Frequent persons on France's street signs
countries
1044 names / 23751 streets
Charles de Gaulle
 1151
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle was a French army officer and statesman who led the Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French...
1151
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle was a French army officer and statesman who led the Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French...
Jean Moulin
 666
Jean Moulin was a French civil servant and resistant who succeeded in unifying the main networks of the French Resistance, a unique act in Europe. He served as the first President of the National...
666
Jean Moulin was a French civil servant and resistant who succeeded in unifying the main networks of the French Resistance, a unique act in Europe. He served as the first President of the National...
Jean Jaurès
 598
Auguste Marie Joseph Jean Léon Jaurès, commonly referred to as Jean Jaurès, was a French Socialist leader. Initially a Moderate Republican, he later became one of the first social democrats and the...
598
Auguste Marie Joseph Jean Léon Jaurès, commonly referred to as Jean Jaurès, was a French Socialist leader. Initially a Moderate Republican, he later became one of the first social democrats and the...
Philippe Leclerc de Hauteclocque
 536
Philippe François Marie Leclerc de Hauteclocque was a Free-French general during the Second World War. He became Marshal of France posthumously in 1952, and is known in France simply as le maréchal...
536
Philippe François Marie Leclerc de Hauteclocque was a Free-French general during the Second World War. He became Marshal of France posthumously in 1952, and is known in France simply as le maréchal...
Louis Pasteur
 486
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist, pharmacist, and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation, and pasteurization, the last of which was...
486
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist, pharmacist, and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation, and pasteurization, the last of which was...
Victor Hugo
 470
Victor-Marie Hugo, vicomte Hugo, sometimes nicknamed the Ocean Man, was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of...
470
Victor-Marie Hugo, vicomte Hugo, sometimes nicknamed the Ocean Man, was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of...
Jean de La Fontaine
 459
Jean de La Fontaine was a French fabulist and one of the most widely read French poets of the 17th century. He is known above all for his Fables, which provided a model for subsequent fabulists...
459
Jean de La Fontaine was a French fabulist and one of the most widely read French poets of the 17th century. He is known above all for his Fables, which provided a model for subsequent fabulists...
Léon Gambetta
 386
Léon Gambetta was a French lawyer and republican politician who proclaimed the French Third Republic in 1870 and played a prominent role in its early government.
386
Léon Gambetta was a French lawyer and republican politician who proclaimed the French Third Republic in 1870 and played a prominent role in its early government.
Ferdinand Foch
 326
Ferdinand Foch was a French general, Marshal of France and member of the Académie Française. He distinguished himself as Supreme Allied Commander on the Western Front during the First World War in...
326
Ferdinand Foch was a French general, Marshal of France and member of the Académie Française. He distinguished himself as Supreme Allied Commander on the Western Front during the First World War in...
Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot
 297
Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot was a French mechanical engineer in the French Army, military scientist and physicist, often described as the "father of thermodynamics". He published only one book, the...
297
Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot was a French mechanical engineer in the French Army, military scientist and physicist, often described as the "father of thermodynamics". He published only one book, the...
Georges Clemenceau
 256
Georges Benjamin Clemenceau was a French statesman who served as Prime Minister of France from 1906 to 1909 and again from 1917 until 1920. A physician turned journalist, he played a central role in...
256
Georges Benjamin Clemenceau was a French statesman who served as Prime Minister of France from 1906 to 1909 and again from 1917 until 1920. A physician turned journalist, he played a central role in...
Aristide Briand
 253
Aristide Pierre Henri Briand was a French statesman who served eleven terms as Prime Minister of France during the French Third Republic. He is mainly remembered for his focus on international issues...
253
Aristide Pierre Henri Briand was a French statesman who served eleven terms as Prime Minister of France during the French Third Republic. He is mainly remembered for his focus on international issues...
Jules Ferry
 248
Jules François Camille Ferry was a French statesman and republican philosopher. He was one of the leaders of the Moderate Republicans and served as Prime Minister of France from 1880 to 1881 and 1883...
248
Jules François Camille Ferry was a French statesman and republican philosopher. He was one of the leaders of the Moderate Republicans and served as Prime Minister of France from 1880 to 1881 and 1883...
Jean de Lattre de Tassigny
 154
Jean Joseph Marie Gabriel de Lattre de Tassigny was a French général d'armée during World War II and the First Indochina War. He was posthumously elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France in 1952.
154
Jean Joseph Marie Gabriel de Lattre de Tassigny was a French général d'armée during World War II and the First Indochina War. He was posthumously elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France in 1952.
Émile Zola
 150
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of...
150
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of...
François Mitterrand
 149
François Maurice Adrien Marie Mitterrand was a French politician who served as President of France from 1981 to 1995, the longest holder of that position in the history of France. As a former...
149
François Maurice Adrien Marie Mitterrand was a French politician who served as President of France from 1981 to 1995, the longest holder of that position in the history of France. As a former...
John the Baptist
 149
John the Baptist was a Jewish preacher active in the area of the Jordan River in the early 1st century AD. He is also known as Saint John the Forerunner in Eastern Orthodoxy, John the Immerser in...
149
John the Baptist was a Jewish preacher active in the area of the Jordan River in the early 1st century AD. He is also known as Saint John the Forerunner in Eastern Orthodoxy, John the Immerser in...
Roger Salengro
 146
Roger Henri Charles Salengro was a French politician. He achieved fame as Minister of the Interior during the Popular Front government in 1936. He committed suicide a few months after taking office,...
146
Roger Henri Charles Salengro was a French politician. He achieved fame as Minister of the Interior during the Popular Front government in 1936. He committed suicide a few months after taking office,...
Pierre Curie
 146
Pierre Curie was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity, and radioactivity. In 1903, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics with his wife, Marie...
146
Pierre Curie was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity, and radioactivity. In 1903, he received the Nobel Prize in Physics with his wife, Marie...
Antoine de Saint-Exupéry
 145
Antoine Marie Jean-Baptiste Roger, comte de Saint-Exupéry, known simply as Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, was a French writer, poet, journalist and aviator. He received several prestigious literary awards...
145
Antoine Marie Jean-Baptiste Roger, comte de Saint-Exupéry, known simply as Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, was a French writer, poet, journalist and aviator. He received several prestigious literary awards...
Saint Peter
 145
Saint Peter, also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ and one of the first leaders of the early Christian Church. He...
145
Saint Peter, also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ and one of the first leaders of the early Christian Church. He...
Anatole France
 142
Anatole France was a French poet, journalist, and novelist with several best-sellers. Ironic and skeptical, he was considered in his day the ideal French man of letters. He was a member of the...
142
Anatole France was a French poet, journalist, and novelist with several best-sellers. Ironic and skeptical, he was considered in his day the ideal French man of letters. He was a member of the...
Martin of Tours
 141
Martin of Tours, also known as Martin the Merciful, was the third bishop of Tours. He has become one of the most familiar and recognizable Christian saints in France, heralded as the patron saint of...
141
Martin of Tours, also known as Martin the Merciful, was the third bishop of Tours. He has become one of the most familiar and recognizable Christian saints in France, heralded as the patron saint of...
Gabriel Péri
 138
Gabriel Péri (Peri) was a prominent French communist journalist and politician who was a member of the French Resistance. He was executed in German-occupied France during the Second World War.
138
Gabriel Péri (Peri) was a prominent French communist journalist and politician who was a member of the French Resistance. He was executed in German-occupied France during the Second World War.
Voltaire
 135
François-Marie Arouet, known by his nom de plume M. de Voltaire, was a French Enlightenment writer, philosopher (philosophe), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit and his criticism of...
135
François-Marie Arouet, known by his nom de plume M. de Voltaire, was a French Enlightenment writer, philosopher (philosophe), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit and his criticism of...
Joseph Joffre
 128
Joseph Jacques Césaire Joffre, was a French general who served as Commander-in-Chief of French forces on the Western Front from the start of World War I until the end of 1916. He is best known for...
128
Joseph Jacques Césaire Joffre, was a French general who served as Commander-in-Chief of French forces on the Western Front from the start of World War I until the end of 1916. He is best known for...
Jean Mermoz
 126
Jean Mermoz was a French aviator, viewed as a hero by other pilots such as Saint-Exupéry, and in his native France, where many schools bear his name. In Brazil, he also is recognized as a pioneer...
126
Jean Mermoz was a French aviator, viewed as a hero by other pilots such as Saint-Exupéry, and in his native France, where many schools bear his name. In Brazil, he also is recognized as a pioneer...
Josquin des Prez
 122
Josquin Lebloitte dit des Prez was a composer of High Renaissance music, who is variously described as French or Franco-Flemish. Considered one of the greatest composers of the Renaissance, he was a...
122
Josquin Lebloitte dit des Prez was a composer of High Renaissance music, who is variously described as French or Franco-Flemish. Considered one of the greatest composers of the Renaissance, he was a...
Joan of Arc
 119
Joan of Arc is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the coronation of Charles VII of France during the...
119
Joan of Arc is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the coronation of Charles VII of France during the...
Jean de La Bruyère
 119
Jean de La Bruyère was a French philosopher and moralist, who was noted for his satire.
119
Jean de La Bruyère was a French philosopher and moralist, who was noted for his satire.
Alphonse de Lamartine
 112
Alphonse Marie Louis de Prat de Lamartine was a French author, poet, and statesman who was instrumental in the foundation of the French Second Republic and the continuation of the tricolore as the...
112
Alphonse Marie Louis de Prat de Lamartine was a French author, poet, and statesman who was instrumental in the foundation of the French Second Republic and the continuation of the tricolore as the...
Jean Monnet
 107
Jean Omer Marie Gabriel Monnet was a French civil servant, entrepreneur, diplomat, financier, administrator, and political visionary. An influential supporter of European unity, he is considered one...
107
Jean Omer Marie Gabriel Monnet was a French civil servant, entrepreneur, diplomat, financier, administrator, and political visionary. An influential supporter of European unity, he is considered one...
Pierre Brossolette
 103
Pierre Brossolette was a French journalist, politician and major hero of the French Resistance in World War II.
103
Pierre Brossolette was a French journalist, politician and major hero of the French Resistance in World War II.
Antoine Lavoisier
 99
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier, also Antoine Lavoisier after the French Revolution, was a French nobleman and chemist who was central to the 18th-century chemical revolution and who had a large...
99
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier, also Antoine Lavoisier after the French Revolution, was a French nobleman and chemist who was central to the 18th-century chemical revolution and who had a large...
Robert Schuman
 98
Jean-Baptiste Nicolas Robert Schuman was a Luxembourg-born French statesman. Schuman was a Christian democratic political thinker and activist. Twice Prime Minister of France, a reformist Minister of...
98
Jean-Baptiste Nicolas Robert Schuman was a Luxembourg-born French statesman. Schuman was a Christian democratic political thinker and activist. Twice Prime Minister of France, a reformist Minister of...
André-Marie Ampère
 98
André-Marie Ampère was a French physicist and mathematician who was one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics". He is also the...
98
André-Marie Ampère was a French physicist and mathematician who was one of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, which he referred to as "electrodynamics". He is also the...
Henri Barbusse
 97
Henri Barbusse was a French novelist, short story writer, journalist, poet and political activist. He began his literary career in the 1890s as a Symbolist poet and continued as a neo-Naturalist...
97
Henri Barbusse was a French novelist, short story writer, journalist, poet and political activist. He began his literary career in the 1890s as a Symbolist poet and continued as a neo-Naturalist...
Adolphe Thiers
 96
Marie Joseph Louis Adolphe Thiers was a French statesman and historian. He was the second elected President of France and first President of the Third Republic.
96
Marie Joseph Louis Adolphe Thiers was a French statesman and historian. He was the second elected President of France and first President of the Third Republic.
Salvador Allende
 92
Salvador Guillermo Allende Gossens was a Chilean socialist politician who served as the 28th president of Chile from 1970 until his death in 1973. As a democratic socialist committed to democracy, he...
92
Salvador Guillermo Allende Gossens was a Chilean socialist politician who served as the 28th president of Chile from 1970 until his death in 1973. As a democratic socialist committed to democracy, he...
Alphonse Juin
 92
Alphonse Pierre Juin was a senior French Army general who became Marshal of France. A graduate of the École Spéciale Militaire class of 1912, he served in Morocco in 1914 in command of native troops....
92
Alphonse Pierre Juin was a senior French Army general who became Marshal of France. A graduate of the École Spéciale Militaire class of 1912, he served in Morocco in 1914 in command of native troops....
Léon Blum
 91
André Léon Blum was a French socialist politician and three-time Prime Minister of France.
91
André Léon Blum was a French socialist politician and three-time Prime Minister of France.
Michael (archangel)
 90
Michael, also called Saint Michael the Archangel, Archangel Michael and Saint Michael the Taxiarch is an archangel in Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baha'i faith. The earliest surviving...
90
Michael, also called Saint Michael the Archangel, Archangel Michael and Saint Michael the Taxiarch is an archangel in Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baha'i faith. The earliest surviving...
John F. Kennedy
 90
John Fitzgerald Kennedy, often referred to as JFK, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the youngest...
90
John Fitzgerald Kennedy, often referred to as JFK, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the youngest...
Frédéric Mistral
 89
Joseph Étienne Frédéric Mistral was an Occitan writer and lexicographer of the Provençal form of the language. He received the 1904 Nobel Prize in Literature "in recognition of the fresh originality...
89
Joseph Étienne Frédéric Mistral was an Occitan writer and lexicographer of the Provençal form of the language. He received the 1904 Nobel Prize in Literature "in recognition of the fresh originality...
Pierre Mendès France
 84
Pierre Isaac Isidore Mendès France was a French politician who served as prime minister of France for eight months from 1954 to 1955. As a member of the Radical Party, he headed a government...
84
Pierre Isaac Isidore Mendès France was a French politician who served as prime minister of France for eight months from 1954 to 1955. As a member of the Radical Party, he headed a government...
Pierre de Coubertin
 83
Charles Pierre de Frédy, Baron de Coubertin, also known as Pierre de Coubertin and Baron de Coubertin, was a French educator and historian, co-founder of the International Olympic Committee, and its...
83
Charles Pierre de Frédy, Baron de Coubertin, also known as Pierre de Coubertin and Baron de Coubertin, was a French educator and historian, co-founder of the International Olympic Committee, and its...
René Cassin
 81
René Samuel Cassin was a French jurist known for co-authoring the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and receiving the Nobel Peace Prize.
81
René Samuel Cassin was a French jurist known for co-authoring the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and receiving the Nobel Peace Prize.
Albert Schweitzer
 77
Ludwig Philipp Albert Schweitzer was an Alsatian polymath. He was a theologian, organist, musicologist, writer, humanitarian, philosopher, and physician. A Lutheran minister, Schweitzer challenged...
77
Ludwig Philipp Albert Schweitzer was an Alsatian polymath. He was a theologian, organist, musicologist, writer, humanitarian, philosopher, and physician. A Lutheran minister, Schweitzer challenged...
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
 76
Jean-Jacques Rousseau was a Genevan philosopher (philosophe), writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects...
76
Jean-Jacques Rousseau was a Genevan philosopher (philosophe), writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects...
Henry Dunant
 75
Henry Dunant, also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, social activist, and co-founder of the Red Cross. His humanitarian efforts won him the first Nobel Peace Prize in 1901.
75
Henry Dunant, also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, social activist, and co-founder of the Red Cross. His humanitarian efforts won him the first Nobel Peace Prize in 1901.
Jules Verne
 75
Jules Gabriel Verne was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the Voyages extraordinaires, a series of bestselling...
75
Jules Gabriel Verne was a French novelist, poet, and playwright. His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the Voyages extraordinaires, a series of bestselling...
Georges Brassens
 74
Georges Charles Brassens was a French singer-songwriter and poet.
74
Georges Charles Brassens was a French singer-songwriter and poet.
Pierre Semard
 74
Pierre Semard was a trade unionist, secretary general of the federation of railway-workers and leader of the French Communist Party. He was shot in prison by the Nazi occupiers in 1942, and is buried...
74
Pierre Semard was a trade unionist, secretary general of the federation of railway-workers and leader of the French Communist Party. He was shot in prison by the Nazi occupiers in 1942, and is buried...
Joseph Gallieni
 73
Joseph Simon Gallieni was a French military officer, active for most of his career as a military commander and administrator in the French colonies where he wrote several books on colonial affairs.
73
Joseph Simon Gallieni was a French military officer, active for most of his career as a military commander and administrator in the French colonies where he wrote several books on colonial affairs.
Saint Anne
 72
According to apocrypha, as well as Christian and Islamic tradition, Saint Anne was the mother of Mary, the wife of Joachim and the maternal grandmother of Jesus. Mary's mother is not named in the...
72
According to apocrypha, as well as Christian and Islamic tradition, Saint Anne was the mother of Mary, the wife of Joachim and the maternal grandmother of Jesus. Mary's mother is not named in the...
Georges Pompidou
 71
Georges Jean Raymond Pompidou was a French politician who served as President of France from 1969 to his death in 1974. He was earlier the longest-ever Prime Minister of France, under President...
71
Georges Jean Raymond Pompidou was a French politician who served as President of France from 1969 to his death in 1974. He was earlier the longest-ever Prime Minister of France, under President...
George Sand
 71
Amantine Lucile Aurore Dupin de Francueil, best known by her pen name George Sand, was a French novelist, memoirist and journalist. One of the most popular writers in Europe in her lifetime, being...
71
Amantine Lucile Aurore Dupin de Francueil, best known by her pen name George Sand, was a French novelist, memoirist and journalist. One of the most popular writers in Europe in her lifetime, being...
Blaise Pascal
 70
Blaise Pascal was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic writer.
70
Blaise Pascal was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic writer.
James the Great
 70
James the Great was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was the second of the apostles to die, and the first to be martyred. Saint James is the patron saint of...
70
James the Great was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was the second of the apostles to die, and the first to be martyred. Saint James is the patron saint of...
Louis IX of France
 70
Louis IX, commonly revered as Saint Louis, was King of France from 1226 until his death in 1270. He is widely recognized as the most distinguished of the Direct Capetians. Following the death of his...
70
Louis IX, commonly revered as Saint Louis, was King of France from 1226 until his death in 1270. He is widely recognized as the most distinguished of the Direct Capetians. Following the death of his...
Jules Guesde
 70
Jules Bazile, known as Jules Guesde was a French socialist journalist and politician.
70
Jules Bazile, known as Jules Guesde was a French socialist journalist and politician.
Paul Bert
 70
Paul Bert was a French zoologist, physiologist and politician. He is sometimes given the sobriquet "Father of Aviation Medicine".
70
Paul Bert was a French zoologist, physiologist and politician. He is sometimes given the sobriquet "Father of Aviation Medicine".
Georges Guynemer
 70
Georges Guynemer was the second highest-scoring French fighter ace with 54 victories during World War I, and a French national hero at the time of his death. Guynemer's death was a profound shock to...
70
Georges Guynemer was the second highest-scoring French fighter ace with 54 victories during World War I, and a French national hero at the time of his death. Guynemer's death was a profound shock to...
Molière
 70
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin, known by his stage name Molière, was a French playwright, actor, and poet, widely regarded as one of the great writers in the French language and world literature. His extant...
70
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin, known by his stage name Molière, was a French playwright, actor, and poet, widely regarded as one of the great writers in the French language and world literature. His extant...
Marcellin Berthelot
 68
Pierre Eugène Marcellin Berthelot was a French chemist and Republican politician noted for the Thomsen–Berthelot principle of thermochemistry. He synthesized many organic compounds from inorganic...
68
Pierre Eugène Marcellin Berthelot was a French chemist and Republican politician noted for the Thomsen–Berthelot principle of thermochemistry. He synthesized many organic compounds from inorganic...
Louise Michel
 68
Louise Michel was a teacher and important figure in the Paris Commune. Following her penal transportation to New Caledonia she embraced anarchism. When returning to France she emerged as an important...
68
Louise Michel was a teacher and important figure in the Paris Commune. Following her penal transportation to New Caledonia she embraced anarchism. When returning to France she emerged as an important...
Albert Camus
 67
Albert Camus was a French philosopher, author, dramatist, journalist, world federalist, and political activist. He was the recipient of the 1957 Nobel Prize in Literature at the age of 44, the...
67
Albert Camus was a French philosopher, author, dramatist, journalist, world federalist, and political activist. He was the recipient of the 1957 Nobel Prize in Literature at the age of 44, the...
Hector Berlioz
 67
Louis-Hector Berlioz was a French Romantic composer and conductor. His output includes orchestral works such as the Symphonie fantastique and Harold in Italy, choral pieces including the Requiem and...
67
Louis-Hector Berlioz was a French Romantic composer and conductor. His output includes orchestral works such as the Symphonie fantastique and Harold in Italy, choral pieces including the Requiem and...
Saint Nicholas
 67
Saint Nicholas of Myra, also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greek descent from the maritime city of Patara in Anatolia during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the...
67
Saint Nicholas of Myra, also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greek descent from the maritime city of Patara in Anatolia during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the...
Gustave Eiffel
 64
Alexandre Gustave Eiffel was a French civil engineer. A graduate of École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures, he made his name with various bridges for the French railway network, most famously the...
64
Alexandre Gustave Eiffel was a French civil engineer. A graduate of École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures, he made his name with various bridges for the French railway network, most famously the...
Irène Joliot-Curie
 63
Irène Joliot-Curie was a French chemist, physicist and politician, the elder daughter of Pierre Curie and Marie Skłodowska–Curie, and the wife of Frédéric Joliot-Curie. Jointly with her husband,...
63
Irène Joliot-Curie was a French chemist, physicist and politician, the elder daughter of Pierre Curie and Marie Skłodowska–Curie, and the wife of Frédéric Joliot-Curie. Jointly with her husband,...
Louis Blériot
 62
Louis Charles Joseph Blériot was a French aviator, inventor, and engineer. He developed the first practical headlamp for cars and established a profitable business manufacturing them, using much of...
62
Louis Charles Joseph Blériot was a French aviator, inventor, and engineer. He developed the first practical headlamp for cars and established a profitable business manufacturing them, using much of...
Maurice Ravel
 62
Joseph Maurice Ravel was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the...
62
Joseph Maurice Ravel was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the...
Édouard Branly
 61
Édouard Eugène Désiré Branly was a French inventor, physicist and professor at the Institut Catholique de Paris. He is primarily known for his early involvement in wireless telegraphy and his...
61
Édouard Eugène Désiré Branly was a French inventor, physicist and professor at the Institut Catholique de Paris. He is primarily known for his early involvement in wireless telegraphy and his...
Saint Roch
 61
Roch, also called Rock in English, was a Majorcan Catholic confessor whose death is commemorated on 16 August and 9 September in Italy; he was especially invoked against the plague. He has the...
61
Roch, also called Rock in English, was a Majorcan Catholic confessor whose death is commemorated on 16 August and 9 September in Italy; he was especially invoked against the plague. He has the...
Auguste and Louis Lumière
 59
The Lumière brothers, Auguste Marie Louis Nicolas Lumière and Louis Jean Lumière, were French manufacturers of photography equipment, best known for their Cinématographe motion picture system and the...
59
The Lumière brothers, Auguste Marie Louis Nicolas Lumière and Louis Jean Lumière, were French manufacturers of photography equipment, best known for their Cinématographe motion picture system and the...
Woodrow Wilson
 59
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president...
59
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president...
François Arago
 59
Dominique François Jean Arago, known simply as François Arago, was a French mathematician, physicist, astronomer, freemason, supporter of the Carbonari revolutionaries and politician.
59
Dominique François Jean Arago, known simply as François Arago, was a French mathematician, physicist, astronomer, freemason, supporter of the Carbonari revolutionaries and politician.
René Laennec
 59
René-Théophile-Hyacinthe Laennec was a French physician and musician. His skill at carving his own wooden flutes led him to invent the stethoscope in 1816, while working at the Hôpital Necker. He...
59
René-Théophile-Hyacinthe Laennec was a French physician and musician. His skill at carving his own wooden flutes led him to invent the stethoscope in 1816, while working at the Hôpital Necker. He...
Leonardo da Vinci
 59
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame...
59
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame...
Alphonse Daudet
 58
Alphonse Daudet was a French novelist. He was the husband of Julia Daudet and father of Edmée, Léon and Lucien Daudet.
58
Alphonse Daudet was a French novelist. He was the husband of Julia Daudet and father of Edmée, Léon and Lucien Daudet.
