupin de Francueil, best known by her pen name George Sand, was a French novelist, memoirist and journalist. One of the most popular writers in Europe in her lifetime, being...
Pauline Julien
 4
Pauline Julien,, nicknamed "La Renarde", was a singer, songwriter, actress, feminist activist and Quebec sovereigntist.
4
Pauline Julien,, nicknamed "La Renarde", was a singer, songwriter, actress, feminist activist and Quebec sovereigntist.
Jordi Bonet
 4
Jordi Bonet i Godó, known professionally as Jordi Bonet, was a Spanish-born Canadian painter, ceramist, muralist, and sculptor who worked principally in Quebec.
4
Jordi Bonet i Godó, known professionally as Jordi Bonet, was a Spanish-born Canadian painter, ceramist, muralist, and sculptor who worked principally in Quebec.
Pierre Corneille
 4
Pierre Corneille was a French tragedian. He is generally considered one of the three great seventeenth-century French dramatists, along with Molière and Racine.
4
Pierre Corneille was a French tragedian. He is generally considered one of the three great seventeenth-century French dramatists, along with Molière and Racine.
Mahatma Gandhi
 4
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from...
4
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from...
Jean-Paul Sartre
 4
Jean-Paul Charles Aymard Sartre was a French philosopher, playwright, novelist, screenwriter, political activist, biographer, and literary critic, considered a leading figure in 20th-century French...
4
Jean-Paul Charles Aymard Sartre was a French philosopher, playwright, novelist, screenwriter, political activist, biographer, and literary critic, considered a leading figure in 20th-century French...
Galileo Galilei
 4
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei, commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei or simply Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. He was born...
4
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei, commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei or simply Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. He was born...
Eugène Delacroix
 4
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix was a French Romantic artist regarded from the outset of his career as the leader of the French Romantic school.
4
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix was a French Romantic artist regarded from the outset of his career as the leader of the French Romantic school.
Roger Boisjoly
 4
Roger Mark Boisjoly was an American mechanical engineer, fluid dynamicist, and an aerodynamicist. He is best known for having raised strenuous objections to the launch of the Space Shuttle Challenger...
4
Roger Mark Boisjoly was an American mechanical engineer, fluid dynamicist, and an aerodynamicist. He is best known for having raised strenuous objections to the launch of the Space Shuttle Challenger...
Macbeth (character)
 4
Lord Macbeth, the Thane of Glamis and quickly the Thane of Cawdor, is the title character and main protagonist in William Shakespeare's Macbeth. The character is loosely based on the historical king...
4
Lord Macbeth, the Thane of Glamis and quickly the Thane of Cawdor, is the title character and main protagonist in William Shakespeare's Macbeth. The character is loosely based on the historical king...
Zoticus of Comana
 3
Zoticus was a 3rd-century martyr and bishop of Comana. Zoticus is known for his opposition to the Montanist heresy. He died in 204 a martyr. A life of Zoticus, the Vita Zotici, was written during the...
3
Zoticus was a 3rd-century martyr and bishop of Comana. Zoticus is known for his opposition to the Montanist heresy. He died in 204 a martyr. A life of Zoticus, the Vita Zotici, was written during the...
Dunstan
 3
Dunstan, OSB was an English bishop. He was successively Abbot of Glastonbury Abbey, Bishop of Worcester, Bishop of London and Archbishop of Canterbury, later canonised. His work restored monastic...
3
Dunstan, OSB was an English bishop. He was successively Abbot of Glastonbury Abbey, Bishop of Worcester, Bishop of London and Archbishop of Canterbury, later canonised. His work restored monastic...
George William Anderson (Canadian politician)
 3
George William Anderson was an English-born farmer, baker and political figure in British Columbia. He represented Victoria in the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia from 1886 to 1894.
3
George William Anderson was an English-born farmer, baker and political figure in British Columbia. He represented Victoria in the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia from 1886 to 1894.
Paul David
 3
Paul David was a Canadian cardiologist, founder of the Montreal Heart Institute, and Senator.
3
Paul David was a Canadian cardiologist, founder of the Montreal Heart Institute, and Senator.
Hadrian
 3
Hadrian was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, the Aeli Hadriani,...
3
Hadrian was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, the Aeli Hadriani,...
Guy Frégault
 3
Guy Frégault was a Canadian historian and writer from Quebec.
3
Guy Frégault was a Canadian historian and writer from Quebec.
Michelangelo
 3
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni, known mononymously as Michelangelo, was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his...
3
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni, known mononymously as Michelangelo, was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his...
Marcus Aurelius
 3
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 and a Stoic philosopher. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, the last of the rulers later known as the Five Good Emperors and...
3
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 and a Stoic philosopher. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, the last of the rulers later known as the Five Good Emperors and...
Jeanne Sauvé
 3
Jeanne Mathilde Sauvé was a Canadian politician and journalist who served as the first and to date only female Speaker of the House (1980–1984) and as the first female Governor General of Canada...
3
Jeanne Mathilde Sauvé was a Canadian politician and journalist who served as the first and to date only female Speaker of the House (1980–1984) and as the first female Governor General of Canada...
Jean Cocteau
 3
Jean Maurice Eugène Clément Cocteau was a French poet, playwright, novelist, designer, film director, visual artist and critic. He was one of the foremost artists of the surrealist, avant-garde, and...
3
Jean Maurice Eugène Clément Cocteau was a French poet, playwright, novelist, designer, film director, visual artist and critic. He was one of the foremost artists of the surrealist, avant-garde, and...
Émile Zola
 3
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of...
3
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of...
Jovette Bernier
 3
Marie-Angèle "Jovette" Alice Bernier was a journalist and writer in Quebec. Because of extensive exposure in the print media and on radio, she was often referred to simply as Jovette.
3
Marie-Angèle "Jovette" Alice Bernier was a journalist and writer in Quebec. Because of extensive exposure in the print media and on radio, she was often referred to simply as Jovette.
Jean-Marie-Rodrigue Villeneuve
 3
Jean-Marie-Rodrigue Villeneuve was a Canadian Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as Archbishop of Quebec from 1931 until his death, and was elevated to the cardinalate in 1933.
3
Jean-Marie-Rodrigue Villeneuve was a Canadian Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as Archbishop of Quebec from 1931 until his death, and was elevated to the cardinalate in 1933.
Arthur Sauvé
 3
Arthur Sauvé, was born in Saint-Hermas.
3
Arthur Sauvé, was born in Saint-Hermas.
Charles de Batz de Castelmore d'Artagnan
 3
Charles de Batz de Castelmore, also known as d'Artagnan and later Count d'Artagnan, was a French Musketeer who served Louis XIV as captain of the Musketeers of the Guard. He died at the siege of...
3
Charles de Batz de Castelmore, also known as d'Artagnan and later Count d'Artagnan, was a French Musketeer who served Louis XIV as captain of the Musketeers of the Guard. He died at the siege of...
Jean Ladrière
 3
Jean Ladrière was a Belgian logician and philosopher, born in Nivelles. He was professor at the University of Louvain (UCLouvain) from 1959 to 1986, where he was chair of the Higher Institute of...
3
Jean Ladrière was a Belgian logician and philosopher, born in Nivelles. He was professor at the University of Louvain (UCLouvain) from 1959 to 1986, where he was chair of the Higher Institute of...
Jean Brillant
 3
Jean Baptiste Arthur Brillant was a Canadian recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and...
3
Jean Baptiste Arthur Brillant was a Canadian recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and...
Othello (character)
 3
Othello is a character in Shakespeare's Othello. The character's origin is traced to the tale "Un Capitano Moro" in Gli Hecatommithi by Giovanni Battista Giraldi Cinthio. There, he is simply referred...