Rossignols
 58
The Rossignols, a family of French cryptographers and cryptanalysts, included Antoine Rossignol (1600–1682), Bonaventure Rossignol and Antoine-Bonaventure Rossignol. The family name means...
58
The Rossignols, a family of French cryptographers and cryptanalysts, included Antoine Rossignol (1600–1682), Bonaventure Rossignol and Antoine-Bonaventure Rossignol. The family name means...
Jacques Brel
 58
Jacques Romain Georges Brel was a Belgian singer and actor who composed and performed theatrical songs. He generated a large, devoted following—initially in Belgium and France, but later throughout...
58
Jacques Romain Georges Brel was a Belgian singer and actor who composed and performed theatrical songs. He generated a large, devoted following—initially in Belgium and France, but later throughout...
Paul Doumer
 56
Joseph Athanase Doumer, commonly known as Paul Doumer, was a French politician who served as the President of France from June 1931 until his assassination in May 1932. He is described as "the Father...
56
Joseph Athanase Doumer, commonly known as Paul Doumer, was a French politician who served as the President of France from June 1931 until his assassination in May 1932. He is described as "the Father...
Marcel Pagnol
 56
Marcel Paul Pagnol was a French novelist, playwright, and filmmaker. Regarded as an auteur, in 1946, he became the first filmmaker elected to the Académie française. Although his work is less...
56
Marcel Paul Pagnol was a French novelist, playwright, and filmmaker. Regarded as an auteur, in 1946, he became the first filmmaker elected to the Académie française. Although his work is less...
Albert Calmette
 56
Albert Calmette, né le 12 juillet 1863 à Nice et mort le 29 octobre 1933 à Paris, est un médecin et bactériologiste militaire français.
56
Albert Calmette, né le 12 juillet 1863 à Nice et mort le 29 octobre 1933 à Paris, est un médecin et bactériologiste militaire français.
Lazare Hoche
 55
Louis Lazare Hoche was a French military leader of the French Revolutionary Wars. He won a victory over Royalist forces in Brittany. His surname is one of the names inscribed under the Arc de...
55
Louis Lazare Hoche was a French military leader of the French Revolutionary Wars. He won a victory over Royalist forces in Brittany. His surname is one of the names inscribed under the Arc de...
Marie Curie
 55
Maria Salomea Skłodowska-Curie, known simply as Marie Curie, was a Polish and naturalised-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first woman to...
55
Maria Salomea Skłodowska-Curie, known simply as Marie Curie, was a Polish and naturalised-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first woman to...
Paul Vaillant-Couturier
 53
Paul Vaillant-Couturier was a French writer and communist. He participated in the founding of the French Communist Party (PCF) in 1920.
53
Paul Vaillant-Couturier was a French writer and communist. He participated in the founding of the French Communist Party (PCF) in 1920.
Claude Debussy
 53
(Achille) Claude Debussy was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most influential composers of the...
53
(Achille) Claude Debussy was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most influential composers of the...
Marcel Marceau
 52
Marcel Marceau was a French mime artist and actor most famous for his stage persona, "Bip the Clown". He referred to mime as the "art of silence", performing professionally worldwide for more than 60...
52
Marcel Marceau was a French mime artist and actor most famous for his stage persona, "Bip the Clown". He referred to mime as the "art of silence", performing professionally worldwide for more than 60...
Jules Michelet
 52
Jules Michelet was a French historian and writer. He is best known for his multivolume work Histoire de France, which traces the history of France from the earliest times to the French Revolution. He...
52
Jules Michelet was a French historian and writer. He is best known for his multivolume work Histoire de France, which traces the history of France from the earliest times to the French Revolution. He...
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
 52
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition resulted in more than 800 works representing virtually...
52
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition resulted in more than 800 works representing virtually...
Pierre-Auguste Renoir
 52
Pierre-Auguste Renoir was a French artist who was a leading painter in the development of the Impressionist style. As a celebrator of beauty and especially feminine sensuality, it has been said that...
52
Pierre-Auguste Renoir was a French artist who was a leading painter in the development of the Impressionist style. As a celebrator of beauty and especially feminine sensuality, it has been said that...
Léo Lagrange
 52
Léo Lagrange was a French Socialist, member of the SFIO, named secretary of State in the Popular Front government of Léon Blum.
52
Léo Lagrange was a French Socialist, member of the SFIO, named secretary of State in the Popular Front government of Léon Blum.
Paul Gauguin
 52
Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin was a French painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, and writer, whose work has been primarily associated with the Post-Impressionist and Symbolist movements. He was also...
52
Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin was a French painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, and writer, whose work has been primarily associated with the Post-Impressionist and Symbolist movements. He was also...
Pierre Corneille
 51
Pierre Corneille was a French tragedian. He is generally considered one of the three great seventeenth-century French dramatists, along with Molière and Racine.
51
Pierre Corneille was a French tragedian. He is generally considered one of the three great seventeenth-century French dramatists, along with Molière and Racine.
Paul Langevin
 51
Paul Langevin was a French physicist who developed Langevin dynamics and the Langevin equation. He was one of the founders of the Comité de vigilance des intellectuels antifascistes, an anti-fascist...
51
Paul Langevin was a French physicist who developed Langevin dynamics and the Langevin equation. He was one of the founders of the Comité de vigilance des intellectuels antifascistes, an anti-fascist...
Jacques Prévert
 51
Jacques Prévert was a French poet and screenwriter. His poems became and remain popular in the French-speaking world, particularly in schools. His best-regarded films formed part of the poetic...
51
Jacques Prévert was a French poet and screenwriter. His poems became and remain popular in the French-speaking world, particularly in schools. His best-regarded films formed part of the poetic...
François-René de Chateaubriand
 51
François-René, vicomte de Chateaubriand was a French writer, politician, diplomat and historian who influenced French literature of the nineteenth century. Descended from an old aristocratic family...
51
François-René, vicomte de Chateaubriand was a French writer, politician, diplomat and historian who influenced French literature of the nineteenth century. Descended from an old aristocratic family...
Paul Verlaine
 51
Paul-Marie Verlaine was a French poet associated with the Symbolist movement and the Decadent movement. He is considered one of the greatest representatives of the fin de siècle in international and...
51
Paul-Marie Verlaine was a French poet associated with the Symbolist movement and the Decadent movement. He is considered one of the greatest representatives of the fin de siècle in international and...
Paul Cézanne
 50
Paul Cézanne was a French Post-Impressionist painter whose work introduced new modes of representation and influenced avant-garde artistic movements of the early 20th century. Cézanne is said to have...
50
Paul Cézanne was a French Post-Impressionist painter whose work introduced new modes of representation and influenced avant-garde artistic movements of the early 20th century. Cézanne is said to have...
Pablo Picasso
 49
Pablo Ruiz Picasso was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist, and theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th century,...
49
Pablo Ruiz Picasso was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist, and theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th century,...
Ernest Renan
 49
Joseph Ernest Renan was a French Orientalist and Semitic scholar, writing on Semitic languages and civilizations, historian of religion, philologist, philosopher, biblical scholar, and critic. He...
49
Joseph Ernest Renan was a French Orientalist and Semitic scholar, writing on Semitic languages and civilizations, historian of religion, philologist, philosopher, biblical scholar, and critic. He...
Jean Macé
 49
Jean François Macé was a French educator, journalist, active freemason and politician. He was perhaps best known as the founder of Ligue de l'enseignement to promote free, universal and secular...
49
Jean François Macé was a French educator, journalist, active freemason and politician. He was perhaps best known as the founder of Ligue de l'enseignement to promote free, universal and secular...
Clément Ader
 47
Clément Ader was a French inventor and engineer who was born near Toulouse in Muret, Haute-Garonne, and died in Toulouse. He is remembered primarily for his pioneering work in aviation. In 1870 he...
47
Clément Ader was a French inventor and engineer who was born near Toulouse in Muret, Haute-Garonne, and died in Toulouse. He is remembered primarily for his pioneering work in aviation. In 1870 he...
Denis Diderot
 46
Denis Diderot was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the Encyclopédie along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a...
46
Denis Diderot was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the Encyclopédie along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a...
Pierre Loti
 46
Pierre Loti was a French naval officer and novelist, known for his exotic novels and short stories.
46
Pierre Loti was a French naval officer and novelist, known for his exotic novels and short stories.
Honoré Gabriel Riqueti, comte de Mirabeau
 46
Honoré Gabriel Riqueti, Count of Mirabeau was a French writer, orator, statesman and a prominent figure of the early stages of the French Revolution.
46
Honoré Gabriel Riqueti, Count of Mirabeau was a French writer, orator, statesman and a prominent figure of the early stages of the French Revolution.
Henri Matisse
 46
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known...
46
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known...
André Malraux
 46
Georges André Malraux was a French novelist, art theorist, and minister of cultural affairs. Malraux's novel La Condition Humaine (1933) won the Prix Goncourt. He was appointed by President Charles...
46
Georges André Malraux was a French novelist, art theorist, and minister of cultural affairs. Malraux's novel La Condition Humaine (1933) won the Prix Goncourt. He was appointed by President Charles...
Yves Rocher
 45
Yves Rocher was a French businessman and founder of the cosmetics company that bears his name. He was a pioneer of the modern use of natural ingredients in cosmetics.
45
Yves Rocher was a French businessman and founder of the cosmetics company that bears his name. He was a pioneer of the modern use of natural ingredients in cosmetics.
Maryse Bastié
 45
Maryse Bastié was a French aviator who set several international records for female aviators during the 1930s.
45
Maryse Bastié was a French aviator who set several international records for female aviators during the 1930s.
Simone Veil
 45
Simone Veil was a French magistrate, Holocaust survivor, and politician who served as Health Minister in several governments and was President of the European Parliament from 1979 to 1982, the first...
45
Simone Veil was a French magistrate, Holocaust survivor, and politician who served as Health Minister in several governments and was President of the European Parliament from 1979 to 1982, the first...
Albert I of Belgium
 44
Albert I was King of the Belgians from 23 December 1909 until his death in 1934.
44
Albert I was King of the Belgians from 23 December 1909 until his death in 1934.
Vincent de Paul
 44
Vincent de Paul, CM, commonly known as Saint Vincent de Paul, was an Occitan French Catholic priest who dedicated himself to serving the poor.
44
Vincent de Paul, CM, commonly known as Saint Vincent de Paul, was an Occitan French Catholic priest who dedicated himself to serving the poor.
Marquis de Condorcet
 43
Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet, known as Nicolas de Condorcet, was a French philosopher and mathematician. His ideas, including support for a free markets, public...
43
Marie Jean Antoine Nicolas de Caritat, Marquis of Condorcet, known as Nicolas de Condorcet, was a French philosopher and mathematician. His ideas, including support for a free markets, public...
Georges Danton
 43
Georges Jacques Danton was a leading figure in the French Revolution. A modest and unknown lawyer on the eve of the Revolution, Danton became a famous orator of the Cordeliers Club and was raised to...
43
Georges Jacques Danton was a leading figure in the French Revolution. A modest and unknown lawyer on the eve of the Revolution, Danton became a famous orator of the Cordeliers Club and was raised to...
Louis Faidherbe
 43
Louis Léon César Faidherbe was a French general and colonial administrator. He created the Senegalese Tirailleurs when he was governor of Senegal.
43
Louis Léon César Faidherbe was a French general and colonial administrator. He created the Senegalese Tirailleurs when he was governor of Senegal.
Franklin D. Roosevelt
 43
Franklin Delano Roosevelt, commonly known by his initials FDR, was an American statesman and politician who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. He was...
43
Franklin Delano Roosevelt, commonly known by his initials FDR, was an American statesman and politician who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. He was...
Frédéric Chopin
 43
Frédéric François Chopin was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist of the Romantic period, who wrote primarily for solo piano. He has maintained worldwide renown as a leading musician of his era,...
43
Frédéric François Chopin was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist of the Romantic period, who wrote primarily for solo piano. He has maintained worldwide renown as a leading musician of his era,...
Lucie Aubrac
 43
Lucie Samuel, born Bernard and known as Lucie Aubrac, was a member of the French Resistance in World War II. A history teacher by occupation, she earned a history agrégation in 1938, a highly...
43
Lucie Samuel, born Bernard and known as Lucie Aubrac, was a member of the French Resistance in World War II. A history teacher by occupation, she earned a history agrégation in 1938, a highly...
Hélène Boucher
 43
Hélène Boucher was a well-known French pilot in the early 1930s, when she set several women's world speed records and the all-comers record for 1,000 km in 1934. She was killed in an accident in the...
43
Hélène Boucher was a well-known French pilot in the early 1930s, when she set several women's world speed records and the all-comers record for 1,000 km in 1934. She was killed in an accident in the...
Napoleon
 42
Napoleon Bonaparte, later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French emperor and military commander who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the...
42
Napoleon Bonaparte, later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French emperor and military commander who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the...
Louis Blanc
 42
Louis Jean Joseph Charles Blanc was a French socialist politician, journalist and historian. He called for the creation of cooperatives in order to guarantee employment for the urban poor. Although...
42
Louis Jean Joseph Charles Blanc was a French socialist politician, journalist and historian. He called for the creation of cooperatives in order to guarantee employment for the urban poor. Although...
Count of St. Germain
 42
The Count of St. Germain or in French Comte de Saint Germain was a European adventurer who achieved prominence in European high society of the mid-18th century due to his interest and achievements in...
42
The Count of St. Germain or in French Comte de Saint Germain was a European adventurer who achieved prominence in European high society of the mid-18th century due to his interest and achievements in...
Rosa Luxemburg
 42
Rosa Luxemburg was a Polish and naturalised-German revolutionary socialist, orthodox Marxist, and anti-War activist during the First World War. She became a key figure of the revolutionary socialist...
42
Rosa Luxemburg was a Polish and naturalised-German revolutionary socialist, orthodox Marxist, and anti-War activist during the First World War. She became a key figure of the revolutionary socialist...
Antoine de Padoue
 42
Fernando Martins de Bulhões, souvent appelé en latin Antonius Ulyssiponensis, en religion frère Antoine, né en 1195 à Lisbonne (Portugal) et mort le 13 juin 1231 près de Padoue (Italie), est un...
42
Fernando Martins de Bulhões, souvent appelé en latin Antonius Ulyssiponensis, en religion frère Antoine, né en 1195 à Lisbonne (Portugal) et mort le 13 juin 1231 près de Padoue (Italie), est un...
Georges Bizet
 42
Georges Bizet was a French composer of the Romantic era. Best known for his operas in a career cut short by his early death, Bizet achieved few successes before his final work, Carmen, which has...
42
Georges Bizet was a French composer of the Romantic era. Best known for his operas in a career cut short by his early death, Bizet achieved few successes before his final work, Carmen, which has...
Alfred de Musset
 41
Alfred Louis Charles de Musset-Pathay was a French dramatist, poet, and novelist. Along with his poetry, he is known for writing the autobiographical novel La Confession d'un enfant du siècle.
41
Alfred Louis Charles de Musset-Pathay was a French dramatist, poet, and novelist. Along with his poetry, he is known for writing the autobiographical novel La Confession d'un enfant du siècle.
Saint Joseph
 41
Joseph was a 1st-century Jewish man of Nazareth who, according to the canonical Gospels, was married to Mary, the mother of Jesus, and was the legal father of Jesus.
41
Joseph was a 1st-century Jewish man of Nazareth who, according to the canonical Gospels, was married to Mary, the mother of Jesus, and was the legal father of Jesus.
Winston Churchill
 41
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again...
41
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again...
Henri Becquerel
 41
Antoine Henri Becquerel was a French engineer, physicist, Nobel laureate, and the first person to discover radioactivity. For work in this field he, along with Marie Skłodowska-Curie and Pierre...
41
Antoine Henri Becquerel was a French engineer, physicist, Nobel laureate, and the first person to discover radioactivity. For work in this field he, along with Marie Skłodowska-Curie and Pierre...
Jean-Baptiste Kléber
 41
Jean-Baptiste Kléber was a French military leader of the French Revolutionary Wars. After serving for one year in the French Royal Army, he entered Habsburg service seven years later. However, his...
41
Jean-Baptiste Kléber was a French military leader of the French Revolutionary Wars. After serving for one year in the French Royal Army, he entered Habsburg service seven years later. However, his...
Michel de Montaigne
 40
Michel Eyquem, Seigneur de Montaigne, commonly known as Michel de Montaigne, was one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance. He is known for popularizing the essay as a...
40
Michel Eyquem, Seigneur de Montaigne, commonly known as Michel de Montaigne, was one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance. He is known for popularizing the essay as a...
Jean-Baptiste Colbert
 39
Jean-Baptiste Colbert was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the...
39
Jean-Baptiste Colbert was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the...
Saint George
 39
Saint George, also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition, he was a soldier in the Roman army. Of Cappadocian Greek origin,...
39
Saint George, also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition, he was a soldier in the Roman army. Of Cappadocian Greek origin,...
Claude Monet
 39
Oscar-Claude Monet was a French painter and founder of impressionist painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his...
39
Oscar-Claude Monet was a French painter and founder of impressionist painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During his...
Roger Vivier
 39
Roger Henri Vivier was a French fashion designer who specialized in shoes. He is best-known for creating the modern day stiletto heel and for placing a chrome-plated buckle on an elegant black pump,...
39
Roger Henri Vivier was a French fashion designer who specialized in shoes. He is best-known for creating the modern day stiletto heel and for placing a chrome-plated buckle on an elegant black pump,...
Raymond Poincaré
 38
Raymond Nicolas Landry Poincaré was a French statesman who served as President of France from 1913 to 1920, and three times as Prime Minister of France.
38
Raymond Nicolas Landry Poincaré was a French statesman who served as President of France from 1913 to 1920, and three times as Prime Minister of France.
Claude Joseph Rouget de Lisle
 37
Claude Joseph Rouget de Lisle, sometimes spelled de l'Isle or de Lile, was a French army officer of the French Revolutionary Wars. He is known for writing the words and music of the Chant de guerre...
37
Claude Joseph Rouget de Lisle, sometimes spelled de l'Isle or de Lile, was a French army officer of the French Revolutionary Wars. He is known for writing the words and music of the Chant de guerre...
Charles Péguy
 37
Charles Pierre Péguy was a French poet, essayist, and editor. His two main philosophies were socialism and nationalism; by 1908 at the latest, after years of uneasy agnosticism, he had become a...
37
Charles Pierre Péguy was a French poet, essayist, and editor. His two main philosophies were socialism and nationalism; by 1908 at the latest, after years of uneasy agnosticism, he had become a...
Johannes Gutenberg
 37
Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg was a German inventor and craftsman who introduced letterpress printing to Europe with his movable-type printing press. Though movable type was already in...
37
Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg was a German inventor and craftsman who introduced letterpress printing to Europe with his movable-type printing press. Though movable type was already in...
Yves Saint Laurent (designer)
 37
Yves Henri Donat Mathieu-Saint-Laurent, referred to as Yves Saint Laurent or YSL, was a French fashion designer who, in 1962, founded his eponymous fashion label. He is regarded as being among the...
37
Yves Henri Donat Mathieu-Saint-Laurent, referred to as Yves Saint Laurent or YSL, was a French fashion designer who, in 1962, founded his eponymous fashion label. He is regarded as being among the...
Ambroise Croizat
 37
Ambroise Croizat was a French syndicalist and communist politician. As the minister of Labour and of Social security, he founded the French Social security system and the retirement system, between...
37
Ambroise Croizat was a French syndicalist and communist politician. As the minister of Labour and of Social security, he founded the French Social security system and the retirement system, between...
Louis Armand
 36
Louis François Armand was a French engineer and senior civil servant who managed several public companies, as well as had a significant role in World War II as an officer in the Resistance. He became...
36
Louis François Armand was a French engineer and senior civil servant who managed several public companies, as well as had a significant role in World War II as an officer in the Resistance. He became...
Galileo Galilei
 36
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei, commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei or simply Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. He was born...
36
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei, commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei or simply Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. He was born...
Romain Rolland
 36
Romain Rolland was a French dramatist, novelist, essayist, art historian and mystic who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1915 "as a tribute to the lofty idealism of his literary...
36
Romain Rolland was a French dramatist, novelist, essayist, art historian and mystic who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1915 "as a tribute to the lofty idealism of his literary...
Honoré d'Estienne d'Orves
 36
Henri Louis Honoré, Count d'Estienne d'Orves was a French Navy officer and one of the major heroes of the French Resistance, said to be the "first martyr of Free France".
36
Henri Louis Honoré, Count d'Estienne d'Orves was a French Navy officer and one of the major heroes of the French Resistance, said to be the "first martyr of Free France".
Pierre de Ronsard
 36
Pierre de Ronsard was a French poet or, as his own generation in France called him, a "prince of poets".
36
Pierre de Ronsard was a French poet or, as his own generation in France called him, a "prince of poets".
Eugeniu Botez
 35
Eugeniu Botez was a Romanian writer, best known for his novel Europolis (1933). Botez wrote under the pseudonym Jean Bart.
35
Eugeniu Botez was a Romanian writer, best known for his novel Europolis (1933). Botez wrote under the pseudonym Jean Bart.
Jacques Cartier
 35
Jacques Cartier was a French-Breton maritime explorer for France. Jacques Cartier was the first European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River,...
35
Jacques Cartier was a French-Breton maritime explorer for France. Jacques Cartier was the first European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River,...
Paul Éluard
 35
Paul Éluard, born Eugène Émile Paul Grindel, was a French poet and one of the founders of the Surrealist movement.
35
Paul Éluard, born Eugène Émile Paul Grindel, was a French poet and one of the founders of the Surrealist movement.
Éric Tabarly
Marcel Paul
 34
Marcel Paul was a French trade unionist and communist politician. He was also a Nazi concentration camp survivor and later served as a member of the French parliament.
34
Marcel Paul was a French trade unionist and communist politician. He was also a Nazi concentration camp survivor and later served as a member of the French parliament.
Denis of Paris
 33
Denis of Paris was a 3rd-century Christian martyr and saint. According to his hagiographies, he was bishop of Paris in the third century and, together with his companions Rusticus and Eleutherius,...
33
Denis of Paris was a 3rd-century Christian martyr and saint. According to his hagiographies, he was bishop of Paris in the third century and, together with his companions Rusticus and Eleutherius,...
François Rabelais
 33
François Rabelais was a French writer who has been called the first great French prose author. A humanist of the French Renaissance and Greek scholar, he attracted opposition from both John Calvin...
33
François Rabelais was a French writer who has been called the first great French prose author. A humanist of the French Renaissance and Greek scholar, he attracted opposition from both John Calvin...
Vincent van Gogh
 33
Vincent Willem van Gogh was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who is among the most famous and influential figures in the history of Western art. In just over a decade, he created approximately 2100...
33
Vincent Willem van Gogh was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who is among the most famous and influential figures in the history of Western art. In just over a decade, he created approximately 2100...
Hubert Lyautey
 33
Louis Hubert Gonzalve Lyautey was a French Army general and colonial administrator. After serving in Indochina and Madagascar, he became the first French Resident-General in Morocco from 1912 to...
33
Louis Hubert Gonzalve Lyautey was a French Army general and colonial administrator. After serving in Indochina and Madagascar, he became the first French Resident-General in Morocco from 1912 to...
Ferdinand Buisson
 33
Ferdinand Édouard Buisson was a French educational bureaucrat, pacifist, and Radical-Socialist politician. He presided over the League of Education from 1902 to 1906 and over the Human Rights League...
33
Ferdinand Édouard Buisson was a French educational bureaucrat, pacifist, and Radical-Socialist politician. He presided over the League of Education from 1902 to 1906 and over the Human Rights League...
Sully Prudhomme
 33
René François Armand "Sully" Prudhomme was a French poet and essayist. He was the first winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1901.
33
René François Armand "Sully" Prudhomme was a French poet and essayist. He was the first winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1901.
Bernard Palissy
 33
Bernard Palissy was a French Huguenot potter, hydraulics engineer and craftsman, famous for having struggled for sixteen years to imitate Chinese porcelain. He is best known for his so-called...
33
Bernard Palissy was a French Huguenot potter, hydraulics engineer and craftsman, famous for having struggled for sixteen years to imitate Chinese porcelain. He is best known for his so-called...
Alexandre Dumas
 33
Alexandre Dumas, also known as Alexandre Dumas père, was a French novelist and playwright.