3
Othello is a character in Shakespeare's Othello. The character's origin is traced to the tale "Un Capitano Moro" in Gli Hecatommithi by Giovanni Battista Giraldi Cinthio. There, he is simply referred...
Magloire
 3
Magloire, better known as Saint Magloire of Dol, is a Breton saint. Little reliable information is known of Magloire as the earliest written sources appeared three centuries after his death. These...
3
Magloire, better known as Saint Magloire of Dol, is a Breton saint. Little reliable information is known of Magloire as the earliest written sources appeared three centuries after his death. These...
Saint Ernest
 3
Saint Ernest was the abbot of the Benedictine Zwiefalten Abbey at Zwiefalten, Germany from 1141 to 1146. He participated in the Second Crusade fought by Christians between 1146 and 1149 to defend the...
3
Saint Ernest was the abbot of the Benedictine Zwiefalten Abbey at Zwiefalten, Germany from 1141 to 1146. He participated in the Second Crusade fought by Christians between 1146 and 1149 to defend the...
William Tremblay (politician)
 3
William Tremblay was a politician in Quebec, Canada and a Member of the Legislative Assembly of Quebec (MLA).
3
William Tremblay was a politician in Quebec, Canada and a Member of the Legislative Assembly of Quebec (MLA).
Father Damien
 3
Father Damien or Saint Damien of Molokai or Saint Damien De Veuster, born Jozef De Veuster, was a Roman Catholic priest from Belgium and member of the Congregation of the Sacred Hearts of Jesus and...
3
Father Damien or Saint Damien of Molokai or Saint Damien De Veuster, born Jozef De Veuster, was a Roman Catholic priest from Belgium and member of the Congregation of the Sacred Hearts of Jesus and...
Arthur Mignault
 3
Arthur Mignault, MD was a French Canadian pharmaceutical entrepreneur, physician and colonel of the Royal Canadian Army Medical Corps, serving in the First World War. He is the founder of the Royal...
3
Arthur Mignault, MD was a French Canadian pharmaceutical entrepreneur, physician and colonel of the Royal Canadian Army Medical Corps, serving in the First World War. He is the founder of the Royal...
André Gagnon
 3
André Gagnon was a Canadian pianist, composer, conductor, arranger, and actor, known for his fusion of classical and pop styles, including compositions Neiges, Smash, Chevauchée, Surprise, Donna, and...
3
André Gagnon was a Canadian pianist, composer, conductor, arranger, and actor, known for his fusion of classical and pop styles, including compositions Neiges, Smash, Chevauchée, Surprise, Donna, and...
Georges Dor
 3
Georges Dor was a Québécois author, composer, playwright, singer, poet, translator, and theatrical producer and director.
3
Georges Dor was a Québécois author, composer, playwright, singer, poet, translator, and theatrical producer and director.
Francis I of France
 3
Francis I was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law...
3
Francis I was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law...
Clotilde
 3
Clotilde, also known as Clothilde, Clotilda, Clotild, Rotilde etc., was a Queen of the Franks. She was supposedly descended from the Gothic king Athanaric and became the second wife of the Frankish...
3
Clotilde, also known as Clothilde, Clotilda, Clotild, Rotilde etc., was a Queen of the Franks. She was supposedly descended from the Gothic king Athanaric and became the second wife of the Frankish...
Vincent van Gogh
 3
Vincent Willem van Gogh was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who is among the most famous and influential figures in the history of Western art. In just over a decade, he created approximately 2100...
3
Vincent Willem van Gogh was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who is among the most famous and influential figures in the history of Western art. In just over a decade, he created approximately 2100...
Adrienne Choquette
 3
Adrienne Choquette was a writer in Quebec, Canada.
3
Adrienne Choquette was a writer in Quebec, Canada.
Joseph de Monbeton de Brouillan
 3
Joseph de Monbeton de Brouillan, dit Saint-Ovide, né en 1676 à Bourrouillan dans le Gers, et décédé le 4 avril 1755 à Saint-Sever dans les Landes, est un militaire français des XVIIe et...
3
Joseph de Monbeton de Brouillan, dit Saint-Ovide, né en 1676 à Bourrouillan dans le Gers, et décédé le 4 avril 1755 à Saint-Sever dans les Landes, est un militaire français des XVIIe et...
René Richard
 3
René Richard was Swiss-born Canadian painter known for his semi-abstract landscapes of the Canadian wilderness and of the country around Baie-Saint-Paul in Quebec.
3
René Richard was Swiss-born Canadian painter known for his semi-abstract landscapes of the Canadian wilderness and of the country around Baie-Saint-Paul in Quebec.
Saint Sebastian
 3
Sebastian was an early Christian saint and martyr. According to traditional belief, he was killed during the Diocletianic Persecution of Christians. He was initially tied to a post or tree and shot...
3
Sebastian was an early Christian saint and martyr. According to traditional belief, he was killed during the Diocletianic Persecution of Christians. He was initially tied to a post or tree and shot...
Albert Rousseau
 3
Albert Rousseau, né le 17 octobre 1908 à Saint-Étienne-de-Lauzon où il est mort le 18 mars 1982, est un artiste-peintre québécois.
3
Albert Rousseau, né le 17 octobre 1908 à Saint-Étienne-de-Lauzon où il est mort le 18 mars 1982, est un artiste-peintre québécois.
Louis Juchereau de St. Denis
 3
Louis Antoine Juchereau de St. Denis was a French-Canadian soldier and explorer best known for his exploration and development of the Louisiana and Spanish Texas regions. He commanded a small...
3
Louis Antoine Juchereau de St. Denis was a French-Canadian soldier and explorer best known for his exploration and development of the Louisiana and Spanish Texas regions. He commanded a small...
Jean-Victor Poncelet
 3
Jean-Victor Poncelet was a French engineer and mathematician who served most notably as the Commanding General of the École Polytechnique. He is considered a reviver of projective geometry, and his...
3
Jean-Victor Poncelet was a French engineer and mathematician who served most notably as the Commanding General of the École Polytechnique. He is considered a reviver of projective geometry, and his...
Louis XIV
 3
Louis XIV, also known as Louis the Great or the Sun King, was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any sovereign. Although...
3
Louis XIV, also known as Louis the Great or the Sun King, was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any sovereign. Although...
Paul Ragueneau
 3
Paul Ragueneau, SJ was a Jesuit missionary in New France.
3
Paul Ragueneau, SJ was a Jesuit missionary in New France.
Jean le Rond d'Alembert
 3
Jean-Baptiste le Rond d'Alembert was a French mathematician, mechanician, physicist, philosopher, and music theorist. Until 1759 he was, together with Denis Diderot, a co-editor of the Encyclopédie....
3
Jean-Baptiste le Rond d'Alembert was a French mathematician, mechanician, physicist, philosopher, and music theorist. Until 1759 he was, together with Denis Diderot, a co-editor of the Encyclopédie....
Pierre Curie
 3
Pierre Curie was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity, and radioactivity. In 1903, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics with his wife, Marie...
3
Pierre Curie was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity, and radioactivity. In 1903, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics with his wife, Marie...
Marcel Proust
 3
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust was a French novelist, literary critic, and essayist who wrote the monumental novel À la recherche du temps perdu which was published in seven volumes...
3
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust was a French novelist, literary critic, and essayist who wrote the monumental novel À la recherche du temps perdu which was published in seven volumes...
Charles Deschamps de Boishébert et de Raffetot
 3
Charles Deschamps de Boishébert was a member of the Compagnies Franches de la Marine and was a significant leader of the Acadian militia's resistance to the Expulsion of the Acadians. He settled and...