33
Alexandre Dumas, also known as Alexandre Dumas père, was a French novelist and playwright.
Émile Roux
 32
Pierre Paul Émile Roux, né le 17 décembre 1853 à Confolens (Charente) et mort le 3 novembre 1933 à Paris, est un médecin, bactériologiste et immunologiste français. Il fut l'un des plus proches...
32
Pierre Paul Émile Roux, né le 17 décembre 1853 à Confolens (Charente) et mort le 3 novembre 1933 à Paris, est un médecin, bactériologiste et immunologiste français. Il fut l'un des plus proches...
Montesquieu
 32
Charles Louis de Secondat, Baron de La Brède et de Montesquieu, generally referred to as simply Montesquieu, was a French judge, man of letters, historian, and political philosopher.
32
Charles Louis de Secondat, Baron de La Brède et de Montesquieu, generally referred to as simply Montesquieu, was a French judge, man of letters, historian, and political philosopher.
Saint Barbara
 32
Saint Barbara, known in the Eastern Orthodox Church as the Great Martyr Barbara, was an early Christian Greek saint and martyr.
32
Saint Barbara, known in the Eastern Orthodox Church as the Great Martyr Barbara, was an early Christian Greek saint and martyr.
Jean Rostand
 32
Jean Edmond Cyrus Rostand was a French biologist, historian of science, and philosopher.
32
Jean Edmond Cyrus Rostand was a French biologist, historian of science, and philosopher.
Charles Baudelaire
 32
Charles Pierre Baudelaire was a French poet who also worked as an essayist, art critic and translator. His poems are described as exhibiting mastery of rhyme and rhythm, containing an exoticism...
32
Charles Pierre Baudelaire was a French poet who also worked as an essayist, art critic and translator. His poems are described as exhibiting mastery of rhyme and rhythm, containing an exoticism...
Théodore Botrel
 32
Jean-Baptiste-Théodore-Marie Botrel was a French singer-songwriter, poet and playwright. He is best known for his popular songs about his native Brittany, of which the most famous is La Paimpolaise....
32
Jean-Baptiste-Théodore-Marie Botrel was a French singer-songwriter, poet and playwright. He is best known for his popular songs about his native Brittany, of which the most famous is La Paimpolaise....
Édith Piaf
 32
Édith Piaf was a French singer best known for performing songs in the cabaret and modern chanson genres. She is widely regarded as France's greatest popular singer and one of the most celebrated...
32
Édith Piaf was a French singer best known for performing songs in the cabaret and modern chanson genres. She is widely regarded as France's greatest popular singer and one of the most celebrated...
Félix Faure
 31
Félix François Faure was the president of France from 1895 until his death in 1899. A native of Paris, he worked as a tanner in his younger years. Faure became a member of the Chamber of Deputies for...
31
Félix François Faure was the president of France from 1895 until his death in 1899. A native of Paris, he worked as a tanner in his younger years. Faure became a member of the Chamber of Deputies for...
Joseph Marie Jacquard
 31
Joseph Marie Charles dit Jacquard was a French weaver and merchant. He played an important role in the development of the earliest programmable loom, which in turn played an important role in the...
31
Joseph Marie Charles dit Jacquard was a French weaver and merchant. He played an important role in the development of the earliest programmable loom, which in turn played an important role in the...
Louis Aragon
 31
Louis Aragon was a French poet who was one of the leading voices of the surrealist movement in France. He co-founded with André Breton and Philippe Soupault the surrealist review Littérature. He was...
31
Louis Aragon was a French poet who was one of the leading voices of the surrealist movement in France. He co-founded with André Breton and Philippe Soupault the surrealist review Littérature. He was...
Gaspard Monge
 30
Gaspard Monge, Comte de Péluse was a French mathematician, commonly presented as the inventor of descriptive geometry, technical drawing, and the father of differential geometry. During the French...
30
Gaspard Monge, Comte de Péluse was a French mathematician, commonly presented as the inventor of descriptive geometry, technical drawing, and the father of differential geometry. During the French...
Paul Arène
 30
Paul-Auguste Arène was a Provençal poet and French writer.
30
Paul-Auguste Arène was a Provençal poet and French writer.
Jeanbon Saint-André
 30
Jean Bon Saint-André was a French politician of the Revolutionary era.
30
Jean Bon Saint-André was a French politician of the Revolutionary era.
Jean-Baptiste Charcot
 30
Jean-Baptiste-Étienne-Auguste Charcot, born in Neuilly-sur-Seine, was a French scientist, medical doctor and polar scientist. His father was the neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot (1825–1893).
30
Jean-Baptiste-Étienne-Auguste Charcot, born in Neuilly-sur-Seine, was a French scientist, medical doctor and polar scientist. His father was the neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot (1825–1893).
Jean Zay
 30
Jean Élie Paul Zay was a French politician. He served as Minister of National Education and Fine Arts from 1936 until 1939. He was imprisoned by the Vichy government from August 1940 until he was...
30
Jean Élie Paul Zay was a French politician. He served as Minister of National Education and Fine Arts from 1936 until 1939. He was imprisoned by the Vichy government from August 1940 until he was...
Nicolaus Copernicus
 30
Nicolaus Copernicus was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its center....
30
Nicolaus Copernicus was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its center....
Clare of Assisi
 29
Chiara Offreduccio, known as Clare of Assisi, was an Italian saint who was one of the first followers of Francis of Assisi.
29
Chiara Offreduccio, known as Clare of Assisi, was an Italian saint who was one of the first followers of Francis of Assisi.
Édouard Vaillant
 29
Marie Édouard Vaillant was a French politician.
29
Marie Édouard Vaillant was a French politician.
Édouard Herriot
 29
Édouard Marie Herriot was a French Radical politician of the Third Republic who served three times as Prime Minister and twice as President of the Chamber of Deputies. He led the first Cartel des...
29
Édouard Marie Herriot was a French Radical politician of the Third Republic who served three times as Prime Minister and twice as President of the Chamber of Deputies. He led the first Cartel des...
Albert Einstein
 29
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is widely held to be one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time. Best known for developing the theory of relativity,...
29
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is widely held to be one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time. Best known for developing the theory of relativity,...
Jacqueline Auriol
 28
Jacqueline Marie-Thérèse Suzanne Auriol was a French aviator who set several world speed records.
28
Jacqueline Marie-Thérèse Suzanne Auriol was a French aviator who set several world speed records.
Catherine of Alexandria
 28
Catherine of Alexandria, also spelled Katherine is, according to tradition, a Christian saint and virgin, who was martyred in the early fourth century at the hands of the emperor Maxentius. According...
28
Catherine of Alexandria, also spelled Katherine is, according to tradition, a Christian saint and virgin, who was martyred in the early fourth century at the hands of the emperor Maxentius. According...
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac
 28
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac was a French chemist and physicist. He is known mostly for his discovery that water is made of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen by volume, for two laws related to gases,...
28
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac was a French chemist and physicist. He is known mostly for his discovery that water is made of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen by volume, for two laws related to gases,...
Marx Dormoy
 28
René Marx Dormoy was a French socialist politician, noted for his opposition to the far right. Under his leadership as Minister of the Interior in the government of Léon Blum, the French police...
28
René Marx Dormoy was a French socialist politician, noted for his opposition to the far right. Under his leadership as Minister of the Interior in the government of Léon Blum, the French police...
Camille Saint-Saëns
 28
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns was a French composer, organist, conductor and pianist of the Romantic era. His best-known works include Introduction and Rondo Capriccioso (1863), the Second Piano...
28
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns was a French composer, organist, conductor and pianist of the Romantic era. His best-known works include Introduction and Rondo Capriccioso (1863), the Second Piano...
Mary, mother of Jesus
 28
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under various titles such as virgin or queen, many of...
28
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under various titles such as virgin or queen, many of...
Charles Gounod
 28
Charles-François Gounod, usually known as Charles Gounod, was a French composer. He wrote twelve operas, of which the most popular has always been Faust (1859); his Roméo et Juliette (1867) also...
28
Charles-François Gounod, usually known as Charles Gounod, was a French composer. He wrote twelve operas, of which the most popular has always been Faust (1859); his Roméo et Juliette (1867) also...
Paul Valéry
 28
Ambroise Paul Toussaint Jules Valéry was a French poet, essayist, and philosopher. In addition to his poetry and fiction, his interests included aphorisms on art, history, letters, music, and current...
28
Ambroise Paul Toussaint Jules Valéry was a French poet, essayist, and philosopher. In addition to his poetry and fiction, his interests included aphorisms on art, history, letters, music, and current...
Benjamin Franklin
 27
Benjamin Franklin was an American polymath, a leading writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Among the most influential intellectuals of his...
27
Benjamin Franklin was an American polymath, a leading writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Among the most influential intellectuals of his...
Julian the Hospitaller
 27
Saint Julian the Hospitaller is a saint venerated in the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches. He is patron saint of the cities of Ghent (Belgium), Saint Julian's (Malta) and Macerata (Italy).
27
Saint Julian the Hospitaller is a saint venerated in the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches. He is patron saint of the cities of Ghent (Belgium), Saint Julian's (Malta) and Macerata (Italy).
Martin Luther King Jr.
 27
Martin Luther King Jr. was an American Christian minister, activist, and political philosopher who was one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination...
27
Martin Luther King Jr. was an American Christian minister, activist, and political philosopher who was one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination...
Saint Eligius
 27
Eligius, venerated as Saint Eligius, was a Frankish goldsmith, courtier, and bishop who was chief counsellor to Dagobert I and later Bishop of Noyon–Tournai. His deeds were recorded in Vita Sancti...
27
Eligius, venerated as Saint Eligius, was a Frankish goldsmith, courtier, and bishop who was chief counsellor to Dagobert I and later Bishop of Noyon–Tournai. His deeds were recorded in Vita Sancti...
Honoré de Balzac
 27
Honoré de Balzac was a French novelist and playwright. The novel sequence La Comédie humaine, which presents a panorama of post-Napoleonic French life, is generally viewed as his magnum opus.
27
Honoré de Balzac was a French novelist and playwright. The novel sequence La Comédie humaine, which presents a panorama of post-Napoleonic French life, is generally viewed as his magnum opus.
Jean Baptiste Perrin
 27
Jean Baptiste Perrin was a French physicist who, in his studies of the Brownian motion of minute particles suspended in liquids, verified Albert Einstein's explanation of this phenomenon and thereby...
27
Jean Baptiste Perrin was a French physicist who, in his studies of the Brownian motion of minute particles suspended in liquids, verified Albert Einstein's explanation of this phenomenon and thereby...
Camille Claudel
 26
Camille Rosalie Claudel was a French sculptor known for her figurative works in bronze and marble. She died in relative obscurity, but later gained recognition for the originality and quality of her...
26
Camille Rosalie Claudel was a French sculptor known for her figurative works in bronze and marble. She died in relative obscurity, but later gained recognition for the originality and quality of her...
Alexandre Auguste Ledru-Rollin
 26
Alexandre Auguste Ledru-Rollin was a French lawyer, politician and one of the leaders of the French Revolution of 1848.
26
Alexandre Auguste Ledru-Rollin was a French lawyer, politician and one of the leaders of the French Revolution of 1848.
Nelson Mandela
 26
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela was a South African anti-apartheid activist, politician, and statesman who served as the first president of South Africa from 1994 to 1999. He was the country's first black...
26
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela was a South African anti-apartheid activist, politician, and statesman who served as the first president of South Africa from 1994 to 1999. He was the country's first black...
Léon Jouhaux
 26
Léon Jouhaux was a French trade union leader who received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1951.
26
Léon Jouhaux was a French trade union leader who received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1951.
Paul the Apostle
 26
Paul, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is...
26
Paul, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is...
Gustave Flaubert
 26
Gustave Flaubert also known as Flambert, was a French novelist. He has been considered the leading exponent of literary realism in his country and abroad. According to the literary theorist Kornelije...
26
Gustave Flaubert also known as Flambert, was a French novelist. He has been considered the leading exponent of literary realism in his country and abroad. According to the literary theorist Kornelije...
Edmond Rostand
 26
Edmond Eugène Alexis Rostand was a French poet and dramatist. He is associated with neo-romanticism and is known best for his 1897 play Cyrano de Bergerac. Rostand's romantic plays contrasted with...
26
Edmond Eugène Alexis Rostand was a French poet and dramatist. He is associated with neo-romanticism and is known best for his 1897 play Cyrano de Bergerac. Rostand's romantic plays contrasted with...
Marie de Rabutin-Chantal, marquise de Sévigné
 26
Marie de Rabutin-Chantal, marquise de Sévigné, also widely known as Madame de Sévigné or Mme de Sévigné, was a French aristocrat, remembered for her letter-writing. Most of her letters, celebrated...
26
Marie de Rabutin-Chantal, marquise de Sévigné, also widely known as Madame de Sévigné or Mme de Sévigné, was a French aristocrat, remembered for her letter-writing. Most of her letters, celebrated...
Camille Desmoulins
 26
Lucie-Simplice-Camille-Benoît Desmoulins was a French journalist, politician and a prominent figure of the French Revolution. He is best known for playing an instrumental role in the events that led...
26
Lucie-Simplice-Camille-Benoît Desmoulins was a French journalist, politician and a prominent figure of the French Revolution. He is best known for playing an instrumental role in the events that led...
Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, Viscount of Turenne
 25
Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, vicomte de Turenne, commonly known as Turenne, was a French general and one of only six Marshals to have been promoted Marshal General of France. The most illustrious...
25
Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, vicomte de Turenne, commonly known as Turenne, was a French general and one of only six Marshals to have been promoted Marshal General of France. The most illustrious...
Saint Stephen
 25
Stephen is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first martyr of Christianity. According to the Acts of the Apostles, he was a deacon in the early church at Jerusalem who angered members of...
25
Stephen is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first martyr of Christianity. According to the Acts of the Apostles, he was a deacon in the early church at Jerusalem who angered members of...
Benjamin Raspail
 25
Benjamin Raspail, was a painter-engraver and politician of the French Third Republic. He was the son of François-Vincent Raspail. Like his father, he was classed as extreme-left, and he went into...
25
Benjamin Raspail, was a painter-engraver and politician of the French Third Republic. He was the son of François-Vincent Raspail. Like his father, he was classed as extreme-left, and he went into...
Thomas Edison
 25
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These...
25
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These...
Marcel Sembat
 25
Marcel Sembat was a French Socialist politician. He served as a member of the National Assembly of France from 1893 to 1922, and as Minister of Public Works from August 26, 1914, to December 12, 1916.
25
Marcel Sembat was a French Socialist politician. He served as a member of the National Assembly of France from 1893 to 1922, and as Minister of Public Works from August 26, 1914, to December 12, 1916.
Pierre Bérégovoy
 25
Pierre Eugène Bérégovoy was a French politician who served as Prime Minister of France under President François Mitterrand from 2 April 1992 to 29 March 1993. He was a member of the Socialist Party...
25
Pierre Eugène Bérégovoy was a French politician who served as Prime Minister of France under President François Mitterrand from 2 April 1992 to 29 March 1993. He was a member of the Socialist Party...
Auguste Rodin
 25
François Auguste René Rodin was a French sculptor generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a...
25
François Auguste René Rodin was a French sculptor generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a...
Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot
 25
Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot was a French inventor who built the world's first full-size and working self-propelled mechanical land-vehicle, the "Fardier à vapeur" – effectively the world's first automobile.
25
Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot was a French inventor who built the world's first full-size and working self-propelled mechanical land-vehicle, the "Fardier à vapeur" – effectively the world's first automobile.
François Mauriac
 25
François Charles Mauriac was a French novelist, dramatist, critic, poet, and journalist, a member of the Académie française, and laureate of the Nobel Prize in Literature (1952). He was awarded the...
25
François Charles Mauriac was a French novelist, dramatist, critic, poet, and journalist, a member of the Académie française, and laureate of the Nobel Prize in Literature (1952). He was awarded the...
Roland Garros (aviator)
 24
Eugène Adrien Roland Georges Garros was a French aviation pioneer and fighter pilot. Garros began a career in aviation in 1909 and performed many early feats before joining the French army and...
24
Eugène Adrien Roland Georges Garros was a French aviation pioneer and fighter pilot. Garros began a career in aviation in 1909 and performed many early feats before joining the French army and...
Danielle Casanova
 24
Danielle Casanova was a French communist activist and member of the French Resistance during World War II. A dentist by occupation, she was a high-ranking figure within the Communist Youth and...
24
Danielle Casanova was a French communist activist and member of the French Resistance during World War II. A dentist by occupation, she was a high-ranking figure within the Communist Youth and...
Isaac Newton
 24
Sir Isaac Newton was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author who was described in his time as a natural philosopher. He was a key...
24
Sir Isaac Newton was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author who was described in his time as a natural philosopher. He was a key...
Simone de Beauvoir
 24
Simone Lucie Ernestine Marie Bertrand de Beauvoir was a French existentialist philosopher, writer, social theorist, and feminist activist. Though she did not consider herself a philosopher, nor was...
24
Simone Lucie Ernestine Marie Bertrand de Beauvoir was a French existentialist philosopher, writer, social theorist, and feminist activist. Though she did not consider herself a philosopher, nor was...
Claude Bernard
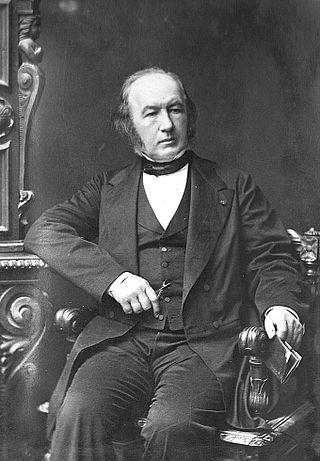 23
Claude Bernard was a French physiologist. Historian I. Bernard Cohen of Harvard University called Bernard "one of the greatest of all men of science". He originated the term milieu intérieur, and the...
23
Claude Bernard was a French physiologist. Historian I. Bernard Cohen of Harvard University called Bernard "one of the greatest of all men of science". He originated the term milieu intérieur, and the...
Albert Thomas (American politician)
 23
Albert Langston Thomas was a Democratic member of the U.S. House of Representatives for 29 years. From Houston, Texas, he was responsible for bringing the Johnson Space Center to Houston.
23
Albert Langston Thomas was a Democratic member of the U.S. House of Representatives for 29 years. From Houston, Texas, he was responsible for bringing the Johnson Space Center to Houston.
Jean Giono
 23
Jean Giono was a French writer who wrote works of fiction mostly set in the Provence region of France.
23
Jean Giono was a French writer who wrote works of fiction mostly set in the Provence region of France.
Gustave Courbet
 23
Jean Désiré Gustave Courbet was a French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. Committed to painting only what he could see, he rejected academic convention and the...
23
Jean Désiré Gustave Courbet was a French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. Committed to painting only what he could see, he rejected academic convention and the...
Louis Pergaud
 23
Louis Pergaud was a French novelist, war poet, and soldier, whose principal works were known as "Animal Stories" due to his featuring animals of the Franche-Comté in lead roles. His most notable work...
23
Louis Pergaud was a French novelist, war poet, and soldier, whose principal works were known as "Animal Stories" due to his featuring animals of the Franche-Comté in lead roles. His most notable work...
Jean Cocteau
 23
Jean Maurice Eugène Clément Cocteau was a French poet, playwright, novelist, designer, film director, visual artist and critic. He was one of the foremost artists of the surrealist, avant-garde, and...
23
Jean Maurice Eugène Clément Cocteau was a French poet, playwright, novelist, designer, film director, visual artist and critic. He was one of the foremost artists of the surrealist, avant-garde, and...
Saint Maurice
 23
Maurice was an Egyptian military leader who headed the legendary Theban Legion of Rome in the 3rd century, and is one of the favourite and most widely venerated saints of that martyred group. He is...
23
Maurice was an Egyptian military leader who headed the legendary Theban Legion of Rome in the 3rd century, and is one of the favourite and most widely venerated saints of that martyred group. He is...
Francisco Ferrer
 23
Francesc Ferrer i Guàrdia, widely known as Francisco Ferrer, was a Spanish radical freethinker, anarchist, and educationist behind a network of secular, private, libertarian schools in and around...
23
Francesc Ferrer i Guàrdia, widely known as Francisco Ferrer, was a Spanish radical freethinker, anarchist, and educationist behind a network of secular, private, libertarian schools in and around...
Hilary of Poitiers
 23
Hilary of Poitiers was Bishop of Poitiers and a Doctor of the Church. He was sometimes referred to as the "Hammer of the Arians" and the "Athanasius of the West". His name comes from the Latin word...
23
Hilary of Poitiers was Bishop of Poitiers and a Doctor of the Church. He was sometimes referred to as the "Hammer of the Arians" and the "Athanasius of the West". His name comes from the Latin word...
Eugène Delacroix
 23
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix was a French Romantic artist regarded from the outset of his career as the leader of the French Romantic school.
23
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix was a French Romantic artist regarded from the outset of his career as the leader of the French Romantic school.
Alexander Fleming
 23
Sir Alexander Fleming was a Scottish physician and microbiologist, best known for discovering the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance, which he named penicillin. His discovery in...
23
Sir Alexander Fleming was a Scottish physician and microbiologist, best known for discovering the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance, which he named penicillin. His discovery in...
Arthur Rimbaud
 23
Jean Nicolas Arthur Rimbaud was a French poet known for his transgressive and surreal themes and for his influence on modern literature and arts, prefiguring surrealism. Born in Charleville, he...
23
Jean Nicolas Arthur Rimbaud was a French poet known for his transgressive and surreal themes and for his influence on modern literature and arts, prefiguring surrealism. Born in Charleville, he...
Jules Vallès
 22
Jules Vallès was a French journalist, author, and left-wing political activist.
22
Jules Vallès was a French journalist, author, and left-wing political activist.
Giuseppe Garibaldi
 22
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi was an Italian general, patriot, revolutionary and republican. He contributed to Italian unification (Risorgimento) and the creation of the Kingdom of Italy. He is considered...
22
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi was an Italian general, patriot, revolutionary and republican. He contributed to Italian unification (Risorgimento) and the creation of the Kingdom of Italy. He is considered...
René Coty
 22
Gustave Jules René Coty was President of France from 1954 to 1959. He was the second and last president of the Fourth French Republic.
22
Gustave Jules René Coty was President of France from 1954 to 1959. He was the second and last president of the Fourth French Republic.
Henri Maurice Berteaux
 22
Henri Maurice Berteaux was the Minister of War in France from 14 November 1904 to 12 November 1905, and from 2 March 1911 until his accidental death on 21 May 1911.
22
Henri Maurice Berteaux was the Minister of War in France from 14 November 1904 to 12 November 1905, and from 2 March 1911 until his accidental death on 21 May 1911.
François Villon
 22
François Villon is the best known French poet of the Late Middle Ages. He was involved in criminal behavior and had multiple encounters with law enforcement authorities. Villon wrote about some of...
22
François Villon is the best known French poet of the Late Middle Ages. He was involved in criminal behavior and had multiple encounters with law enforcement authorities. Villon wrote about some of...
Saint Sebastian
 22
Sebastian was an early Christian saint and martyr. According to traditional belief, he was killed during the Diocletianic Persecution of Christians. He was initially tied to a post or tree and shot...
22
Sebastian was an early Christian saint and martyr. According to traditional belief, he was killed during the Diocletianic Persecution of Christians. He was initially tied to a post or tree and shot...
François-Alexandre Verdier
 22
François-Alexandre Verdier was French painter, draftsman and engraver.
He was a student and assistant of Charles Le Brun.
22
François-Alexandre Verdier was French painter, draftsman and engraver.
He was a student and assistant of Charles Le Brun.
Camille Pelletan
 22
Charles Camille Pelletan was a French politician, historian and journalist, Minister of Marine in Emile Combes' Bloc des gauches cabinet from 1902 to 1905. He was part of the left-wing of the...
22
Charles Camille Pelletan was a French politician, historian and journalist, Minister of Marine in Emile Combes' Bloc des gauches cabinet from 1902 to 1905. He was part of the left-wing of the...
Saint Quentin
 22
Quentin also known as Quentin of Amiens, was an early Christian saint.
22
Quentin also known as Quentin of Amiens, was an early Christian saint.
Louis Braille
 22
Louis Braille was a French educator and the inventor of a reading and writing system named after him, braille, intended for use by visually impaired people. His system is used worldwide and remains...