3
Charles Deschamps de Boishébert was a member of the Compagnies Franches de la Marine and was a significant leader of the Acadian militia's resistance to the Expulsion of the Acadians. He settled and...
Victor Delamarre
 3
Victor Delamarre est un haltérophile canadien-français. Il est surtout connu pour avoir réussi à effectuer un dévissé d'un seul bras une masse de 140 kg, soulevant de ce fait le double de sa masse....
3
Victor Delamarre est un haltérophile canadien-français. Il est surtout connu pour avoir réussi à effectuer un dévissé d'un seul bras une masse de 140 kg, soulevant de ce fait le double de sa masse....
Justine Lacoste-Beaubien
 3
Justine Lacoste-Beaubien was one of the founders of the children's hospital Sainte-Justine Hospital.
3
Justine Lacoste-Beaubien was one of the founders of the children's hospital Sainte-Justine Hospital.
Arthur Rousseau
 3
Arthur Rousseau was a Canadian politician and a former Mayor of Trois-Rivières.
3
Arthur Rousseau was a Canadian politician and a former Mayor of Trois-Rivières.
Odette Oligny
 3
Odette Oligny, née Bernot le 25 novembre 1900 à Troyes et morte le 1er mai 1962 à Montréal, est une journaliste et écrivaine franco-québécoise. Elle a utilisé le nom de plume Michelle de Vaubert.
3
Odette Oligny, née Bernot le 25 novembre 1900 à Troyes et morte le 1er mai 1962 à Montréal, est une journaliste et écrivaine franco-québécoise. Elle a utilisé le nom de plume Michelle de Vaubert.
André-Marie Ampère
 3
André-Marie Ampère was a French physicist and mathematician who was one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics". He is also the...
3
André-Marie Ampère was a French physicist and mathematician who was one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics". He is also the...
André Malraux
 3
Georges André Malraux was a French novelist, art theorist, and minister of cultural affairs. Malraux's novel La Condition Humaine (1933) won the Prix Goncourt. He was appointed by President Charles...
3
Georges André Malraux was a French novelist, art theorist, and minister of cultural affairs. Malraux's novel La Condition Humaine (1933) won the Prix Goncourt. He was appointed by President Charles...
Marcel Pagnol
 3
Marcel Paul Pagnol was a French novelist, playwright, and filmmaker. Regarded as an auteur, in 1946, he became the first filmmaker elected to the Académie française. Although his work is less...
3
Marcel Paul Pagnol was a French novelist, playwright, and filmmaker. Regarded as an auteur, in 1946, he became the first filmmaker elected to the Académie française. Although his work is less...
Franz Liszt
 3
Franz Liszt was a Hungarian composer, virtuoso pianist, conductor and teacher of the Romantic period. With a diverse body of work spanning more than six decades, he is considered to be one of the...
3
Franz Liszt was a Hungarian composer, virtuoso pianist, conductor and teacher of the Romantic period. With a diverse body of work spanning more than six decades, he is considered to be one of the...
John Bosco
 3
John Melchior Bosco, SDB, popularly known as Don Bosco, was an Italian Catholic priest, educator and writer of the 19th century. While working in Turin, where the population suffered many of the ill...
3
John Melchior Bosco, SDB, popularly known as Don Bosco, was an Italian Catholic priest, educator and writer of the 19th century. While working in Turin, where the population suffered many of the ill...
Jean Duceppe
 3
Jean Hotte-Duceppe was a Canadian stage and television actor from Montreal, Quebec.
3
Jean Hotte-Duceppe was a Canadian stage and television actor from Montreal, Quebec.
Robert Choquette
Louis Philippe I
 3
Louis Philippe I, nicknamed the Citizen King, was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, and the penultimate monarch of France. As Louis Philippe, Duke of Chartres, he distinguished himself commanding...
3
Louis Philippe I, nicknamed the Citizen King, was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, and the penultimate monarch of France. As Louis Philippe, Duke of Chartres, he distinguished himself commanding...
Faust
 3
Faust is the protagonist of a classic German legend based on the historical Johann Georg Faust.
3
Faust is the protagonist of a classic German legend based on the historical Johann Georg Faust.
Louis Roy
 3
Louis Roy, better known as "Mélou", is a Canadian outlaw biker and gangster, said to have been the richest Hells Angel in Quebec.
3
Louis Roy, better known as "Mélou", is a Canadian outlaw biker and gangster, said to have been the richest Hells Angel in Quebec.
Alfred Pinsonneault
 3
Alfred Pinsonneault was a Quebec farmer and political figure. He represented Laprairie in the House of Commons of Canada as a Conservative member from 1867 to 1887.
3
Alfred Pinsonneault was a Quebec farmer and political figure. He represented Laprairie in the House of Commons of Canada as a Conservative member from 1867 to 1887.
Don Quixote
 3
Don Quixote is a Spanish epic novel by Miguel de Cervantes. It was originally published in two parts, in 1605 and 1615. Considered a founding work of Western literature, it is often labelled as the...
3
Don Quixote is a Spanish epic novel by Miguel de Cervantes. It was originally published in two parts, in 1605 and 1615. Considered a founding work of Western literature, it is often labelled as the...
Tantalus
 3
Tantalus, also called Atys, was a Greek mythological figure, most famous for his punishment in Tartarus: for trying to trick the gods into eating his son, he was made to stand in a pool of water...
3
Tantalus, also called Atys, was a Greek mythological figure, most famous for his punishment in Tartarus: for trying to trick the gods into eating his son, he was made to stand in a pool of water...
Rose of Lima
 3
Rose of Lima, TOSD was a member of the Third Order of Saint Dominic in Lima, Peru, who became known for both her life of severe penance and her care of the poverty stricken of the city through her...
3
Rose of Lima, TOSD was a member of the Third Order of Saint Dominic in Lima, Peru, who became known for both her life of severe penance and her care of the poverty stricken of the city through her...
Nicolaus Copernicus
 3
Nicolaus Copernicus was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its center....
3
Nicolaus Copernicus was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its center....
Gottlieb Daimler
 3
Gottlieb Wilhelm Daimler was a German engineer, industrial designer and industrialist born in Schorndorf, in what is now Germany. He was a pioneer of internal-combustion engines and automobile...
3
Gottlieb Wilhelm Daimler was a German engineer, industrial designer and industrialist born in Schorndorf, in what is now Germany. He was a pioneer of internal-combustion engines and automobile...
Arthur Villeneuve
 3
Arthur Villeneuve, was a Québécois painter and member of the Order of Canada.
3
Arthur Villeneuve, was a Québécois painter and member of the Order of Canada.
Alexis Carrel
 3
Alexis Carrel was a French surgeon and biologist who spent most of his scientific career in the United States. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1912 for pioneering vascular...
3
Alexis Carrel was a French surgeon and biologist who spent most of his scientific career in the United States. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1912 for pioneering vascular...
Jean Despres
 3
Jean Despres (1903–1988) was a perfume industry businessman, known for his work with Coty
3
Jean Despres (1903–1988) was a perfume industry businessman, known for his work with Coty
Jules Huot
 3
Jules Huot was a French-Canadian professional golfer.
3
Jules Huot was a French-Canadian professional golfer.
Augustine A. MacDonald
 3
Augustine Adolphus MacDonald, OC was a physician and political figure on Prince Edward Island. He represented 1st Kings in the Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island as a Conservative from 1915...
3
Augustine Adolphus MacDonald, OC was a physician and political figure on Prince Edward Island. He represented 1st Kings in the Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island as a Conservative from 1915...
Clare of Assisi
 3
Chiara Offreduccio, known as Clare of Assisi, was an Italian saint who was one of the first followers of Francis of Assisi.
3
Chiara Offreduccio, known as Clare of Assisi, was an Italian saint who was one of the first followers of Francis of Assisi.