22
Louis Braille was a French educator and the inventor of a reading and writing system named after him, braille, intended for use by visually impaired people. His system is used worldwide and remains...
Pierre Georges
 22
Pierre Georges, better known as Colonel Fabien, was one of the two members of the French Communist Party who perpetrated the first assassinations of German personnel during the Occupation of France...
22
Pierre Georges, better known as Colonel Fabien, was one of the two members of the French Communist Party who perpetrated the first assassinations of German personnel during the Occupation of France...
Louis Jouvet
 21
Jules Eugène Louis Jouvet was a French actor, theatre director and filmmaker.
21
Jules Eugène Louis Jouvet was a French actor, theatre director and filmmaker.
Jean-Martin Charcot
 21
Jean-Martin Charcot was a famous French neurologist and professor of anatomical pathology. He worked on groundbreaking work about hypnosis and hysteria, in particular with his hysteria patient Louise...
21
Jean-Martin Charcot was a famous French neurologist and professor of anatomical pathology. He worked on groundbreaking work about hypnosis and hysteria, in particular with his hysteria patient Louise...
Amédée Courbet
 21
Anatole-Amédée-Prosper Courbet was a French admiral who won a series of important land and naval victories during the Tonkin Campaign (1883–86) and the Sino-French War.
21
Anatole-Amédée-Prosper Courbet was a French admiral who won a series of important land and naval victories during the Tonkin Campaign (1883–86) and the Sino-French War.
Boris Vian
 21
Boris Vian was a French polymath who is primarily remembered for his novels. Those published under the pseudonym Vernon Sullivan were bizarre parodies of criminal fiction, highly controversial at the...
21
Boris Vian was a French polymath who is primarily remembered for his novels. Those published under the pseudonym Vernon Sullivan were bizarre parodies of criminal fiction, highly controversial at the...
Aristide Bergès
 21
Aristide Bergès né à Lorp-Sentaraille le 4 septembre 1833 et mort à Villard-Bonnot le 28 février 1904, est un industriel papetier et ingénieur hydraulicien français du XIXe siècle.
21
Aristide Bergès né à Lorp-Sentaraille le 4 septembre 1833 et mort à Villard-Bonnot le 28 février 1904, est un industriel papetier et ingénieur hydraulicien français du XIXe siècle.
Guy de Maupassant
 21
Henri René Albert Guy de Maupassant was a 19th-century French author, celebrated as a master of the short story, as well as a representative of the naturalist school, depicting human lives, destinies...
21
Henri René Albert Guy de Maupassant was a 19th-century French author, celebrated as a master of the short story, as well as a representative of the naturalist school, depicting human lives, destinies...
Jean-Baptiste Lebas
 21
Jean-Baptiste Lebas was a French Socialist politician, deputy to the National Assembly of France during the Third Republic, who served twice as minister under Léon Blum’s governments. He was mayor of...
21
Jean-Baptiste Lebas was a French Socialist politician, deputy to the National Assembly of France during the Third Republic, who served twice as minister under Léon Blum’s governments. He was mayor of...
Étienne Dolet
 21
Étienne Dolet was a French scholar, translator and printer. Dolet was a controversial figure throughout his lifetime. His early attacks upon the Inquisition, the city council and other authorities in...
21
Étienne Dolet was a French scholar, translator and printer. Dolet was a controversial figure throughout his lifetime. His early attacks upon the Inquisition, the city council and other authorities in...
Tristan Corbière
 21
Tristan Corbière, born Édouard-Joachim Corbière, was a French poet born in Coat-Congar, Ploujean in Brittany, where he lived most of his life before dying of tuberculosis at the age of 29. He was a...
21
Tristan Corbière, born Édouard-Joachim Corbière, was a French poet born in Coat-Congar, Ploujean in Brittany, where he lived most of his life before dying of tuberculosis at the age of 29. He was a...
Ferdinand de Lesseps
 21
Ferdinand Marie, Comte de Lesseps was a French diplomat and later developer of the Suez Canal, which in 1869 joined the Mediterranean and Red Seas, substantially reducing sailing distances and times...
21
Ferdinand Marie, Comte de Lesseps was a French diplomat and later developer of the Suez Canal, which in 1869 joined the Mediterranean and Red Seas, substantially reducing sailing distances and times...
Victor Schœlcher
 21
Victor Schœlcher was a French abolitionist, writer, politician and journalist, best known for his leading role in the abolition of slavery in France in 1848, during the Second Republic.
21
Victor Schœlcher was a French abolitionist, writer, politician and journalist, best known for his leading role in the abolition of slavery in France in 1848, during the Second Republic.
Audomar
 21
Audomar, better known as Omer, was a bishop of Thérouanne, after whom nearby Saint-Omer in northern France was named. He is venerated as a saint in the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches.
21
Audomar, better known as Omer, was a bishop of Thérouanne, after whom nearby Saint-Omer in northern France was named. He is venerated as a saint in the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches.
Hubertus
 21
Hubertus or Hubert was a Christian saint who became the first bishop of Liège in 708 A.D. He is the patron saint of hunters, mathematicians, opticians and metalworkers. Known as the "Apostle of the...
21
Hubertus or Hubert was a Christian saint who became the first bishop of Liège in 708 A.D. He is the patron saint of hunters, mathematicians, opticians and metalworkers. Known as the "Apostle of the...
Marcel Dassault
 21
Marcel Dassault was a French engineer and industrialist who spent his career in aircraft manufacturing.
21
Marcel Dassault was a French engineer and industrialist who spent his career in aircraft manufacturing.
Guy Môquet
 21
Guy Prosper Eustache Môquet was a young French Communist militant. During the German occupation of France in World War II, he was taken hostage by the Nazis and executed by firing squad in...
21
Guy Prosper Eustache Môquet was a young French Communist militant. During the German occupation of France in World War II, he was taken hostage by the Nazis and executed by firing squad in...
Vincent Auriol
 20
Vincent Jules Auriol was a French politician who served as President of France from 1947 to 1954.
20
Vincent Jules Auriol was a French politician who served as President of France from 1947 to 1954.
Elsa Triolet
 20
Ella Yuryevna Kagan, known as Elsa Triolet, was a Russian-French writer and translator.
20
Ella Yuryevna Kagan, known as Elsa Triolet, was a Russian-French writer and translator.
Maurice Thorez
 20
Maurice Thorez was a French politician and longtime leader of the French Communist Party (PCF) from 1930 until his death. He also served as Deputy Prime Minister of France from 1946 to 1947.
20
Maurice Thorez was a French politician and longtime leader of the French Communist Party (PCF) from 1930 until his death. He also served as Deputy Prime Minister of France from 1946 to 1947.
Augustin-Jean Fresnel
 20
Augustin-Jean Fresnel was a French civil engineer and physicist whose research in optics led to the almost unanimous acceptance of the wave theory of light, excluding any remnant of Newton's...
20
Augustin-Jean Fresnel was a French civil engineer and physicist whose research in optics led to the almost unanimous acceptance of the wave theory of light, excluding any remnant of Newton's...
Georges Charpak
Albinus of Angers
 20
Saint Albinus of Angers, also known as Saint Albin in English, was a French abbot and bishop. Born to a noble Gallo-Roman family at Vannes, Brittany, St. Albinus was a monk and from 504 A.D. Abbot of...
20
Saint Albinus of Angers, also known as Saint Albin in English, was a French abbot and bishop. Born to a noble Gallo-Roman family at Vannes, Brittany, St. Albinus was a monk and from 504 A.D. Abbot of...
Aimé Césaire
 20
Aimé Fernand David Césaire was a Francophone Martinican poet, author, and politician. He was "one of the founders of the Négritude movement in Francophone literature" and coined the word négritude in...
20
Aimé Fernand David Césaire was a Francophone Martinican poet, author, and politician. He was "one of the founders of the Négritude movement in Francophone literature" and coined the word négritude in...
René Descartes
 19
René Descartes was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathematics was paramount to his method of...
19
René Descartes was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Mathematics was paramount to his method of...
Mark the Evangelist
 19
Mark the Evangelist also known as John Mark or Saint Mark, is the person who is traditionally ascribed to be the author of the Gospel of Mark. Modern Bible scholars have concluded that the Gospel of...
19
Mark the Evangelist also known as John Mark or Saint Mark, is the person who is traditionally ascribed to be the author of the Gospel of Mark. Modern Bible scholars have concluded that the Gospel of...
Abbé Pierre
 19
Abbé Pierre, was a French Catholic priest, member of the Resistance during World War II, and deputy of the Popular Republican Movement (MRP).
19
Abbé Pierre, was a French Catholic priest, member of the Resistance during World War II, and deputy of the Popular Republican Movement (MRP).
Françoise Dolto
 19
Françoise Dolto was a French pediatrician and psychoanalyst.
19
Françoise Dolto was a French pediatrician and psychoanalyst.
Alain Colas
 19
Alain Colas was a French sailor, the first to complete a solitary round-the-world race in a multihull. He met Éric Tabarly in Sydney in 1967, and bought Pen Duick IV from him in 1970, and won the...
19
Alain Colas was a French sailor, the first to complete a solitary round-the-world race in a multihull. He met Éric Tabarly in Sydney in 1967, and bought Pen Duick IV from him in 1970, and won the...
Jean-Baptiste Clément
 19
Jean-Baptiste Clément was a French chansonnier, journalist, socialist activist and communard. He is mostly known for his work Le Temps des cerises, which is strongly associated with the Paris Commune.
19
Jean-Baptiste Clément was a French chansonnier, journalist, socialist activist and communard. He is mostly known for his work Le Temps des cerises, which is strongly associated with the Paris Commune.
Louis Antoine de Saint-Just
 19
Louis Antoine Léon de Saint-Just, sometimes nicknamed the Archangel of Terror, was a French revolutionary, political philosopher, member and president of the French National Convention, a Jacobin...
19
Louis Antoine Léon de Saint-Just, sometimes nicknamed the Archangel of Terror, was a French revolutionary, political philosopher, member and president of the French National Convention, a Jacobin...
Joachim du Bellay
 19
Joachim du Bellay was a French poet, critic, and a founder of La Pléiade. He notably wrote the manifesto of the group: Défense et illustration de la langue française, which aimed at promoting French...
19
Joachim du Bellay was a French poet, critic, and a founder of La Pléiade. He notably wrote the manifesto of the group: Défense et illustration de la langue française, which aimed at promoting French...
Saint Christopher
 19
Saint Christopher is venerated by several Christian denominations as a martyr killed in the reign of the 3rd-century Roman emperor Decius, or alternatively under the emperor Maximinus Daia. There...
19
Saint Christopher is venerated by several Christian denominations as a martyr killed in the reign of the 3rd-century Roman emperor Decius, or alternatively under the emperor Maximinus Daia. There...
Anatole Le Braz
 19
Anatole le Braz, the "Bard of Brittany", was a Breton poet, folklore collector, and translator. He was highly regarded amongst both European and American scholars, and was known for his warmth and...
19
Anatole le Braz, the "Bard of Brittany", was a Breton poet, folklore collector, and translator. He was highly regarded amongst both European and American scholars, and was known for his warmth and...
Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
 19
Comte Henri Marie Raymond de Toulouse-Lautrec-Monfa, known as Toulouse Lautrec, was a French painter, printmaker, draughtsman, caricaturist, and illustrator whose immersion in the colourful and...
19
Comte Henri Marie Raymond de Toulouse-Lautrec-Monfa, known as Toulouse Lautrec, was a French painter, printmaker, draughtsman, caricaturist, and illustrator whose immersion in the colourful and...
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester
 18
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, later sometimes referred to as Simon V de Montfort to distinguish him from his namesake relatives, was an English nobleman of French origin and a member of...
18
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, later sometimes referred to as Simon V de Montfort to distinguish him from his namesake relatives, was an English nobleman of French origin and a member of...
Pierre Bertholon de Saint-Lazare
 18
Pierre Bertholon de Saint-Lazare was a French physicist and a member of the Society of Sciences of Montpellier. He was known for his experiments with electricity.
18
Pierre Bertholon de Saint-Lazare was a French physicist and a member of the Society of Sciences of Montpellier. He was known for his experiments with electricity.
Yuri Gagarin
 18
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful crewed spaceflight, became the first human to journey into outer space. Travelling on Vostok 1, Gagarin...
18
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful crewed spaceflight, became the first human to journey into outer space. Travelling on Vostok 1, Gagarin...
Jean-François Millet
 18
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the...
18
Jean-François Millet was a French artist and one of the founders of the Barbizon school in rural France. Millet is noted for his paintings of peasant farmers and can be categorized as part of the...
Pierre Waldeck-Rousseau
 18
Pierre Marie René Ernest Waldeck-Rousseau was a French Republican politician who served for three years as the Prime Minister of France.
18
Pierre Marie René Ernest Waldeck-Rousseau was a French Republican politician who served for three years as the Prime Minister of France.
Samuel de Champlain
 18
Samuel de Champlain was a French explorer, navigator, cartographer, draftsman, soldier, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He made between 21 and 29 trips across the Atlantic Ocean,...
18
Samuel de Champlain was a French explorer, navigator, cartographer, draftsman, soldier, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He made between 21 and 29 trips across the Atlantic Ocean,...
Alfred Kastler
 18
Alfred Kastler was a French physicist, and Nobel Prize laureate. He is known for the development of optical pumping.
18
Alfred Kastler was a French physicist, and Nobel Prize laureate. He is known for the development of optical pumping.
Saint Blaise
 18
Blaise of Sebaste was a physician and bishop of Sebastea in historical Lesser Armenia who is venerated as a Christian saint and martyr. He is counted as one of the Fourteen Holy Helpers.
18
Blaise of Sebaste was a physician and bishop of Sebastea in historical Lesser Armenia who is venerated as a Christian saint and martyr. He is counted as one of the Fourteen Holy Helpers.
Nicolas Appert
 18
Nicolas Appert was a French confectioner and inventor who, in the early 19th century, invented airtight food preservation. Appert, known as the "father of food science", described his invention as a...
18
Nicolas Appert was a French confectioner and inventor who, in the early 19th century, invented airtight food preservation. Appert, known as the "father of food science", described his invention as a...
Marc Sangnier
 18
Marc Sangnier was a French Roman Catholic thinker and politician, who in 1894 founded Le Sillon, a social Catholic movement.
18
Marc Sangnier was a French Roman Catholic thinker and politician, who in 1894 founded Le Sillon, a social Catholic movement.
Émile Basly
 18
Émile Basly is one of the great figures of trade unionism in mining in the mineral field of Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France, along with Arthur Lamendin. He is primarily known for his participation in the...
18
Émile Basly is one of the great figures of trade unionism in mining in the mineral field of Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France, along with Arthur Lamendin. He is primarily known for his participation in the...
Alphonse, Count of Poitiers
 17
Alphonse was the Count of Poitou from 1225 and Count of Toulouse from 1249. As count of Toulouse, he also governed the Marquisate of Provence.
17
Alphonse was the Count of Poitou from 1225 and Count of Toulouse from 1249. As count of Toulouse, he also governed the Marquisate of Provence.
Pablo Neruda
 17
Pablo Neruda was a Chilean poet-diplomat and politician who won the 1971 Nobel Prize in Literature. Neruda became known as a poet when he was 13 years old and wrote in a variety of styles, including...
17
Pablo Neruda was a Chilean poet-diplomat and politician who won the 1971 Nobel Prize in Literature. Neruda became known as a poet when he was 13 years old and wrote in a variety of styles, including...
Vladimir Lenin
 17
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov, better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, Soviet politician, and political theorist who was the founder and first leader of the Russian Soviet Federative...
17
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov, better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, Soviet politician, and political theorist who was the founder and first leader of the Russian Soviet Federative...
Olivier de Serres
 17
Olivier de Serres was a French author and soil scientist whose Théâtre d'Agriculture (1600) was the accepted textbook of French agriculture in the 17th century.
17
Olivier de Serres was a French author and soil scientist whose Théâtre d'Agriculture (1600) was the accepted textbook of French agriculture in the 17th century.
Simone Signoret
 17
Simone Signoret was a French actress. She received various accolades, including an Academy Award, three BAFTA Awards, a César Award, a Primetime Emmy Award, and the Cannes Film Festival Award for...
17
Simone Signoret was a French actress. She received various accolades, including an Academy Award, three BAFTA Awards, a César Award, a Primetime Emmy Award, and the Cannes Film Festival Award for...
Antonio Vivaldi
 17
Antonio Lucio Vivaldi was an Italian composer, virtuoso violinist and impresario of Baroque music. Along with Johann Sebastian Bach and George Frideric Handel, Vivaldi ranks amongst the greatest...
17
Antonio Lucio Vivaldi was an Italian composer, virtuoso violinist and impresario of Baroque music. Along with Johann Sebastian Bach and George Frideric Handel, Vivaldi ranks amongst the greatest...
Jean Bouin
 17
Alexandre François Étienne Jean Bouin was a French middle-distance runner. He competed in the 1500m at the 1908 Olympics and the 5000m at the 1912 Olympics. He won a silver medal in the 5000m in...
17
Alexandre François Étienne Jean Bouin was a French middle-distance runner. He competed in the 1500m at the 1908 Olympics and the 5000m at the 1912 Olympics. He won a silver medal in the 5000m in...
Montgolfier brothers
 17
The Montgolfier brothers – Joseph-Michel Montgolfier and Jacques-Étienne Montgolfier – were aviation pioneers, balloonists and paper manufacturers from the commune Annonay in Ardèche, France. They...
17
The Montgolfier brothers – Joseph-Michel Montgolfier and Jacques-Étienne Montgolfier – were aviation pioneers, balloonists and paper manufacturers from the commune Annonay in Ardèche, France. They...
Marie-Pierre Kœnig
 16
Marie Joseph Pierre François Kœnig or Koenig was a French general during World War II during which he commanded a Free French Brigade at the Battle of Bir Hakeim in North Africa in 1942. He started a...
16
Marie Joseph Pierre François Kœnig or Koenig was a French general during World War II during which he commanded a Free French Brigade at the Battle of Bir Hakeim in North Africa in 1942. He started a...
Lazare Carnot
 16
Lazare Nicolas Marguerite, Comte Carnot was a French mathematician, physicist, military officer, politician and a leading member of the Committee of Public Safety during the French Revolution. His...
16
Lazare Nicolas Marguerite, Comte Carnot was a French mathematician, physicist, military officer, politician and a leading member of the Committee of Public Safety during the French Revolution. His...
Paul Lafargue
 16
Paul Lafargue was a Cuban-born French revolutionary Marxist socialist, political writer, economist, journalist, literary critic, and activist; he was Karl Marx's son-in-law, having married his second...
16
Paul Lafargue was a Cuban-born French revolutionary Marxist socialist, political writer, economist, journalist, literary critic, and activist; he was Karl Marx's son-in-law, having married his second...
Maurice Sarrail
 16
Maurice Paul Emmanuel Sarrail was a French general of the First World War. Sarrail's openly socialist political connections made him a rarity amongst the Catholics, conservatives and monarchists who...
16
Maurice Paul Emmanuel Sarrail was a French general of the First World War. Sarrail's openly socialist political connections made him a rarity amongst the Catholics, conservatives and monarchists who...
Julius Caesar
 16
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war,...
16
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war,...
Gabriel Fauré
 16
Gabriel Urbain Fauré was a French composer, organist, pianist and teacher. He was one of the foremost French composers of his generation, and his musical style influenced many 20th-century composers....
16
Gabriel Urbain Fauré was a French composer, organist, pianist and teacher. He was one of the foremost French composers of his generation, and his musical style influenced many 20th-century composers....
Anne of Brittany
 16
Anne of Brittany was reigning Duchess of Brittany from 1488 until her death, and Queen of France from 1491 to 1498 and from 1499 to her death. She was the only woman to have been queen consort of...
16
Anne of Brittany was reigning Duchess of Brittany from 1488 until her death, and Queen of France from 1491 to 1498 and from 1499 to her death. She was the only woman to have been queen consort of...
Joseph Lakanal
 16
Joseph Lakanal was a French politician, and an original member of the Institut de France.
16
Joseph Lakanal was a French politician, and an original member of the Institut de France.
Alfred Nobel
 16
Alfred Bernhard Nobel was a Swedish chemist, inventor, engineer and businessman. He is known for inventing dynamite as well as having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prize. He also made...
16
Alfred Bernhard Nobel was a Swedish chemist, inventor, engineer and businessman. He is known for inventing dynamite as well as having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prize. He also made...
Marguerite Yourcenar
 16
Marguerite Yourcenar was a Belgian-born French novelist and essayist who became a US citizen in 1947. Winner of the Prix Femina and the Erasmus Prize, she was the first woman elected to the Académie...
16
Marguerite Yourcenar was a Belgian-born French novelist and essayist who became a US citizen in 1947. Winner of the Prix Femina and the Erasmus Prize, she was the first woman elected to the Académie...
Genevieve
 16
Genevieve was a consecrated virgin, and is the patron saint of Paris in the Catholic and Orthodox traditions. Her feast day is on 3 January.
16
Genevieve was a consecrated virgin, and is the patron saint of Paris in the Catholic and Orthodox traditions. Her feast day is on 3 January.
Louis de Broglie
 16
Louis Victor Pierre Raymond, 7th Duc de Broglie was a French aristocrat and physicist who made groundbreaking contributions to quantum theory. In his 1924 PhD thesis, he postulated the wave nature of...
16
Louis Victor Pierre Raymond, 7th Duc de Broglie was a French aristocrat and physicist who made groundbreaking contributions to quantum theory. In his 1924 PhD thesis, he postulated the wave nature of...
Charles Nungesser
 16
Charles Eugène Jules Marie Nungesser was a French ace pilot and adventurer. Nungesser was a renowned ace in France, ranking third highest in the country with 43 air combat victories during World War...
16
Charles Eugène Jules Marie Nungesser was a French ace pilot and adventurer. Nungesser was a renowned ace in France, ranking third highest in the country with 43 air combat victories during World War...
Yves Montand
 16
Ivo Livi was an Italian-born French actor and singer. He is said to be one of France's greatest 20th-century artists.
16
Ivo Livi was an Italian-born French actor and singer. He is said to be one of France's greatest 20th-century artists.
Auguste Comte
 15
Isidore Auguste Marie François Xavier Comte was a French philosopher, mathematician and writer who formulated the doctrine of positivism. He is often regarded as the first philosopher of science in...
15
Isidore Auguste Marie François Xavier Comte was a French philosopher, mathematician and writer who formulated the doctrine of positivism. He is often regarded as the first philosopher of science in...
Jean-Pierre Timbaud
 15
Jean-Pierre Timbaud was the secretary of the steelworkers’ trade union section of the Confédération Générale du Travail (CGT). He took part in the strikes which preceded the Popular Front. During the...
15
Jean-Pierre Timbaud was the secretary of the steelworkers’ trade union section of the Confédération Générale du Travail (CGT). He took part in the strikes which preceded the Popular Front. During the...
Saint Giles
 15
Saint Giles, also known as Giles the Hermit, was a hermit or monk active in the lower Rhône most likely in the 7th century. Revered as a saint, his cult became widely diffused but his hagiography is...
15
Saint Giles, also known as Giles the Hermit, was a hermit or monk active in the lower Rhône most likely in the 7th century. Revered as a saint, his cult became widely diffused but his hagiography is...
Francis of Assisi
 15
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, known as Francis of Assisi, was an Italian mystic, poet and Catholic friar who founded the religious order of the Franciscans. He was inspired to lead a Christian...
15
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, known as Francis of Assisi, was an Italian mystic, poet and Catholic friar who founded the religious order of the Franciscans. He was inspired to lead a Christian...
Auguste Brizeux
 15
Julien Auguste Pélage Brizeux was a French poet. He was said to belong to a family of Irish origin, long settled in Brittany. He was educated for the law, but in 1827 he produced at the Théâtre...
15
Julien Auguste Pélage Brizeux was a French poet. He was said to belong to a family of Irish origin, long settled in Brittany. He was educated for the law, but in 1827 he produced at the Théâtre...
Pierre-Gilles de Gennes
 15
Pierre-Gilles de Gennes was a French physicist and the Nobel Prize laureate in physics in 1991.
15
Pierre-Gilles de Gennes was a French physicist and the Nobel Prize laureate in physics in 1991.
Jacques Monod
 15
Jacques Lucien Monod was a French biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1965, sharing it with François Jacob and André Lwoff "for their discoveries concerning genetic...
15
Jacques Lucien Monod was a French biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1965, sharing it with François Jacob and André Lwoff "for their discoveries concerning genetic...
Olivier V de Clisson
 15
Olivier V de Clisson, nicknamed "The Butcher", was a Breton soldier, the son of Olivier IV de Clisson. His father had been put to death by the French in 1343 on the suspicion of having willingly...
15
Olivier V de Clisson, nicknamed "The Butcher", was a Breton soldier, the son of Olivier IV de Clisson. His father had been put to death by the French in 1343 on the suspicion of having willingly...
Fernand Léger
 15
Joseph Fernand Henri Léger was a French painter, sculptor, and filmmaker. In his early works he created a personal form of cubism which he gradually modified into a more figurative, populist style....
15
Joseph Fernand Henri Léger was a French painter, sculptor, and filmmaker. In his early works he created a personal form of cubism which he gradually modified into a more figurative, populist style....
Antoine Watteau
 15
Jean-Antoine Watteau was a French painter and draughtsman whose brief career spurred the revival of interest in colour and movement, as seen in the tradition of Correggio and Rubens. He revitalized...
15
Jean-Antoine Watteau was a French painter and draughtsman whose brief career spurred the revival of interest in colour and movement, as seen in the tradition of Correggio and Rubens. He revitalized...
Paul Claudel
 15
Paul Claudel was a French poet, dramatist and diplomat, and the younger brother of the sculptor Camille Claudel. He was most famous for his verse dramas, which often convey his devout Catholicism.
15
Paul Claudel was a French poet, dramatist and diplomat, and the younger brother of the sculptor Camille Claudel. He was most famous for his verse dramas, which often convey his devout Catholicism.
Leonard of Port Maurice
 15
Leonard of Port Maurice, O.F.M., was an Italian Franciscan preacher and ascetic writer.
15
Leonard of Port Maurice, O.F.M., was an Italian Franciscan preacher and ascetic writer.
Anne de Rochechouart de Mortemart
 15
Anne de Rochechouart, was a wealthy French aristocrat. She inherited a large fortune from her great-grandmother, the founder of the Veuve Clicquot Champagne house. She was known for her involvement...
15
Anne de Rochechouart, was a wealthy French aristocrat. She inherited a large fortune from her great-grandmother, the founder of the Veuve Clicquot Champagne house. She was known for her involvement...
Johann Sebastian Bach
 15
Johann Sebastian Bach was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his prolific authorship of music across a variety of instruments and forms, including; orchestral...
15
Johann Sebastian Bach was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his prolific authorship of music across a variety of instruments and forms, including; orchestral...
Philippe Lebon
 15
Philippe le Bon (D'Humbersin) was a French engineer, born in Brachay, France.
15
Philippe le Bon (D'Humbersin) was a French engineer, born in Brachay, France.
Henri Bergson
 15
Henri-Louis Bergson was a French philosopher, who was influential in the traditions of analytic philosophy and continental philosophy, especially during the first half of the 20th century until the...
15
Henri-Louis Bergson was a French philosopher, who was influential in the traditions of analytic philosophy and continental philosophy, especially during the first half of the 20th century until the...
Édouard Manet
 15
Édouard Manet was a French modernist painter. He was one of the first 19th-century artists to paint modern life, as well as a pivotal figure in the transition from Realism to Impressionism.
15
Édouard Manet was a French modernist painter. He was one of the first 19th-century artists to paint modern life, as well as a pivotal figure in the transition from Realism to Impressionism.
Amandus
 15
Amandus, commonly called Saint Amand, was a bishop of Tongeren-Maastricht and one of the catholic missionaries of Flanders. He is venerated as a saint, particularly in France and Belgium.
15
Amandus, commonly called Saint Amand, was a bishop of Tongeren-Maastricht and one of the catholic missionaries of Flanders. He is venerated as a saint, particularly in France and Belgium.
Alfred de Vigny
 15
Alfred Victor, Comte de Vigny was a French poet and early French Romanticist. He also produced novels, plays, and translations of Shakespeare.
15
Alfred Victor, Comte de Vigny was a French poet and early French Romanticist. He also produced novels, plays, and translations of Shakespeare.
Gérard Philipe
 14
Gérard Philipe was a prominent French actor who appeared in 32 films between 1944 and 1959. He came to prominence during the later period of the poetic realism movement of French Cinema in the late...
14
Gérard Philipe was a prominent French actor who appeared in 32 films between 1944 and 1959. He came to prominence during the later period of the poetic realism movement of French Cinema in the late...
Henri Poincaré
 14
Jules Henri Poincaré was a French mathematician, theoretical physicist, engineer, and philosopher of science. He is often described as a polymath, and in mathematics as "The Last Universalist", since...
14
Jules Henri Poincaré was a French mathematician, theoretical physicist, engineer, and philosopher of science. He is often described as a polymath, and in mathematics as "The Last Universalist", since...
Arthur Lamendin
 14
Arthur Lamendin, né le 2 mars 1852 à Lourches dans le Nord et mort le 3 novembre 1920 à Neuville-sur-Escaut, est un syndicaliste et homme politique français. Il est avec Émile Basly l'une des grandes...
14
Arthur Lamendin, né le 2 mars 1852 à Lourches dans le Nord et mort le 3 novembre 1920 à Neuville-sur-Escaut, est un syndicaliste et homme politique français. Il est avec Émile Basly l'une des grandes...
Edgar Degas
 14
Edgar Degas was a French Impressionist artist famous for his pastel drawings and oil paintings.
14
Edgar Degas was a French Impressionist artist famous for his pastel drawings and oil paintings.
Nicéphore Niépce
 14
Joseph Nicéphore Niépce was a French inventor and one of the earliest pioneers of photography. Niépce developed heliography, a technique he used to create the world's oldest surviving product of a...
14
Joseph Nicéphore Niépce was a French inventor and one of the earliest pioneers of photography. Niépce developed heliography, a technique he used to create the world's oldest surviving product of a...
Jean-Baptiste de La Salle
 14
Jean-Baptiste de La Salle was a French priest, educational reformer, and founder of the Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools. He is a saint of the Catholic Church and the patron saint...
14
Jean-Baptiste de La Salle was a French priest, educational reformer, and founder of the Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools. He is a saint of the Catholic Church and the patron saint...
Christopher Columbus
 14
Christopher Columbus was an Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed four Spanish-based voyages across the Atlantic Ocean sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs, opening...
14
Christopher Columbus was an Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed four Spanish-based voyages across the Atlantic Ocean sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs, opening...
Jules Auguste Lemire
 14
Jules Auguste Lemire, French priest and social reformer, was born at Vieux-Berquin (Nord).
14
Jules Auguste Lemire, French priest and social reformer, was born at Vieux-Berquin (Nord).
Germaine Tillion
 14
Germaine Tillion was a French ethnologist, known for her work in Algeria in the 1950s on behalf of the Government of France. A member of the French Resistance in World War II, she spent time in...
14
Germaine Tillion was a French ethnologist, known for her work in Algeria in the 1950s on behalf of the Government of France. A member of the French Resistance in World War II, she spent time in...
Jacques de Vaucanson
 13
Jacques de Vaucanson was a French inventor and artist who built the first all-metal lathe. This invention was crucial for the Industrial Revolution. The lathe is known as the mother of machine tools,...
13
Jacques de Vaucanson was a French inventor and artist who built the first all-metal lathe. This invention was crucial for the Industrial Revolution. The lathe is known as the mother of machine tools,...
Pope John XXIII
 13
Pope John XXIII was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 28 October 1958 until his death in June 1963.
13
Pope John XXIII was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 28 October 1958 until his death in June 1963.
Eugène Varlin
 13
Eugène Varlin was a French socialist, anarchist, communard and member of the First International. He was one of the pioneers of French syndicalism.
13
Eugène Varlin was a French socialist, anarchist, communard and member of the First International. He was one of the pioneers of French syndicalism.
Camille Guérin
 13
Jean-Marie Camille Guérin was a French veterinarian, bacteriologist and immunologist who, together with Albert Calmette, developed the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), a vaccine for immunization...
13
Jean-Marie Camille Guérin was a French veterinarian, bacteriologist and immunologist who, together with Albert Calmette, developed the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), a vaccine for immunization...
Pierre Puvis de Chavannes
 13
Pierre Puvis de Chavannes was a French painter known for his mural painting, who came to be known as "the painter for France". He became the co-founder and president of the Société Nationale des...
13
Pierre Puvis de Chavannes was a French painter known for his mural painting, who came to be known as "the painter for France". He became the co-founder and president of the Société Nationale des...
Saint Cecilia
 13
Saint Cecilia, also spelled Cecelia, was a Roman virgin martyr and is venerated in Catholic, Orthodox, Anglican, and some Lutheran churches, such as the Church of Sweden. She became the patroness of...
13
Saint Cecilia, also spelled Cecelia, was a Roman virgin martyr and is venerated in Catholic, Orthodox, Anglican, and some Lutheran churches, such as the Church of Sweden. She became the patroness of...
Jean-Honoré Fragonard
 13
Jean-Honoré Fragonard was a French painter and printmaker whose late Rococo manner was distinguished by remarkable facility, exuberance, and hedonism. One of the most prolific artists active in the...
13
Jean-Honoré Fragonard was a French painter and printmaker whose late Rococo manner was distinguished by remarkable facility, exuberance, and hedonism. One of the most prolific artists active in the...
Nicolas Brémontier
 13
Nicolas-Thomas Brémontier est un ingénieur français, né le 30 juillet 1738 au Tronquay, dans l'Eure, et mort de tuberculose le 16 août 1809 à Paris. Sa renommée est liée à la fixation des dunes, dont...
13
Nicolas-Thomas Brémontier est un ingénieur français, né le 30 juillet 1738 au Tronquay, dans l'Eure, et mort de tuberculose le 16 août 1809 à Paris. Sa renommée est liée à la fixation des dunes, dont...
Dieudonné Costes
 13
Dieudonné Costes was a French fighter ace during World War I, and later distance records-breaking aviator.
13
Dieudonné Costes was a French fighter ace during World War I, and later distance records-breaking aviator.
Jean-Paul Sartre
 13
Jean-Paul Charles Aymard Sartre was a French philosopher, playwright, novelist, screenwriter, political activist, biographer, and literary critic, considered a leading figure in 20th-century French...
13
Jean-Paul Charles Aymard Sartre was a French philosopher, playwright, novelist, screenwriter, political activist, biographer, and literary critic, considered a leading figure in 20th-century French...
André Gide
 13
André Paul Guillaume Gide was a French author whose writings spanned a wide variety of styles and topics. He was awarded the 1947 Nobel Prize in Literature. Gide's career ranged from his beginnings...
13
André Paul Guillaume Gide was a French author whose writings spanned a wide variety of styles and topics. He was awarded the 1947 Nobel Prize in Literature. Gide's career ranged from his beginnings...
Max Jacob
 13
Max Jacob was a French poet, painter, writer, and critic.
13
Max Jacob was a French poet, painter, writer, and critic.
Marcel Cachin
 13
Marcel Cachin was a French Communist politician and editor of the daily newspaper L'Humanite.
13
Marcel Cachin was a French Communist politician and editor of the daily newspaper L'Humanite.
Xavier Grall
 13
Xavier Grall (1930–1981) was a journalist and poet from Brittany, France, who was a strong advocate of Breton nationalism during the Third Emsav. His work glorifies a mystical Brittany.
13
Xavier Grall (1930–1981) was a journalist and poet from Brittany, France, who was a strong advocate of Breton nationalism during the Third Emsav. His work glorifies a mystical Brittany.
Ludwig van Beethoven
 13
Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music...
13
Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music...
Paul Painlevé
 13
Paul Painlevé was a French mathematician and statesman. He served twice as Prime Minister of the Third Republic: 12 September – 13 November 1917 and 17 April – 22 November 1925. His entry into...
13
Paul Painlevé was a French mathematician and statesman. He served twice as Prime Minister of the Third Republic: 12 September – 13 November 1917 and 17 April – 22 November 1925. His entry into...
Helena, mother of Constantine I
 13
Flavia Julia Helena, also known as Helena of Constantinople and in Christianity as Saint Helena, was an Augusta of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine the Great. She was born in the...
13
Flavia Julia Helena, also known as Helena of Constantinople and in Christianity as Saint Helena, was an Augusta of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine the Great. She was born in the...
François La Vieille
 13
François-Sébastien La Vieille, né le 20 janvier 1829 à Urville-Hague et mort le 24 août 1886 à Panama, est un homme politique français.
13
François-Sébastien La Vieille, né le 20 janvier 1829 à Urville-Hague et mort le 24 août 1886 à Panama, est un homme politique français.
Jeanne de Laval
 13
Jeanne de Laval, was the second wife and titular Queen consort of René I of Anjou, King of Naples, Sicily, titular King of Jerusalem, Aragon, and Majorca; Duke of Anjou, Bar, and Lorraine; and Count...
13
Jeanne de Laval, was the second wife and titular Queen consort of René I of Anjou, King of Naples, Sicily, titular King of Jerusalem, Aragon, and Majorca; Duke of Anjou, Bar, and Lorraine; and Count...
Georges Méliès
 13
Marie-Georges-Jean Méliès was a French magician, actor, and film director. He led many technical and narrative developments in the early days of cinema.
13
Marie-Georges-Jean Méliès was a French magician, actor, and film director. He led many technical and narrative developments in the early days of cinema.
Constantine the Great
 13
Constantine I, also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a pivotal role in elevating the status of...
13
Constantine I, also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a pivotal role in elevating the status of...
Arnaud Beltrame
 13
Arnaud Jean-Georges Beltrame was a lieutenant colonel in the French Gendarmerie nationale and deputy commander of the Departmental Gendarmerie's Aude unit, who was murdered by an Islamic terrorist at...
13
Arnaud Jean-Georges Beltrame was a lieutenant colonel in the French Gendarmerie nationale and deputy commander of the Departmental Gendarmerie's Aude unit, who was murdered by an Islamic terrorist at...
Jean-Baptiste Lully
 13
Jean-Baptiste Lully was a French composer, dancer and instrumentalist of Italian birth, who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he spent most of his...
13
Jean-Baptiste Lully was a French composer, dancer and instrumentalist of Italian birth, who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he spent most of his...
Louis Antoine de Bougainville
 12
Louis-Antoine, Comte de Bougainville was a French admiral and explorer. A contemporary of the British explorer James Cook, he took part in the Seven Years' War in North America and the American...
12
Louis-Antoine, Comte de Bougainville was a French admiral and explorer. A contemporary of the British explorer James Cook, he took part in the Seven Years' War in North America and the American...
Monsieur de Sainte-Colombe
 12
Jean (?) de Sainte-Colombe (c. 1640 – c. 1700) was a French composer and violist. He was a celebrated master of the viola da gamba and was credited (by Jean Rousseau in his Traité de la viole (1687))...
12
Jean (?) de Sainte-Colombe (c. 1640 – c. 1700) was a French composer and violist. He was a celebrated master of the viola da gamba and was credited (by Jean Rousseau in his Traité de la viole (1687))...
Melaine
 12
Saint Melaine was a 6th-century Bishop of Rennes in Brittany.
12
Saint Melaine was a 6th-century Bishop of Rennes in Brittany.
Guillaume Apollinaire
 12
Guillaume Apollinaire was a French poet, playwright, short story writer, novelist and art critic of Polish descent.
12
Guillaume Apollinaire was a French poet, playwright, short story writer, novelist and art critic of Polish descent.
Paul Féval, père
 12
Paul Henri Corentin Féval, père was a French novelist and dramatist.
12
Paul Henri Corentin Féval, père was a French novelist and dramatist.
Honoré Daumier
 12
Honoré-Victorin Daumier was a French painter, sculptor, and printmaker, whose many works offer commentary on the social and political life in France, from the Revolution of 1830 to the fall of the...
12
Honoré-Victorin Daumier was a French painter, sculptor, and printmaker, whose many works offer commentary on the social and political life in France, from the Revolution of 1830 to the fall of the...
Marguerite de Navarre
 12
Marguerite de Navarre, also known as Marguerite of Angoulême and Margaret of Navarre, was a princess of France, Duchess of Alençon and Berry, and Queen of Navarre by her second marriage to King Henry...
12
Marguerite de Navarre, also known as Marguerite of Angoulême and Margaret of Navarre, was a princess of France, Duchess of Alençon and Berry, and Queen of Navarre by her second marriage to King Henry...
Louis Auguste Blanqui
 12
Louis Auguste Blanqui was a French socialist and political activist, notable for his revolutionary theory of Blanquism.
12
Louis Auguste Blanqui was a French socialist and political activist, notable for his revolutionary theory of Blanquism.
Louis Guilloux
 12
Louis Guilloux was a Breton writer born in Saint-Brieuc, Brittany, where he lived throughout his life. He is known for his Social Realist novels describing working-class life and political struggles...
12
Louis Guilloux was a Breton writer born in Saint-Brieuc, Brittany, where he lived throughout his life. He is known for his Social Realist novels describing working-class life and political struggles...
Jacques Duclos
Robert Desnos
 12
Robert Desnos was a French poet who played a key role in the Surrealist movement.
12
Robert Desnos was a French poet who played a key role in the Surrealist movement.
Berthe Morisot
 12
Berthe Marie Pauline Morisot was a French painter and a member of the circle of painters in Paris who became known as the Impressionists.
12
Berthe Marie Pauline Morisot was a French painter and a member of the circle of painters in Paris who became known as the Impressionists.
House of Montmorency
 12
The House of Montmorency was one of the oldest and most distinguished noble families in France.
12
The House of Montmorency was one of the oldest and most distinguished noble families in France.
Louis Barthou
 12
Jean Louis Barthou was a French politician of the Third Republic who served as Prime Minister of France for eight months in 1913. In social policy, his time as prime minister saw the introduction of...
12
Jean Louis Barthou was a French politician of the Third Republic who served as Prime Minister of France for eight months in 1913. In social policy, his time as prime minister saw the introduction of...
Pierre Dupont
 12
Pierre Dupont was a French songwriter.
12
Pierre Dupont was a French songwriter.
Jean Ferrat
 12
Jean Ferrat was a French singer-songwriter and poet. He specialized in singing poetry, particularly that of Louis Aragon. He had a left-wing sympathy that found its way into a few songs.
12
Jean Ferrat was a French singer-songwriter and poet. He specialized in singing poetry, particularly that of Louis Aragon. He had a left-wing sympathy that found its way into a few songs.
Henri Giraud
 12
Henri Honoré Giraud was a French military officer who was a leader of the Free French Forces during the Second World War until he was forced to retire in 1944.
12
Henri Honoré Giraud was a French military officer who was a leader of the Free French Forces during the Second World War until he was forced to retire in 1944.
Ferdinand Magellan
 12
Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the East Indies across the Pacific Ocean to open a maritime trade route, during which...
12
Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the East Indies across the Pacific Ocean to open a maritime trade route, during which...
Marguerite Duras
 12
Marguerite Germaine Marie Donnadieu, known as Marguerite Duras, was a French novelist, playwright, screenwriter, essayist, and experimental filmmaker. Her script for the film Hiroshima mon amour...
12
Marguerite Germaine Marie Donnadieu, known as Marguerite Duras, was a French novelist, playwright, screenwriter, essayist, and experimental filmmaker. Her script for the film Hiroshima mon amour...
Erik Satie
 12
Eric Alfred Leslie Satie, who signed his name Erik Satie after 1884, was a French composer and pianist. He was the son of a French father and a British mother. He studied at the Paris Conservatoire,...
12
Eric Alfred Leslie Satie, who signed his name Erik Satie after 1884, was a French composer and pianist. He was the son of a French father and a British mother. He studied at the Paris Conservatoire,...
Jean-Philippe Rameau
 12
Jean-Philippe Rameau was a French composer and music theorist. Regarded as one of the most important French composers and music theorists of the 18th century, he replaced Jean-Baptiste Lully as the...
12
Jean-Philippe Rameau was a French composer and music theorist. Regarded as one of the most important French composers and music theorists of the 18th century, he replaced Jean-Baptiste Lully as the...
Jacques Cousteau
 12
Jacques-Yves Cousteau, was a French naval officer, oceanographer, filmmaker and author. He co-invented the first successful open-circuit self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA), called...
12
Jacques-Yves Cousteau, was a French naval officer, oceanographer, filmmaker and author. He co-invented the first successful open-circuit self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA), called...
Mathurin Méheut
 12
Mathurin Méheut was a French painter, ceramist, engraver, and etcher best known for his depictions of Breton scenes, the sea, and nature.
12
Mathurin Méheut was a French painter, ceramist, engraver, and etcher best known for his depictions of Breton scenes, the sea, and nature.
Colette Besson
 12
Colette Besson was a French athlete, the surprise winner of the 400 m at the 1968 Summer Olympics in Mexico City.
12
Colette Besson was a French athlete, the surprise winner of the 400 m at the 1968 Summer Olympics in Mexico City.
Karl Marx
 11
Karl Marx was a German-born philosopher, economist, political theorist, historian, sociologist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. His best-known works are the 1848 pamphlet The Communist...
11
Karl Marx was a German-born philosopher, economist, political theorist, historian, sociologist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. His best-known works are the 1848 pamphlet The Communist...
Léon Bourgeois
 11
Léon Victor Auguste Bourgeois was a French statesman. His ideas influenced the Radical Party regarding a wide range of issues.
11
Léon Victor Auguste Bourgeois was a French statesman. His ideas influenced the Radical Party regarding a wide range of issues.
Arthur Le Moyne de La Borderie
 11
Arthur Le Moyne de La Borderie, was a Breton historian, regarded as a father of Brittany's historiography.
11
Arthur Le Moyne de La Borderie, was a Breton historian, regarded as a father of Brittany's historiography.
Rosa Bonheur
 11
Rosa Bonheur was a French artist known best as a painter of animals (animalière). She also made sculptures in a realist style. Her paintings include Ploughing in the Nivernais, first exhibited at the...
11
Rosa Bonheur was a French artist known best as a painter of animals (animalière). She also made sculptures in a realist style. Her paintings include Ploughing in the Nivernais, first exhibited at the...
Nicolas Boileau-Despréaux
 11
Nicolas Boileau-Despréaux, often known simply as Boileau, was a French poet and critic. He did much to reform the prevailing form of French poetry, in the same way that Blaise Pascal did to reform...
11
Nicolas Boileau-Despréaux, often known simply as Boileau, was a French poet and critic. He did much to reform the prevailing form of French poetry, in the same way that Blaise Pascal did to reform...
William the Conqueror
 11
William the Conqueror, sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy from 1035 onward....
11
William the Conqueror, sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy from 1035 onward....
Jean Guéhenno
 11
Jean Guéhenno born Marcel-Jules-Marie Guéhenno was a French essayist, writer and literary critic.
11
Jean Guéhenno born Marcel-Jules-Marie Guéhenno was a French essayist, writer and literary critic.
André Chénier
 11
André Marie Chénier was a French poet of Greek and Franco-Levantine origin, associated with the events of the French Revolution, during which he was sentenced to death. His sensual, emotive poetry...
11
André Marie Chénier was a French poet of Greek and Franco-Levantine origin, associated with the events of the French Revolution, during which he was sentenced to death. His sensual, emotive poetry...
Stendhal
 11
Marie-Henri Beyle, better known by his pen name Stendhal, was a 19th-century French writer. Best known for the novels Le Rouge et le Noir and La Chartreuse de Parme, he is highly regarded for the...
11
Marie-Henri Beyle, better known by his pen name Stendhal, was a 19th-century French writer. Best known for the novels Le Rouge et le Noir and La Chartreuse de Parme, he is highly regarded for the...
Emmanuel Chabrier
 11
Alexis-Emmanuel Chabrier was a French Romantic composer and pianist. His bourgeois family did not approve of a musical career for him, and he studied law in Paris and then worked as a civil servant...
11
Alexis-Emmanuel Chabrier was a French Romantic composer and pianist. His bourgeois family did not approve of a musical career for him, and he studied law in Paris and then worked as a civil servant...
Sadi Carnot (statesman)
 11
Marie François Sadi Carnot was a French statesman, who served as the President of France from 1887 until his assassination in 1894.
11
Marie François Sadi Carnot was a French statesman, who served as the President of France from 1887 until his assassination in 1894.
Georges Courteline
 11
Georges Courteline born Georges Victor Marcel Moinaux was a French dramatist and novelist, a satirist notable for his sharp wit and cynical humor.
11
Georges Courteline born Georges Victor Marcel Moinaux was a French dramatist and novelist, a satirist notable for his sharp wit and cynical humor.
Théophile Gautier
 11
Pierre Jules Théophile Gautier was a French poet, dramatist, novelist, journalist, and art and literary critic.
11
Pierre Jules Théophile Gautier was a French poet, dramatist, novelist, journalist, and art and literary critic.
Gustave Delory
 11
Gustave Delory, né le 10 septembre 1857 à Lille et mort le 17 août 1925 dans cette même ville, est un homme politique français. Élu maire de Lille en 1896, il devient l'un des premiers maires...
11
Gustave Delory, né le 10 septembre 1857 à Lille et mort le 17 août 1925 dans cette même ville, est un homme politique français. Élu maire de Lille en 1896, il devient l'un des premiers maires...
Georges Besse
 11
Georges Besse was a French businessman who helped lead several large state-controlled companies. He was assassinated outside his Paris home by the armed group Action directe while he was the CEO of...
11
Georges Besse was a French businessman who helped lead several large state-controlled companies. He was assassinated outside his Paris home by the armed group Action directe while he was the CEO of...
Paul-Émile Victor
 11
Paul-Émile Victor was a French ethnologist and explorer.
11
Paul-Émile Victor was a French ethnologist and explorer.
Eugène Edine Pottier
 11
Eugène Edme Pottier was a French revolutionary, poet, freemason and transport worker.
11
Eugène Edme Pottier was a French revolutionary, poet, freemason and transport worker.
Bernard Montgomery
 11
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein,, nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and...
11
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein,, nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and...
Maurice Genevoix
 11
Maurice Genevoix was a French author and WW1 veteran who is best known for his book, Ceux de 14.
11
Maurice Genevoix was a French author and WW1 veteran who is best known for his book, Ceux de 14.
Franz Schubert
 11
Franz Peter Schubert was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short life, Schubert left behind a vast oeuvre, including more than 600 secular vocal works,...
11
Franz Peter Schubert was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short life, Schubert left behind a vast oeuvre, including more than 600 secular vocal works,...
Hervé Bazin
 11
Hervé Bazin was a French writer, whose best-known novels covered semi-autobiographical topics of teenage rebellion and dysfunctional families.
11
Hervé Bazin was a French writer, whose best-known novels covered semi-autobiographical topics of teenage rebellion and dysfunctional families.
Anita Conti
 11
Anita Conti was a French explorer and photographer, and the first French female oceanographer.
11
Anita Conti was a French explorer and photographer, and the first French female oceanographer.
Charlemagne
 11
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and Emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding all these titles until his death in 814. Charlemagne succeeded in...
11
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and Emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding all these titles until his death in 814. Charlemagne succeeded in...
Léo Ferré
 11
Léo Ferré was a French-born Monégasque poet and composer, and a dynamic and controversial live performer. He released some forty albums over this period, composing the music and the majority of the...
11
Léo Ferré was a French-born Monégasque poet and composer, and a dynamic and controversial live performer. He released some forty albums over this period, composing the music and the majority of the...
Jean Aicard
 11
Jean François Victor Aicard was a French poet, dramatist, and novelist.
11
Jean François Victor Aicard was a French poet, dramatist, and novelist.
Adrien Albert Marie de Mun
 11
Adrien Albert Marie, Comte de Mun, was a French political figure, nobleman, journalist, social reformer, and reactionary of the nineteenth century. Born into a noble family de Mun joined the French...
11
Adrien Albert Marie, Comte de Mun, was a French political figure, nobleman, journalist, social reformer, and reactionary of the nineteenth century. Born into a noble family de Mun joined the French...
Alessandro Volta
 11
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta was an Italian physicist and chemist who was a pioneer of electricity and power and is credited as the inventor of the electric battery and the discoverer...
11
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta was an Italian physicist and chemist who was a pioneer of electricity and power and is credited as the inventor of the electric battery and the discoverer...
Eugène Le Roy
 11
Eugène Le Roy was a French author.
11
Eugène Le Roy was a French author.
Henri Fabre
 11
Henri Fabre was a French aviator and the inventor of the first successful seaplane, the Fabre Hydravion.
11
Henri Fabre was a French aviator and the inventor of the first successful seaplane, the Fabre Hydravion.
Maurice Chevalier
 11
Maurice Auguste Chevalier was a French singer, actor, and entertainer. He is perhaps best known for his signature songs, including "Livin' In The Sunlight", "Valentine", "Louise", "Mimi", and "Thank...
11
Maurice Auguste Chevalier was a French singer, actor, and entertainer. He is perhaps best known for his signature songs, including "Livin' In The Sunlight", "Valentine", "Louise", "Mimi", and "Thank...
Archimedes
 11
Archimedes of Syracuse was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is...
11
Archimedes of Syracuse was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is...
Saint Fiacre
 11
Fiacre is the name of three different Irish saints, the most famous of which is Fiacre of Breuil, the priest, abbot, hermit, and gardener of the seventh century who was famous for his sanctity and...
11
Fiacre is the name of three different Irish saints, the most famous of which is Fiacre of Breuil, the priest, abbot, hermit, and gardener of the seventh century who was famous for his sanctity and...
Raoul Dufy
 11
Raoul Dufy was a French painter associated with the Fauvist movement. He gained recognition for his vibrant and decorative style, which became popular in various forms, such as textile designs, and...
11
Raoul Dufy was a French painter associated with the Fauvist movement. He gained recognition for his vibrant and decorative style, which became popular in various forms, such as textile designs, and...
Louise Weiss
 11
Louise Weiss was a French author, journalist, feminist, and European politician.
11
Louise Weiss was a French author, journalist, feminist, and European politician.
Henri Farman
 11
Henri Farman was a British-French aviator and aircraft designer and manufacturer with his brother Maurice Farman. Before dedicating himself to aviation he gained fame as a sportsman, specifically in...
11
Henri Farman was a British-French aviator and aircraft designer and manufacturer with his brother Maurice Farman. Before dedicating himself to aviation he gained fame as a sportsman, specifically in...
Pierre-Simon Laplace
 10
Pierre-Simon, Marquis de Laplace was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He...
10
Pierre-Simon, Marquis de Laplace was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He...
George de Villebois-Mareuil
 10
George Henri Anne-Marie Victor count de Villebois-Mareuil or by his shortened name George de Villebois-Mareuil was a former colonel in the French infantry who fought and died on the side of the Boers...
10
George Henri Anne-Marie Victor count de Villebois-Mareuil or by his shortened name George de Villebois-Mareuil was a former colonel in the French infantry who fought and died on the side of the Boers...
Dwight D. Eisenhower
 10
Dwight David Eisenhower, nicknamed Ike, was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme...
10
Dwight David Eisenhower, nicknamed Ike, was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme...
Émile Combes
 10
Émile Justin Louis Combes was a French politician and freemason who led the Lefts Bloc cabinet from June 1902 to January 1905.
10
Émile Justin Louis Combes was a French politician and freemason who led the Lefts Bloc cabinet from June 1902 to January 1905.
François Christophe de Kellermann
 10
François-Étienne-Christophe Kellermann or de Kellermann, 1st Duke of Valmy was a French military commander, later the Général d'Armée, a Marshal of the Empire and freemason. Marshal Kellermann served...
10
François-Étienne-Christophe Kellermann or de Kellermann, 1st Duke of Valmy was a French military commander, later the Général d'Armée, a Marshal of the Empire and freemason. Marshal Kellermann served...
Thomas the Apostle
 10
Thomas the Apostle, also known as Didymus, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Thomas is commonly known as "Doubting Thomas" because he initially doubted the...
10
Thomas the Apostle, also known as Didymus, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Thomas is commonly known as "Doubting Thomas" because he initially doubted the...
André Maginot
 10
André Maginot was a French civil servant, soldier and Member of Parliament. He is best known for his advocacy of the string of forts known as the Maginot Line.
10
André Maginot was a French civil servant, soldier and Member of Parliament. He is best known for his advocacy of the string of forts known as the Maginot Line.
Honoratus of Amiens
 10
Saint Honoratus of Amiens was the seventh bishop of Amiens. His feast day is May 16.
10
Saint Honoratus of Amiens was the seventh bishop of Amiens. His feast day is May 16.
Anne Frank
 10
Annelies Marie Frank was a German-born Jewish girl who kept a diary in which she documented life in hiding under Nazi persecution during the German occupation of the Netherlands. She is a celebrated...
10
Annelies Marie Frank was a German-born Jewish girl who kept a diary in which she documented life in hiding under Nazi persecution during the German occupation of the Netherlands. She is a celebrated...
Claude Chappe
 10
Claude Chappe was a French inventor who in 1792 demonstrated a practical semaphore system that eventually spanned all of France. His system consisted of a series of towers, each within line of sight...
10
Claude Chappe was a French inventor who in 1792 demonstrated a practical semaphore system that eventually spanned all of France. His system consisted of a series of towers, each within line of sight...
Cyricus and Julitta
Édouard Belin
 10
Édouard Belin was a French photographer and inventor. In 1907 Belin invented a phototelegraphic apparatus called the Bélinographe (télestéréographe)—a system for receiving photographs over telephone...
10
Édouard Belin was a French photographer and inventor. In 1907 Belin invented a phototelegraphic apparatus called the Bélinographe (télestéréographe)—a system for receiving photographs over telephone...
Didier of Cahors
 10
Saint Didier, also known as Desiderius, was a Merovingian-era royal official of aristocratic Gallo-Roman extraction.
10
Saint Didier, also known as Desiderius, was a Merovingian-era royal official of aristocratic Gallo-Roman extraction.
Geneviève de Gaulle-Anthonioz
 10
Geneviève de Gaulle-Anthonioz was a member of the French Resistance in World War II, during which she was sent to Ravensbrück concentration camp. After the war, she was president of the charity...
10
Geneviève de Gaulle-Anthonioz was a member of the French Resistance in World War II, during which she was sent to Ravensbrück concentration camp. After the war, she was president of the charity...
Victor Basch
 10
Basch Viktor Vilém, or Victor-Guillaume Basch was a French Jewish politician and professor of germanistics and philosophy at the Sorbonne descending from Hungary. He was engaged in the Zionist...
10
Basch Viktor Vilém, or Victor-Guillaume Basch was a French Jewish politician and professor of germanistics and philosophy at the Sorbonne descending from Hungary. He was engaged in the Zionist...
Louis Charles Breguet
 10
Louis Charles Breguet was a French aircraft designer and builder, one of the early aviation pioneers.
10
Louis Charles Breguet was a French aircraft designer and builder, one of the early aviation pioneers.
René Guy Cadou
 10
René Guy Cadou est un poète français, né le 15 février 1920 à Sainte-Reine-de-Bretagne et mort le 20 mars 1951 à 31 ans à Louisfert (Loire-Atlantique). Il a publié de 1936 à 1951. Ses œuvres...
10
René Guy Cadou est un poète français, né le 15 février 1920 à Sainte-Reine-de-Bretagne et mort le 20 mars 1951 à 31 ans à Louisfert (Loire-Atlantique). Il a publié de 1936 à 1951. Ses œuvres...
Raoul Follereau
 10
Raoul Follereau, né le 17 août 1903 à Nevers et mort le 6 décembre 1977 dans le 16e arrondissement de Paris, est un écrivain et journaliste français.
10
Raoul Follereau, né le 17 août 1903 à Nevers et mort le 6 décembre 1977 dans le 16e arrondissement de Paris, est un écrivain et journaliste français.
Georges Braque
 10
Georges Braque was a major 20th-century French painter, collagist, draughtsman, printmaker and sculptor. His most notable contributions were in his alliance with Fauvism from 1905, and the role he...
10
Georges Braque was a major 20th-century French painter, collagist, draughtsman, printmaker and sculptor. His most notable contributions were in his alliance with Fauvism from 1905, and the role he...
Robert Surcouf
 10
Robert Surcouf was a French privateer, businessman and slave trader who operated in the Indian Ocean from 1789 to 1808 during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Capturing over 40 prizes,...
10
Robert Surcouf was a French privateer, businessman and slave trader who operated in the Indian Ocean from 1789 to 1808 during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Capturing over 40 prizes,...
Raoul Briquet
 10
Raoul Briquet, né le 4 novembre 1875 à Douai (Nord) et mort le 25 mars 1917 à Bapaume (Pas-de-Calais), est un homme politique français.
10
Raoul Briquet, né le 4 novembre 1875 à Douai (Nord) et mort le 25 mars 1917 à Bapaume (Pas-de-Calais), est un homme politique français.
Medardus
 10
Medardus or Medard was the Bishop of Noyon. He moved the seat of the diocese from Vermand to Noviomagus Veromanduorum in northern France. Medardus was one of the most honored bishops of his time,...
10
Medardus or Medard was the Bishop of Noyon. He moved the seat of the diocese from Vermand to Noviomagus Veromanduorum in northern France. Medardus was one of the most honored bishops of his time,...
Théodore Monod
 10
Théodore André Monod was a French naturalist, humanist, scholar and explorer.
10
Théodore André Monod was a French naturalist, humanist, scholar and explorer.
Didier Daurat
 10
Didier Daurat was a pioneer of French aviation. He was a fighter pilot during World War I, distinguishing himself by spotting the Paris Gun which was pounding Paris. After the war, he joined an...
10
Didier Daurat was a pioneer of French aviation. He was a fighter pilot during World War I, distinguishing himself by spotting the Paris Gun which was pounding Paris. After the war, he joined an...
Edgar Quinet
 10
Edgar Quinet was a French historian and intellectual.
10
Edgar Quinet was a French historian and intellectual.
René Mouchotte
 10
Commandant René Mouchotte DFC was a World War II pilot of the French Air Force, who escaped from Vichy French–controlled Oran to join the Free French forces. Serving with RAF Fighter Command, he rose...
10
Commandant René Mouchotte DFC was a World War II pilot of the French Air Force, who escaped from Vichy French–controlled Oran to join the Free French forces. Serving with RAF Fighter Command, he rose...
Stéphane Hessel
 10
Stéphane Frédéric Hessel was a French diplomat, ambassador, writer, concentration camp survivor, Resistance member and BCRA agent. Born German, he became a naturalised French citizen in 1939. He...
10
Stéphane Frédéric Hessel was a French diplomat, ambassador, writer, concentration camp survivor, Resistance member and BCRA agent. Born German, he became a naturalised French citizen in 1939. He...
Jean Gabin
 10
Jean-Alexis Moncorgé, known as Jean Gabin, was a French actor and singer. Considered a key figure in French cinema, he starred in several classic films, including Pépé le Moko (1937), La grande...
10
Jean-Alexis Moncorgé, known as Jean Gabin, was a French actor and singer. Considered a key figure in French cinema, he starred in several classic films, including Pépé le Moko (1937), La grande...
Roland Barthes
 10
Roland Gérard Barthes was a French literary theorist, essayist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician. His work engaged in the analysis of a variety of sign systems, mainly derived from Western...
10
Roland Gérard Barthes was a French literary theorist, essayist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician. His work engaged in the analysis of a variety of sign systems, mainly derived from Western...
Añjela Duval
 10
Marie-Angèle Duval was a Breton writer and poet of Breton literature, best remembered for her works Kan an douar (1973), Traoñ an Dour (1982), Tad-kozh Roperz-Huon (1822-1902) (1982), and Me, Anjela...
10
Marie-Angèle Duval was a Breton writer and poet of Breton literature, best remembered for her works Kan an douar (1973), Traoñ an Dour (1982), Tad-kozh Roperz-Huon (1822-1902) (1982), and Me, Anjela...
André Citroën
 10
André-Gustave Citroën was a French industrialist and the founder of French automaker Citroën. He is also remembered for his application of double helical gears.
10
André-Gustave Citroën was a French industrialist and the founder of French automaker Citroën. He is also remembered for his application of double helical gears.
Clément Marot
 10
Clément Marot was a French Renaissance poet.
10
Clément Marot was a French Renaissance poet.
René Dumont
 10
René Dumont was a French engineer in agronomy, a sociologist, and an environmental politician.
10
René Dumont was a French engineer in agronomy, a sociologist, and an environmental politician.
Flora Tristan
 10
Flore Célestine Thérèse Henriette Tristán y Moscoso, better known as Flora Tristan, was a French-Peruvian writer and socialist activist. She made important contributions to early feminist theory, and...
10
Flore Célestine Thérèse Henriette Tristán y Moscoso, better known as Flora Tristan, was a French-Peruvian writer and socialist activist. She made important contributions to early feminist theory, and...
Josephine Baker
 10
Freda Josephine Baker, naturalized as Joséphine Baker, was an American-born French dancer, singer and actress. Her career was centered primarily in Europe, mostly in France. She was the first black...
10
Freda Josephine Baker, naturalized as Joséphine Baker, was an American-born French dancer, singer and actress. Her career was centered primarily in Europe, mostly in France. She was the first black...
François Mansart
 9
François Mansart was a French architect credited with introducing classicism into Baroque architecture of France. The Encyclopædia Britannica cites him as the most accomplished of 17th-century French...
9
François Mansart was a French architect credited with introducing classicism into Baroque architecture of France. The Encyclopædia Britannica cites him as the most accomplished of 17th-century French...
Raymond Queneau
 9
Raymond Queneau was a French novelist, poet, critic, editor and co-founder and president of Oulipo, notable for his wit and cynical humour.
9
Raymond Queneau was a French novelist, poet, critic, editor and co-founder and president of Oulipo, notable for his wit and cynical humour.
Henri de Saint-Simon
 9
Claude Henri de Rouvroy, comte de Saint-Simon, better known as Henri de Saint-Simon, was a French political, economic and socialist theorist and businessman whose thought had a substantial influence...
9
Claude Henri de Rouvroy, comte de Saint-Simon, better known as Henri de Saint-Simon, was a French political, economic and socialist theorist and businessman whose thought had a substantial influence...
Charles Mangin
 9
Charles Emmanuel Marie Mangin was a French general during World War I.
9
Charles Emmanuel Marie Mangin was a French general during World War I.
François Truffaut
 9
François Roland Truffaut was a French filmmaker, actor, and critic. He is widely regarded as one of the founders of the French New Wave. With a career of more than 25 years, he is an icon of the...
9
François Roland Truffaut was a French filmmaker, actor, and critic. He is widely regarded as one of the founders of the French New Wave. With a career of more than 25 years, he is an icon of the...
Théodore Aubanel
 9
Théodore Aubanel was a Provençal poet. He was born in Avignon in a family of printers.
9
Théodore Aubanel was a Provençal poet. He was born in Avignon in a family of printers.
Guglielmo Marconi
 9
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi was an Italian inventor and electrical engineer, known for his creation of a practical radio wave–based wireless telegraph system. This led to...
9
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi was an Italian inventor and electrical engineer, known for his creation of a practical radio wave–based wireless telegraph system. This led to...
Sarah Bernhardt
 9
Sarah Bernhardt was a French stage actress who starred in some of the more popular French plays of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including La Dame aux Camélias by Alexandre Dumas fils, Ruy...
9
Sarah Bernhardt was a French stage actress who starred in some of the more popular French plays of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including La Dame aux Camélias by Alexandre Dumas fils, Ruy...
Charles Le Goffic
 9
Charles Le Goffic was a Breton poet, novelist and historian whose influence was especially strong in his native Brittany. He was a member of the Académie française.
9
Charles Le Goffic was a Breton poet, novelist and historian whose influence was especially strong in his native Brittany. He was a member of the Académie française.
Paul Fort
 9
Jules-Jean-Paul Fort was a French poet associated with the Symbolist movement. At the age of 18, reacting against the Naturalistic theatre, Fort founded the Théâtre d'Art (1890–93). He also founded...
9
Jules-Jean-Paul Fort was a French poet associated with the Symbolist movement. At the age of 18, reacting against the Naturalistic theatre, Fort founded the Théâtre d'Art (1890–93). He also founded...
Raoul Dautry
 9
Raoul Dautry was a French engineer, business leader and politician. He was born on 16 September 1880 at Montluçon in the department of Allier; he died on 21 August 1951 at Lourmarin in the department...
9
Raoul Dautry was a French engineer, business leader and politician. He was born on 16 September 1880 at Montluçon in the department of Allier; he died on 21 August 1951 at Lourmarin in the department...
Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux
 9
Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux was a French sculptor and painter during the Second Empire under Napoleon III.
9
Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux was a French sculptor and painter during the Second Empire under Napoleon III.
Aristide Maillol
 9
Aristide Joseph Bonaventure Maillol was a French sculptor, painter, and printmaker.
9
Aristide Joseph Bonaventure Maillol was a French sculptor, painter, and printmaker.
Françoise Giroud
 9
Françoise Giroud, born Lea France Gourdji, was a French journalist, screenwriter, writer, and politician.
9
Françoise Giroud, born Lea France Gourdji, was a French journalist, screenwriter, writer, and politician.
Alfred Sisley
 9
Alfred Sisley was an Impressionist landscape painter who was born and spent most of his life in France, but retained British citizenship. He was the most consistent of the Impressionists in his...
9
Alfred Sisley was an Impressionist landscape painter who was born and spent most of his life in France, but retained British citizenship. He was the most consistent of the Impressionists in his...
Louison Bobet
 9
Louis "Louison" Bobet was a French professional road racing cyclist. He was the first great French rider of the post-war period and the first rider to win the Tour de France in three successive...
9
Louis "Louison" Bobet was a French professional road racing cyclist. He was the first great French rider of the post-war period and the first rider to win the Tour de France in three successive...
Jacques Anquetil
 9
Jacques Anquetil was a French road racing cyclist and the first cyclist to win the Tour de France five times, in 1957 and from 1961 to 1964.
9
Jacques Anquetil was a French road racing cyclist and the first cyclist to win the Tour de France five times, in 1957 and from 1961 to 1964.
Edmond Michelet
 9
Edmond Michelet was a French politician. He is the father of the writer Claude Michelet.
9
Edmond Michelet was a French politician. He is the father of the writer Claude Michelet.
Pierre-Georges Latécoère
 9
Pierre-Georges Latécoère was a pioneer of aeronautics. Born in Bagnères-de-Bigorre, he studied in the École Centrale Paris and, during the First World War, started a business in aeronautics. He...
9
Pierre-Georges Latécoère was a pioneer of aeronautics. Born in Bagnères-de-Bigorre, he studied in the École Centrale Paris and, during the First World War, started a business in aeronautics. He...
Eugène Freyssinet
 9
Eugène Freyssinet was a French structural and civil engineer. He was the major pioneer of prestressed concrete.
9
Eugène Freyssinet was a French structural and civil engineer. He was the major pioneer of prestressed concrete.
Salvador Dalí
 9
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol, known as Salvador Dalí, was a Spanish surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the...
9
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol, known as Salvador Dalí, was a Spanish surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the...
Léo Delibes
 9
Clément Philibert Léo Delibes was a French Romantic composer, best known for his ballets and operas. His works include the ballets Coppélia (1870) and Sylvia (1876) and the opera Lakmé (1883), which...
9
Clément Philibert Léo Delibes was a French Romantic composer, best known for his ballets and operas. His works include the ballets Coppélia (1870) and Sylvia (1876) and the opera Lakmé (1883), which...
Konrad Adenauer
 9
Konrad Hermann Joseph Adenauer was a German statesman who served as the first chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany from 1949 to 1963. From 1946 to 1966, he was the first leader of the...
9
Konrad Hermann Joseph Adenauer was a German statesman who served as the first chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany from 1949 to 1963. From 1946 to 1966, he was the first leader of the...
Marcel Proust
 9
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust was a French novelist, literary critic, and essayist who wrote the monumental novel À la recherche du temps perdu which was published in seven volumes...
9
Valentin Louis Georges Eugène Marcel Proust was a French novelist, literary critic, and essayist who wrote the monumental novel À la recherche du temps perdu which was published in seven volumes...
Eugène Sue
 8
Marie-Joseph "Eugène" Sue was a French novelist. He was one of several authors who popularized the genre of the serial novel in France with his very popular and widely imitated The Mysteries of...
8
Marie-Joseph "Eugène" Sue was a French novelist. He was one of several authors who popularized the genre of the serial novel in France with his very popular and widely imitated The Mysteries of...
Simone Morand
 8
Simone Morand, est une professeure de musique française.
8
Simone Morand, est une professeure de musique française.
Henri Sellier
 8
Henri Charles Sellier was a French administrator, urban planner and Socialist politician.
He did much to develop garden cities in the Paris region.
He was Minister of Health in 1936–37.
8
Henri Charles Sellier was a French administrator, urban planner and Socialist politician.
He did much to develop garden cities in the Paris region.
He was Minister of Health in 1936–37.
Joseph Bertrand
 8
Joseph Louis François Bertrand was a French mathematician whose work emphasized number theory, differential geometry, probability theory, economics and thermodynamics.
8
Joseph Louis François Bertrand was a French mathematician whose work emphasized number theory, differential geometry, probability theory, economics and thermodynamics.
Paul Louis Courier
 8
Paul Louis Courier, French Hellenist and political writer.
8
Paul Louis Courier, French Hellenist and political writer.
Noël du Fail
 8
Noël du Fail, seigneur de La Hérissaye was a French jurist and writer of the Renaissance. His collections of tales are an important document of rural life in the sixteenth century in Brittany.
8
Noël du Fail, seigneur de La Hérissaye was a French jurist and writer of the Renaissance. His collections of tales are an important document of rural life in the sixteenth century in Brittany.
Frédéric Passy
 8
Frédéric Passy was a French economist and pacifist who was a founding member of several peace societies and the Inter-Parliamentary Union. He was also an author and politician, sitting in the Chamber...
8
Frédéric Passy was a French economist and pacifist who was a founding member of several peace societies and the Inter-Parliamentary Union. He was also an author and politician, sitting in the Chamber...
Horace Vernet
 8
Émile Jean-Horace Vernet more commonly known as simply Horace Vernet, was a French painter of battles, portraits, and Orientalist subjects.
8
Émile Jean-Horace Vernet more commonly known as simply Horace Vernet, was a French painter of battles, portraits, and Orientalist subjects.
Romanus of Rouen
 8
Saint Romanus of Rouen was a scribe, clerical sage, and bishop of Rouen. He would have lived under Dagobert I (629–39), though his date of birth is unknown. His life is known in legend and tradition...
8
Saint Romanus of Rouen was a scribe, clerical sage, and bishop of Rouen. He would have lived under Dagobert I (629–39), though his date of birth is unknown. His life is known in legend and tradition...
Francis I of France
 8
Francis I was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law...
8
Francis I was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law...
Vercingetorix
 8
Vercingetorix was a Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. After...
8
Vercingetorix was a Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. After...
Marc Seguin
 8
Marc Seguin was a French engineer, inventor of the wire-cable suspension bridge and the multi-tubular steam-engine boiler.
8
Marc Seguin was a French engineer, inventor of the wire-cable suspension bridge and the multi-tubular steam-engine boiler.
Célestin Freinet
 8
Célestin Freinet was a noted French pedagogue and educational reformer.
8
Célestin Freinet was a noted French pedagogue and educational reformer.
Prosper Mérimée
 8
Prosper Mérimée was a French writer in the movement of Romanticism, one of the pioneers of the novella, a short novel or long short story. He was also a noted archaeologist and historian, an...
8
Prosper Mérimée was a French writer in the movement of Romanticism, one of the pioneers of the novella, a short novel or long short story. He was also a noted archaeologist and historian, an...
Henri Durre
 8
Henri Durre, né le 15 septembre 1867 à Maubeuge (Nord) et mort le 28 octobre 1918 à Anzin (Nord), est un homme politique français.
8
Henri Durre, né le 15 septembre 1867 à Maubeuge (Nord) et mort le 28 octobre 1918 à Anzin (Nord), est un homme politique français.
Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres
 8
Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres was a French Neoclassical painter. Ingres was profoundly influenced by past artistic traditions and aspired to become the guardian of academic orthodoxy against the...
8
Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres was a French Neoclassical painter. Ingres was profoundly influenced by past artistic traditions and aspired to become the guardian of academic orthodoxy against the...
Francis de Pressensé
 8
Francis Charles Dehault de Pressensé was a French politician and journalist.
8
Francis Charles Dehault de Pressensé was a French politician and journalist.
Mahatma Gandhi
 8
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from...
8
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from...
Jeanne Jugan
 8
Jeanne Jugan, religious name Mary of the Cross, was a French religious sister who became known for the dedication of her life to the neediest of the elderly poor. Her service resulted in the...
8
Jeanne Jugan, religious name Mary of the Cross, was a French religious sister who became known for the dedication of her life to the neediest of the elderly poor. Her service resulted in the...
Henri Guillaumet
 8
Henri Guillaumet was a French aviator.
8
Henri Guillaumet was a French aviator.
Louis Franchet d'Espèrey
 8
Louis Félix Marie François Franchet d'Espèrey was a French general during World War I. As commander of the large Allied army based at Salonika, he conducted the successful Macedonian campaign, which...
8
Louis Félix Marie François Franchet d'Espèrey was a French general during World War I. As commander of the large Allied army based at Salonika, he conducted the successful Macedonian campaign, which...
Fernand Pelloutier
 8
Fernand Léonce Émile Pelloutier (1867–1901) was a French journalist, trade union organiser and anarcho-syndicalist theoretician. A revolutionary from an early age, after beginning a career in...
8
Fernand Léonce Émile Pelloutier (1867–1901) was a French journalist, trade union organiser and anarcho-syndicalist theoretician. A revolutionary from an early age, after beginning a career in...
Baptiste Marcet
 8
Baptiste Marcet est le fondateur de la Fédération nationale des mutilés du travail.
8
Baptiste Marcet est le fondateur de la Fédération nationale des mutilés du travail.
Alain Fournier
 8
Alain Fournier (1943–2000) was a computer graphics researcher and professor at the University of British Columbia.
8
Alain Fournier (1943–2000) was a computer graphics researcher and professor at the University of British Columbia.
Fernand Forest
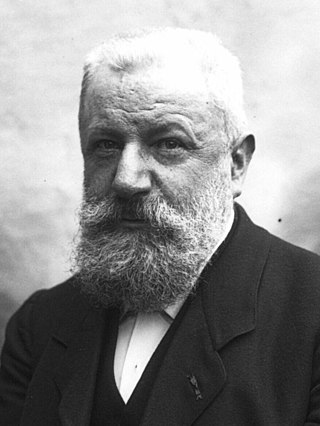 8
Pierre dit Fernand Forest est un inventeur français, né à Clermont-Ferrand le 13 octobre 1851 et mort à La Condamine (Monaco) le 12 avril 1914.
8
Pierre dit Fernand Forest est un inventeur français, né à Clermont-Ferrand le 13 octobre 1851 et mort à La Condamine (Monaco) le 12 avril 1914.
René Char
 8
René Émile Char was a French poet and member of the French Resistance.
8
René Émile Char was a French poet and member of the French Resistance.
Jean Vilar
 8
Jean Vilar was a French actor and theatre director.
8
Jean Vilar was a French actor and theatre director.
Olof Palme
 8
Sven Olof Joachim Palme was a Swedish politician and statesman who served as Prime Minister of Sweden from 1969 to 1976 and 1982 to 1986. Palme led the Swedish Social Democratic Party from 1969 until...
8
Sven Olof Joachim Palme was a Swedish politician and statesman who served as Prime Minister of Sweden from 1969 to 1976 and 1982 to 1986. Palme led the Swedish Social Democratic Party from 1969 until...
Paul Bourget
 8
Paul Charles Joseph Bourget was a French poet, novelist and critic. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature five times.
8
Paul Charles Joseph Bourget was a French poet, novelist and critic. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature five times.
Marcel Cerdan
 8
Marcellin "Marcel" Cerdan was a French professional boxer and world middleweight champion who was considered by many boxing experts and fans to be France's greatest boxer, and beyond to be one of the...
8
Marcellin "Marcel" Cerdan was a French professional boxer and world middleweight champion who was considered by many boxing experts and fans to be France's greatest boxer, and beyond to be one of the...
César Franck
 8
César-Auguste-Jean-Guillaume-Hubert Franck was a French Romantic composer, pianist, organist, and music teacher born in present-day Belgium.
8
César-Auguste-Jean-Guillaume-Hubert Franck was a French Romantic composer, pianist, organist, and music teacher born in present-day Belgium.
Angèle Vannier
 8
Angèle Vannier, née le 12 août 1917 à Saint-Servan, et morte le 2 décembre 1980 à Bazouges-la-Pérouse, est une poétesse française.
8
Angèle Vannier, née le 12 août 1917 à Saint-Servan, et morte le 2 décembre 1980 à Bazouges-la-Pérouse, est une poétesse française.
Claude Nougaro
 8
Claude Nougaro was a French jazz singer and poet.
8
Claude Nougaro was a French jazz singer and poet.
Winwaloe
 8
Winwaloe was the founder and first abbot of Landévennec Abbey, also known as the Monastery of Winwaloe. It was just south of Brest in Brittany, now part of France.
8
Winwaloe was the founder and first abbot of Landévennec Abbey, also known as the Monastery of Winwaloe. It was just south of Brest in Brittany, now part of France.
Marc Chagall
 8
Marc Chagall was a Russian-French artist. An early modernist, he was associated with the École de Paris as well as several major artistic styles and created works in a wide range of artistic formats,...
8
Marc Chagall was a Russian-French artist. An early modernist, he was associated with the École de Paris as well as several major artistic styles and created works in a wide range of artistic formats,...
Suzanne Lenglen
 8
Suzanne Rachel Flore Lenglen was a French tennis player. She was the inaugural world No. 1 from 1921 to 1926, winning eight Grand Slam titles in singles and twenty-one in total. She was also a...
8
Suzanne Rachel Flore Lenglen was a French tennis player. She was the inaugural world No. 1 from 1921 to 1926, winning eight Grand Slam titles in singles and twenty-one in total. She was also a...
Henri Étienne Sainte-Claire Deville
 8
Henri Étienne Sainte-Claire Deville was a French chemist.
8
Henri Étienne Sainte-Claire Deville was a French chemist.
Bartholomew Columbus
 8
Bartholomew Columbus was an Italian explorer from the Republic of Genoa and the younger brother of Christopher Columbus.
8
Bartholomew Columbus was an Italian explorer from the Republic of Genoa and the younger brother of Christopher Columbus.
Maurice Utrillo
 7
Maurice Utrillo, born Maurice Valadon; 26 December 1883 – 5 November 1955), was a French painter of the School of Paris who specialized in cityscapes. From the Montmartre quarter of Paris, France,...
7
Maurice Utrillo, born Maurice Valadon; 26 December 1883 – 5 November 1955), was a French painter of the School of Paris who specialized in cityscapes. From the Montmartre quarter of Paris, France,...
Jacques Tati
 7
Jacques Tati was a French mime, filmmaker, actor and screenwriter. In an Entertainment Weekly poll of the Greatest Movie Directors, he was voted the 46th greatest of all time, although he directed...
7
Jacques Tati was a French mime, filmmaker, actor and screenwriter. In an Entertainment Weekly poll of the Greatest Movie Directors, he was voted the 46th greatest of all time, although he directed...
Jules Paul Benjamin Delessert
 7
Jules Paul Benjamin Delessert was a French banker and naturalist. He was an honorary member of the Académie des Sciences and many species were named from his natural history collections.
7
Jules Paul Benjamin Delessert was a French banker and naturalist. He was an honorary member of the Académie des Sciences and many species were named from his natural history collections.
Étienne Marcel
 7
Étienne Marcel was provost of the merchants of Paris under King John II of France, called John the Good. He distinguished himself in the defence of the small craftsmen and guildsmen who made up most...
7
Étienne Marcel was provost of the merchants of Paris under King John II of France, called John the Good. He distinguished himself in the defence of the small craftsmen and guildsmen who made up most...
Queen Victoria
 7
Victoria was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days—which was longer than those of any of her...
7
Victoria was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days—which was longer than those of any of her...
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
 7
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon was a French socialist, politician, philosopher, and economist who founded mutualist philosophy and is considered by many to be the "father of anarchism". He was the first...
7
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon was a French socialist, politician, philosopher, and economist who founded mutualist philosophy and is considered by many to be the "father of anarchism". He was the first...
Saturnin
 7
Saturnin of Toulouse was one of the "Apostles to the Gauls" sent out during the consulate of Decius and Gratus (250–251) to Christianise Gaul after the persecutions under Emperor Decius had all but...
7
Saturnin of Toulouse was one of the "Apostles to the Gauls" sent out during the consulate of Decius and Gratus (250–251) to Christianise Gaul after the persecutions under Emperor Decius had all but...
Saint Alban
 7
Saint Alban is venerated as the first-recorded British Christian martyr, for which reason he is considered to be the British protomartyr. Along with fellow Saints Julius and Aaron, Alban is one of...
7
Saint Alban is venerated as the first-recorded British Christian martyr, for which reason he is considered to be the British protomartyr. Along with fellow Saints Julius and Aaron, Alban is one of...
Gioachino Rossini
 7
Gioachino Antonio Rossini was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces and some sacred music. He set new standards...
7
Gioachino Antonio Rossini was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces and some sacred music. He set new standards...
Henri Grégoire
 7
Henri Jean-Baptiste Grégoire, often referred to as the Abbé Grégoire, was a French Catholic priest, constitutional bishop of Blois and a revolutionary leader. He was an ardent slavery abolitionist...
7
Henri Jean-Baptiste Grégoire, often referred to as the Abbé Grégoire, was a French Catholic priest, constitutional bishop of Blois and a revolutionary leader. He was an ardent slavery abolitionist...
Emmanuel Brousse
 7
Emmanuel Brousse, né le 23 août 1866 à Perpignan (Pyrénées-Orientales) et mort le 17 novembre 1926 à Paris, est un imprimeur, journaliste et homme politique français, membre de l'Alliance...
7
Emmanuel Brousse, né le 23 août 1866 à Perpignan (Pyrénées-Orientales) et mort le 17 novembre 1926 à Paris, est un imprimeur, journaliste et homme politique français, membre de l'Alliance...
Eugénie de Montijo
 7
Doña María Eugenia Ignacia Agustina de Palafox y Kirkpatrick, 19th Countess of Teba, 16th Marquise of Ardales, known as Eugénie de Montijo, was Empress of the French from her marriage to Napoleon III...
7
Doña María Eugenia Ignacia Agustina de Palafox y Kirkpatrick, 19th Countess of Teba, 16th Marquise of Ardales, known as Eugénie de Montijo, was Empress of the French from her marriage to Napoleon III...
Joseph Roumanille
 7
Joseph Roumanille was a Provençal poet. He was born at Saint-Rémy-de-Provence (Bouches-du-Rhône), and is commonly known in southern France as the father of the Félibrige, for he first conceived the...
7
Joseph Roumanille was a Provençal poet. He was born at Saint-Rémy-de-Provence (Bouches-du-Rhône), and is commonly known in southern France as the father of the Félibrige, for he first conceived the...
Saint Brioc
 7
Brioc was a 5th-century Welsh holy man who became the first abbot of Saint-Brieuc in Brittany. He is one of the seven founder saints of Brittany.
7
Brioc was a 5th-century Welsh holy man who became the first abbot of Saint-Brieuc in Brittany. He is one of the seven founder saints of Brittany.
Michael Faraday
 7
Michael Faraday was a British scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction,...
7
Michael Faraday was a British scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction,...
Hippolytus of Rome
 7
Hippolytus of Rome was a Bishop of Rome and one of the most important second-third century Christian theologians, whose provenance, identity and corpus remain elusive to scholars and historians....
7
Hippolytus of Rome was a Bishop of Rome and one of the most important second-third century Christian theologians, whose provenance, identity and corpus remain elusive to scholars and historians....
Saint Dominic
 7
Saint Dominic,, also known as Dominic de Guzmán, was a Castilian Catholic priest and the founder of the Dominican Order. He is the patron saint of astronomers and natural scientists, and he and his...
7
Saint Dominic,, also known as Dominic de Guzmán, was a Castilian Catholic priest and the founder of the Dominican Order. He is the patron saint of astronomers and natural scientists, and he and his...
Giovanni Domenico Cassini
 7
Giovanni Domenico Cassini, also known as Jean-Dominique Cassini was an Italian mathematician, astronomer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the County of Nice,...
7
Giovanni Domenico Cassini, also known as Jean-Dominique Cassini was an Italian mathematician, astronomer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the County of Nice,...
Lucien Sampaix
 7
Lucien Sampaix est un journaliste communiste français, né à Sedan le 13 mai 1899 et otage fusillé par les nazis durant l'Occupation, à Caen, le 15 décembre 1941.
7
Lucien Sampaix est un journaliste communiste français, né à Sedan le 13 mai 1899 et otage fusillé par les nazis durant l'Occupation, à Caen, le 15 décembre 1941.
Edgar Faure
 7
Edgar Jean Faure was a French politician, lawyer, essayist, historian and memoirist who served as Prime Minister of France in 1952 and again between 1955 and 1956. Prior to his election to the...
7
Edgar Jean Faure was a French politician, lawyer, essayist, historian and memoirist who served as Prime Minister of France in 1952 and again between 1955 and 1956. Prior to his election to the...
Raymond Aron
 7
Raymond Claude Ferdinand Aron was a French philosopher, sociologist, political scientist, historian and journalist, one of France's most prominent thinkers of the 20th century.
7
Raymond Claude Ferdinand Aron was a French philosopher, sociologist, political scientist, historian and journalist, one of France's most prominent thinkers of the 20th century.
Victor Grignard
 7
Francois Auguste Victor Grignard was a French chemist who won the Nobel Prize for his discovery of the eponymously named Grignard reagent and Grignard reaction, both of which are important in the...
7
Francois Auguste Victor Grignard was a French chemist who won the Nobel Prize for his discovery of the eponymously named Grignard reagent and Grignard reaction, both of which are important in the...
Paul Sabatier
 7
Paul Sabatier may refer to:Paul Sabatier (chemist) (1854–1941), French chemist and Nobel Prize winner
Paul Sabatier (theologian) (1858–1928), French clergyman and historian
7
Paul Sabatier may refer to:Paul Sabatier (chemist) (1854–1941), French chemist and Nobel Prize winner
Paul Sabatier (theologian) (1858–1928), French clergyman and historian
Napoleon III
 7
Napoleon III was the first president of France from 1848 to 1852, and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 until he was deposed in absentia on 4 September 1870.
7
Napoleon III was the first president of France from 1848 to 1852, and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 until he was deposed in absentia on 4 September 1870.
Jean Renoir
 7
Jean Renoir was a French film director, screenwriter, actor, producer and author. As a film director and actor, he made more than forty films from the silent era to the end of the 1960s. His films La...
7
Jean Renoir was a French film director, screenwriter, actor, producer and author. As a film director and actor, he made more than forty films from the silent era to the end of the 1960s. His films La...
Michel Ney
 7
Michel Ney, 1st Prince de la Moskowa, 1st Duke of Elchingen was a French military commander and Marshal of the Empire who fought in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars.
7
Michel Ney, 1st Prince de la Moskowa, 1st Duke of Elchingen was a French military commander and Marshal of the Empire who fought in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars.
Maurice Barrès
 7
Auguste-Maurice Barrès was a French novelist, journalist, philosopher, and politician. Spending some time in Italy, he became a figure in French literature with the release of his work The Cult of...
7
Auguste-Maurice Barrès was a French novelist, journalist, philosopher, and politician. Spending some time in Italy, he became a figure in French literature with the release of his work The Cult of...
Charles Darwin
 7
Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a...
7
Charles Robert Darwin was an English naturalist, geologist and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a...
André Breton
 7
André Robert Breton was a French writer and poet, the co-founder, leader, and principal theorist of surrealism. His writings include the first Surrealist Manifesto of 1924, in which he defined...
7
André Robert Breton was a French writer and poet, the co-founder, leader, and principal theorist of surrealism. His writings include the first Surrealist Manifesto of 1924, in which he defined...
Élisée Reclus
 7
Jacques Élisée Reclus was a French geographer, writer and anarchist. He produced his 19-volume masterwork, La Nouvelle Géographie universelle, la terre et les hommes, over a period of nearly 20 years...
7
Jacques Élisée Reclus was a French geographer, writer and anarchist. He produced his 19-volume masterwork, La Nouvelle Géographie universelle, la terre et les hommes, over a period of nearly 20 years...
Charles Perrault
 7
Charles Perrault was a French author and member of the Académie Française. He laid the foundations for a new literary genre, the fairy tale, with his works derived from earlier folk tales, published...
7
Charles Perrault was a French author and member of the Académie Française. He laid the foundations for a new literary genre, the fairy tale, with his works derived from earlier folk tales, published...
Charles Fourier
 7
François Marie Charles Fourier was a French philosopher, an influential early socialist thinker, and one of the founders of utopian socialism. Some of his views, held to be radical in his lifetime,...
7
François Marie Charles Fourier was a French philosopher, an influential early socialist thinker, and one of the founders of utopian socialism. Some of his views, held to be radical in his lifetime,...
Saints Cosmas and Damian
 7
Cosmas and Damian were two Arab physicians and early Christian martyrs. They practised their profession in the seaport of Aegeae, then in the Roman province of Cilicia.
7
Cosmas and Damian were two Arab physicians and early Christian martyrs. They practised their profession in the seaport of Aegeae, then in the Roman province of Cilicia.
King Arthur
 7
King Arthur is a legendary king of Britain, a hero of English mythology, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
7
King Arthur is a legendary king of Britain, a hero of English mythology, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
Sophie Germain
 7
Marie-Sophie Germain was a French mathematician, physicist, and philosopher. Despite initial opposition from her parents and difficulties presented by society, she gained education from books in her...
7
Marie-Sophie Germain was a French mathematician, physicist, and philosopher. Despite initial opposition from her parents and difficulties presented by society, she gained education from books in her...
Guy Mollet
 7
Guy Alcide Mollet was a French politician. He led the socialist French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO) from 1946 to 1969 and was the French Prime Minister from 1956 to 1957.
7
Guy Alcide Mollet was a French politician. He led the socialist French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO) from 1946 to 1969 and was the French Prime Minister from 1956 to 1957.
Giuseppe Verdi
 7
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi was an Italian composer best known for his operas. He was born near Busseto to a provincial family of moderate means, receiving a musical education with the help of...
7
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi was an Italian composer best known for his operas. He was born near Busseto to a provincial family of moderate means, receiving a musical education with the help of...
Madeleine Brès
 7
Madeleine Alexandrine Brès, born Gebelin, was a French pediatrician and the first French woman to earn a medical degree in 1875, with a thesis on breastfeeding.
7
Madeleine Alexandrine Brès, born Gebelin, was a French pediatrician and the first French woman to earn a medical degree in 1875, with a thesis on breastfeeding.
Louise de Bettignies
 7
Louise Marie Jeanne Henriette de Bettignies was a French secret agent who spied on the Germans for the British during World War I using the pseudonym of Alice Dubois.
7
Louise Marie Jeanne Henriette de Bettignies was a French secret agent who spied on the Germans for the British during World War I using the pseudonym of Alice Dubois.
Pierre Landais
 7
Pierre Landais (1430–1485) was a Breton politician who became the principal adviser and chief minister to Francis II, Duke of Brittany. Francis left Landais in control of the affairs of the duchy,...
7
Pierre Landais (1430–1485) was a Breton politician who became the principal adviser and chief minister to Francis II, Duke of Brittany. Francis left Landais in control of the affairs of the duchy,...
Eugène Boudin
 7
Eugène Louis Boudin was one of the first French landscape painters to paint outdoors. Boudin was a marine painter, and expert in the rendering of all that goes upon the sea and along its shores. His...
7
Eugène Louis Boudin was one of the first French landscape painters to paint outdoors. Boudin was a marine painter, and expert in the rendering of all that goes upon the sea and along its shores. His...
Lancelot
 7
Lancelot du Lac, also written as Launcelot and other variants, is a character in some versions of Arthurian legend where he is typically depicted as King Arthur's close companion and one of the...
7
Lancelot du Lac, also written as Launcelot and other variants, is a character in some versions of Arthurian legend where he is typically depicted as King Arthur's close companion and one of the...
Françoise Sagan
 7
Françoise Sagan was a French playwright, novelist, and screenwriter. Sagan was known for works with strong romantic themes involving wealthy and disillusioned bourgeois characters. Her best-known...
7
Françoise Sagan was a French playwright, novelist, and screenwriter. Sagan was known for works with strong romantic themes involving wealthy and disillusioned bourgeois characters. Her best-known...
Léon Faye
 7
Léon Faye, né le 10 juin 1899 à Vergt (Dordogne) et mort le 30 janvier 1945 au camp de concentration de Sonnenburg à l'âge de 45 ans, est un officier français qui, pendant la Seconde Guerre mondiale,...
7
Léon Faye, né le 10 juin 1899 à Vergt (Dordogne) et mort le 30 janvier 1945 au camp de concentration de Sonnenburg à l'âge de 45 ans, est un officier français qui, pendant la Seconde Guerre mondiale,...
Alain Gerbault
 7
Alain Jacques Georges Marie Gerbault was a French sailor, writer and tennis champion, who made a circumnavigation of the world as a single-handed sailor. He eventually settled in the islands of south...
7
Alain Jacques Georges Marie Gerbault was a French sailor, writer and tennis champion, who made a circumnavigation of the world as a single-handed sailor. He eventually settled in the islands of south...
Zéphyrin Camélinat
 7
Zéphyrin Camélinat was a French politician, writer, communard, socialist and communist.
7
Zéphyrin Camélinat was a French politician, writer, communard, socialist and communist.
Jean de La Varende
 7
Jean de La Varende was a French writer. He wrote novels, short stories, biographies and monographs, in particular on the subject of Normandy. He initially tried to become a naval officer like his...
7
Jean de La Varende was a French writer. He wrote novels, short stories, biographies and monographs, in particular on the subject of Normandy. He initially tried to become a naval officer like his...
Marguerite Perey
 7
Marguerite Catherine Perey was a French physicist and a student of Marie Curie. In 1939, Perey discovered the element francium by purifying samples of lanthanum that contained actinium. In 1962, she...
7
Marguerite Catherine Perey was a French physicist and a student of Marie Curie. In 1939, Perey discovered the element francium by purifying samples of lanthanum that contained actinium. In 1962, she...
Charles Trenet
 7
Louis Charles Augustin Georges Trenet was a renowned French singer-songwriter who composed both the music and the lyrics to nearly 1,000 songs over a career that lasted more than 60 years. These...
7
Louis Charles Augustin Georges Trenet was a renowned French singer-songwriter who composed both the music and the lyrics to nearly 1,000 songs over a career that lasted more than 60 years. These...
Marco Polo
 7
Marco Polo was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in The Travels of Marco Polo, a book that...
7
Marco Polo was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in The Travels of Marco Polo, a book that...
Charles Delestraint
 7
Charles Delestraint was a French Army lieutenant general and member of the French Resistance during World War II. He also befriended Charles de Gaulle. Delestraint was killed by the Gestapo in 1945.
7
Charles Delestraint was a French Army lieutenant general and member of the French Resistance during World War II. He also befriended Charles de Gaulle. Delestraint was killed by the Gestapo in 1945.
Ettore Bugatti
 7
Ettore Arco Isidoro Bugatti was an Italian-French automobile designer and manufacturer. He is remembered as the founder and proprietor of the automobile manufacturing company Automobiles E. Bugatti,...
7
Ettore Arco Isidoro Bugatti was an Italian-French automobile designer and manufacturer. He is remembered as the founder and proprietor of the automobile manufacturing company Automobiles E. Bugatti,...
François Couperin
 7
François Couperin was a French Baroque composer, organist and harpsichordist. He was known as Couperin le Grand to distinguish him from other members of the musically talented Couperin family.
7
François Couperin was a French Baroque composer, organist and harpsichordist. He was known as Couperin le Grand to distinguish him from other members of the musically talented Couperin family.
Raimu
 7
Jules Auguste Muraire, whose stage name was Raimu, was a French actor. He is most famous for playing César in the 'Marseilles trilogy'.
7
Jules Auguste Muraire, whose stage name was Raimu, was a French actor. He is most famous for playing César in the 'Marseilles trilogy'.
Jules Mousseron
 7
Jules Mousseron, né le 1er janvier 1868 à Denain (Nord) où il est mort le 24 novembre 1943, est un poète français de langue picarde et mineur de fond à la Compagnie des mines d'Anzin. Il est...
7
Jules Mousseron, né le 1er janvier 1868 à Denain (Nord) où il est mort le 24 novembre 1943, est un poète français de langue picarde et mineur de fond à la Compagnie des mines d'Anzin. Il est...
Paul Signac
 6
Paul Victor Jules Signac was a French Neo-Impressionist painter who, with Georges Seurat, helped develop the artistic technique Pointillism.
6
Paul Victor Jules Signac was a French Neo-Impressionist painter who, with Georges Seurat, helped develop the artistic technique Pointillism.
François de Sales
 6
Saint François de Sales, né le 21 août 1567 au château de Sales près de Thorens-Glières en Savoie et mort le 28 décembre 1622 à Lyon, est un prélat savoyard. Nommé évêque de Genève en 1602, il ne put...
6
Saint François de Sales, né le 21 août 1567 au château de Sales près de Thorens-Glières en Savoie et mort le 28 décembre 1622 à Lyon, est un prélat savoyard. Nommé évêque de Genève en 1602, il ne put...
Jean Lurçat
 6
Jean Lurçat was a French artist noted for his role in the revival of contemporary tapestry.
6
Jean Lurçat was a French artist noted for his role in the revival of contemporary tapestry.
Guy Ropartz
 6
Joseph Guy Marie Ropartz was a French composer and conductor. His compositions included five symphonies, three violin sonatas, cello sonatas, six string quartets, a piano trio and string trio, stage...
6
Joseph Guy Marie Ropartz was a French composer and conductor. His compositions included five symphonies, three violin sonatas, cello sonatas, six string quartets, a piano trio and string trio, stage...
Émile Driant
 6
Émile Augustin Cyprien Driant was a French writer, politician, and army officer. He was the first high-ranking casualty of the Battle of Verdun during World War I.
6
Émile Augustin Cyprien Driant was a French writer, politician, and army officer. He was the first high-ranking casualty of the Battle of Verdun during World War I.
Jacques Cassard
 6
Jacques Cassard was a French naval officer and privateer.
6
Jacques Cassard was a French naval officer and privateer.
Louis Néel
 6
Louis Eugène Félix Néel was a French physicist born in Lyon who received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1970 for his studies of the magnetic properties of solids.
6
Louis Eugène Félix Néel was a French physicist born in Lyon who received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1970 for his studies of the magnetic properties of solids.
Martha
 6
Martha is a biblical figure described in the Gospels of Luke and John. Together with her siblings Lazarus and Mary of Bethany, she is described as living in the village of Bethany near Jerusalem. She...
6
Martha is a biblical figure described in the Gospels of Luke and John. Together with her siblings Lazarus and Mary of Bethany, she is described as living in the village of Bethany near Jerusalem. She...
Alexandre Ribot
 6
Alexandre-Félix-Joseph Ribot was a French politician, four times Prime Minister.
6
Alexandre-Félix-Joseph Ribot was a French politician, four times Prime Minister.
Willy Brandt
 6
Willy Brandt was a German politician and statesman who was leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) from 1964 to 1987 and served as the chancellor of West Germany from 1969 to 1974. He...
6
Willy Brandt was a German politician and statesman who was leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) from 1964 to 1987 and served as the chancellor of West Germany from 1969 to 1974. He...
Benoît Frachon
 6
Benoît Frachon was a French metalworker and trade union leader who was one of the leaders of the French Communist Party and of the French Resistance during World War II (1939–45). He was...
6
Benoît Frachon was a French metalworker and trade union leader who was one of the leaders of the French Communist Party and of the French Resistance during World War II (1939–45). He was...
Charles Floquet
 6
Charles Thomas Floquet was a French lawyer and statesman.
6
Charles Thomas Floquet was a French lawyer and statesman.
André Messager
 6
André Charles Prosper Messager was a French composer, organist, pianist and conductor. His compositions include eight ballets and thirty opéras comiques, opérettes and other stage works, among which...
6
André Charles Prosper Messager was a French composer, organist, pianist and conductor. His compositions include eight ballets and thirty opéras comiques, opérettes and other stage works, among which...
Michel-Joseph Maunoury
 6
Michel-Joseph Maunoury was a commander of French forces in the early days of World War I who was posthumously elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France.
6
Michel-Joseph Maunoury was a commander of French forces in the early days of World War I who was posthumously elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France.
Gérard de Nerval
 6
Gérard de Nerval, the pen name of the French writer, poet, and translator Gérard Labrunie, was a French essayist, poet, translator, and travel writer. He was a major figure during the era of French...
6
Gérard de Nerval, the pen name of the French writer, poet, and translator Gérard Labrunie, was a French essayist, poet, translator, and travel writer. He was a major figure during the era of French...
Ludovic Trarieux
 6
Jacques Ludovic Trarieux was a French Republican statesman, lawyer, prominent Dreyfusard, and pioneer of international human rights.
6
Jacques Ludovic Trarieux was a French Republican statesman, lawyer, prominent Dreyfusard, and pioneer of international human rights.
Caroline Aigle
 6
Commandant Caroline Aigle was a French aviator who achieved a historical first when, at the age of 25, she became the first woman fighter pilot in the French Air Force. Her promising military career...
6
Commandant Caroline Aigle was a French aviator who achieved a historical first when, at the age of 25, she became the first woman fighter pilot in the French Air Force. Her promising military career...
Little Sister Magdeleine of Jesus
 6
Madeleine Hutin, taking the name Little Sister Magdeleine of Jesus, founded a Roman Catholic community of religious sisters, the Little Sisters of Jesus, on 8 September 1939 in Touggourt, French...
6
Madeleine Hutin, taking the name Little Sister Magdeleine of Jesus, founded a Roman Catholic community of religious sisters, the Little Sisters of Jesus, on 8 September 1939 in Touggourt, French...
Vincent Scotto
 6
Vincent Scotto was a French composer.
6
Vincent Scotto was a French composer.
Charles Garnier (architect)
 6
Jean-Louis Charles Garnier was a French architect, perhaps best known as the architect of the Palais Garnier and the Opéra de Monte-Carlo.
6
Jean-Louis Charles Garnier was a French architect, perhaps best known as the architect of the Palais Garnier and the Opéra de Monte-Carlo.
Louis Daguerre
 6
Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre was a French artist and photographer, recognized for his invention of the eponymous daguerreotype process of photography. He became known as one of the fathers of...
6
Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre was a French artist and photographer, recognized for his invention of the eponymous daguerreotype process of photography. He became known as one of the fathers of...
George V
 6
George V was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
6
George V was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Henri-Jean Guillaume Martin
 6
Henri-Jean Guillaume "Henri" Martin was a French painter. Elected to the Académie des Beaux-Arts in 1917, he has been described as a prolific master whose work has touches of melancholy, dreaminess...
6
Henri-Jean Guillaume "Henri" Martin was a French painter. Elected to the Académie des Beaux-Arts in 1917, he has been described as a prolific master whose work has touches of melancholy, dreaminess...
René Clair
 6
René Clair, born René-Lucien Chomette, was a French filmmaker and writer. He first established his reputation in the 1920s as a director of silent films in which comedy was often mingled with...
6
René Clair, born René-Lucien Chomette, was a French filmmaker and writer. He first established his reputation in the 1920s as a director of silent films in which comedy was often mingled with...
Lino Ventura
 6
Angiolino Giuseppe Pasquale Ventura, known as Lino Ventura, was an Italian-born actor and philanthropist, who lived and worked for most of his life in France. He was considered one of the greatest...
6
Angiolino Giuseppe Pasquale Ventura, known as Lino Ventura, was an Italian-born actor and philanthropist, who lived and worked for most of his life in France. He was considered one of the greatest...
Marcel Carné
 6
Marcel Albert Carné was a French film director. A key figure in the poetic realism movement, Carné's best known films include Port of Shadows (1938), Le Jour Se Lève (1939), Les Visiteurs du Soir...
6
Marcel Albert Carné was a French film director. A key figure in the poetic realism movement, Carné's best known films include Port of Shadows (1938), Le Jour Se Lève (1939), Les Visiteurs du Soir...
Frédéric Joliot-Curie
 6
Jean Frédéric Joliot-Curie was a French physicist and husband of Irène Joliot-Curie, with whom he was jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1935 for their discovery of induced...
6
Jean Frédéric Joliot-Curie was a French physicist and husband of Irène Joliot-Curie, with whom he was jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1935 for their discovery of induced...
Robert Doisneau
 6
Robert Doisneau was a French photographer. From the 1930s, he photographed the streets of Paris. He was a champion of humanist photography and with Henri Cartier-Bresson a pioneer of photojournalism.
6
Robert Doisneau was a French photographer. From the 1930s, he photographed the streets of Paris. He was a champion of humanist photography and with Henri Cartier-Bresson a pioneer of photojournalism.
René Viviani
 6
Jean Raphaël Adrien René Viviani was a French politician of the Third Republic, who served as Prime Minister for the first year of World War I. He was born in Sidi Bel Abbès, in French Algeria. In...
6
Jean Raphaël Adrien René Viviani was a French politician of the Third Republic, who served as Prime Minister for the first year of World War I. He was born in Sidi Bel Abbès, in French Algeria. In...
Charles Michels
 6
Charles Michels was a trade unionist and communist militant. He was deputy of the 15th arrondissement in Paris. During the Second World War, Michels was one of the 48 hostages shot in Chateaubriant,...
6
Charles Michels was a trade unionist and communist militant. He was deputy of the 15th arrondissement in Paris. During the Second World War, Michels was one of the 48 hostages shot in Chateaubriant,...
Alexis de Tocqueville
 6
Alexis Charles Henri Clérel, comte de Tocqueville, usually known as just Tocqueville, was a French aristocrat, diplomat, sociologist, political scientist, political philosopher, and historian. He is...
6
Alexis Charles Henri Clérel, comte de Tocqueville, usually known as just Tocqueville, was a French aristocrat, diplomat, sociologist, political scientist, political philosopher, and historian. He is...
Bernard Moitessier
 6
Bernard Moitessier was a French sailor, most notable for his participation in the 1968 Sunday Times Golden Globe Race, the first non-stop, singlehanded, round the world yacht race. With the fastest...
6
Bernard Moitessier was a French sailor, most notable for his participation in the 1968 Sunday Times Golden Globe Race, the first non-stop, singlehanded, round the world yacht race. With the fastest...
Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot
 6
Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot, or simply Camille Corot, was a French landscape and portrait painter as well as a printmaker in etching. A pivotal figure in landscape painting, his vast output...
6
Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot, or simply Camille Corot, was a French landscape and portrait painter as well as a printmaker in etching. A pivotal figure in landscape painting, his vast output...
Georges Frêche
 6
Georges Frêche was a French politician. He served as President of the Languedoc-Roussillon Region from 2004 until his death: prior to that, he had been mayor of Montpellier for 27 years, and was also...
6
Georges Frêche was a French politician. He served as President of the Languedoc-Roussillon Region from 2004 until his death: prior to that, he had been mayor of Montpellier for 27 years, and was also...
Charles de Foucauld
 6
Charles Eugène de Foucauld de Pontbriand, PFJ was a French soldier, explorer, geographer, ethnographer, Catholic priest and hermit who lived among the Tuareg people in the Sahara in Algeria. He was...
6
Charles Eugène de Foucauld de Pontbriand, PFJ was a French soldier, explorer, geographer, ethnographer, Catholic priest and hermit who lived among the Tuareg people in the Sahara in Algeria. He was...
Jean Giraudoux
 6
Hippolyte Jean Giraudoux was a French novelist, essayist, diplomat and playwright. He is considered among the most important French dramatists of the period between World War I and World War II.
6
Hippolyte Jean Giraudoux was a French novelist, essayist, diplomat and playwright. He is considered among the most important French dramatists of the period between World War I and World War II.
Paul Sérusier
 6
Paul Sérusier was a French painter who was a pioneer of abstract art and an inspiration for the avant-garde Nabis movement, Synthetism and Cloisonnism.
6
Paul Sérusier was a French painter who was a pioneer of abstract art and an inspiration for the avant-garde Nabis movement, Synthetism and Cloisonnism.
Jean-François Le Gonidec
 6
Jean François Marie Le Gonidec de Kerdaniel was a Breton grammarian who codified the Breton language.
6
Jean François Marie Le Gonidec de Kerdaniel was a Breton grammarian who codified the Breton language.
Bernard Chochoy
 6
Bernard Chochoy, né le 14 août 1908 à Nielles-lès-Bléquin (Pas-de-Calais) et décédé le 23 avril 1981 à Versailles (Yvelines), est un homme politique français.
6
Bernard Chochoy, né le 14 août 1908 à Nielles-lès-Bléquin (Pas-de-Calais) et décédé le 23 avril 1981 à Versailles (Yvelines), est un homme politique français.
Jean-Henri Fabre
 6
Jean-Henri Casimir Fabre was a French naturalist, entomologist, and author known for the lively style of his popular books on the lives of insects.
6
Jean-Henri Casimir Fabre was a French naturalist, entomologist, and author known for the lively style of his popular books on the lives of insects.
Charles Tillon
 6
Charles Joseph Tillon was a French metal worker, Communist, trade union leader, politician and leader of the French Resistance during World War II (1939–45).
6
Charles Joseph Tillon was a French metal worker, Communist, trade union leader, politician and leader of the French Resistance during World War II (1939–45).
Francis Garnier
 6
Marie Joseph François Garnier was a French officer, inspector of Indigenous Affairs of Cochinchina and explorer. He eventually became mission leader of the Mekong Exploration Commission in 19th...
6
Marie Joseph François Garnier was a French officer, inspector of Indigenous Affairs of Cochinchina and explorer. He eventually became mission leader of the Mekong Exploration Commission in 19th...
Savinian and Potentian
 6
Saints Savinian and Potentian are martyrs commemorated as the patron saints and founders of the diocese of Sens, France. Savinian should not be confused with another early French martyr, Sabinian of...
6
Saints Savinian and Potentian are martyrs commemorated as the patron saints and founders of the diocese of Sens, France. Savinian should not be confused with another early French martyr, Sabinian of...
Marie Laurencin
 6
Marie Laurencin was a French painter and printmaker. She became an important figure in the Parisian avant-garde as a member of the Cubists associated with the Section d'Or.
6
Marie Laurencin was a French painter and printmaker. She became an important figure in the Parisian avant-garde as a member of the Cubists associated with the Section d'Or.
Henri Verneuil
 6
Henri Verneuil was a French-Armenian playwright and filmmaker, who made a successful career in France. He was nominated for Oscar and Palme d'Or awards, and won Locarno International Film Festival,...
6
Henri Verneuil was a French-Armenian playwright and filmmaker, who made a successful career in France. He was nominated for Oscar and Palme d'Or awards, and won Locarno International Film Festival,...
Lady of the Lake
 6
The Lady of the Lake is a name or a title used by several either fairy or fairy-like but human enchantresses in the Matter of Britain, the body of medieval literature and mythology associated with...
6
The Lady of the Lake is a name or a title used by several either fairy or fairy-like but human enchantresses in the Matter of Britain, the body of medieval literature and mythology associated with...
Adrienne Bolland
 6
Adrienne Bolland, born Boland, was a French test pilot. She was the first woman to fly over the Andes between Chile and Argentina. She was later described as "France's most accomplished female...
6
Adrienne Bolland, born Boland, was a French test pilot. She was the first woman to fly over the Andes between Chile and Argentina. She was later described as "France's most accomplished female...
Michel-Ange Duquesne de Menneville
 6
Michel-Ange Duquesne de Menneville, Marquis Duquesne was a French Governor General of New France. He was born in Toulon, France.
6
Michel-Ange Duquesne de Menneville, Marquis Duquesne was a French Governor General of New France. He was born in Toulon, France.
Brice of Tours
 6
Brice of Tours was a 5th-century Frankish bishop, the fourth Bishop of Tours, succeeding Martin of Tours in 397.
6
Brice of Tours was a 5th-century Frankish bishop, the fourth Bishop of Tours, succeeding Martin of Tours in 397.
Jean Yole
 6
Jean Yole, né Léopold Robert à Soullans (Vendée) le 7 septembre 1878 et mort à Vendrennes (Vendée) le 2 novembre 1956, est un écrivain et homme politique français, maire de Vendrennes et sénateur de...
6
Jean Yole, né Léopold Robert à Soullans (Vendée) le 7 septembre 1878 et mort à Vendrennes (Vendée) le 2 novembre 1956, est un écrivain et homme politique français, maire de Vendrennes et sénateur de...
Alfred Sauvy
 6
Alfred Sauvy was a demographer, anthropologist and historian of the French economy. Sauvy coined the term Third World in reference to countries that were unaligned with either the Western bloc or the...
6
Alfred Sauvy was a demographer, anthropologist and historian of the French economy. Sauvy coined the term Third World in reference to countries that were unaligned with either the Western bloc or the...
Annie Girardot
 6
Annie Suzanne Girardot was a French actress. She often played strong-willed, independent, hard-working, and often lonely women, imbuing her characters with an earthiness and reality that endeared her...
6
Annie Suzanne Girardot was a French actress. She often played strong-willed, independent, hard-working, and often lonely women, imbuing her characters with an earthiness and reality that endeared her...
Charles Bourseul
 6
Charles Bourseul was a pioneer in development of the "make and break" telephone about 20 years before Bell made a practical telephone.
6
Charles Bourseul was a pioneer in development of the "make and break" telephone about 20 years before Bell made a practical telephone.
Louise Lévêque de Vilmorin
 6
Marie Louise Lévêque de Vilmorin was a French novelist, poet and journalist. Vilmorin was best known as a writer of delicate but mordant tales, often set in aristocratic or artistic milieu.
6
Marie Louise Lévêque de Vilmorin was a French novelist, poet and journalist. Vilmorin was best known as a writer of delicate but mordant tales, often set in aristocratic or artistic milieu.
Théodore de Banville
 6
Théodore Faullain de Banville was a French poet and writer. His work was influential on the Symbolist movement in French literature in the late 19th century.
6
Théodore Faullain de Banville was a French poet and writer. His work was influential on the Symbolist movement in French literature in the late 19th century.
Jean Lannes
 6
Jean Lannes, 1st Duke of Montebello, Prince of Siewierz, was a French military commander and a Marshal of the Empire who served during both the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
6
Jean Lannes, 1st Duke of Montebello, Prince of Siewierz, was a French military commander and a Marshal of the Empire who served during both the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
Hector Malot
 5
Hector-Henri Malot was a French writer born in La Bouille, Seine-Maritime. He studied law in Rouen and Paris, but eventually literature became his passion. He worked as a dramatic critic for Lloyd...
5
Hector-Henri Malot was a French writer born in La Bouille, Seine-Maritime. He studied law in Rouen and Paris, but eventually literature became his passion. He worked as a dramatic critic for Lloyd...
Hospitaller Malta
 5
Hospitaller Malta, officially the Monastic State of the Order of Malta, and known within Maltese history as the Knights' Period, was a polity which existed between 1530 and 1798 when the...
5
Hospitaller Malta, officially the Monastic State of the Order of Malta, and known within Maltese history as the Knights' Period, was a polity which existed between 1530 and 1798 when the...
Charles Nicolle
 5
Charles Jules Henri Nicolle was a French bacteriologist who received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his identification of lice as the transmitter of epidemic typhus.
5
Charles Jules Henri Nicolle was a French bacteriologist who received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his identification of lice as the transmitter of epidemic typhus.
Charles Cros
 5
Charles Cros or Émile-Hortensius-Charles Cros was a French poet and inventor. He was born in Fabrezan, Aude.
5
Charles Cros or Émile-Hortensius-Charles Cros was a French poet and inventor. He was born in Fabrezan, Aude.
Michelangelo
 5
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni, known mononymously as Michelangelo, was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his...
5
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni, known mononymously as Michelangelo, was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his...
Noël Édouard, vicomte de Curières de Castelnau
 5
Noël Édouard, vicomte de Curières de Castelnau was a French army general, army group commander and Chief of Staff of the Armed Forces during the First World War. Elected deputy in 1919 and president...
5
Noël Édouard, vicomte de Curières de Castelnau was a French army general, army group commander and Chief of Staff of the Armed Forces during the First World War. Elected deputy in 1919 and president...
Henry Bordeaux
 5
Henry Bordeaux was a French writer and lawyer.
5
Henry Bordeaux was a French writer and lawyer.
Jules Simon
 5
Jules François Simon was a French statesman and philosopher, and one of the leaders of the Moderate Republicans in the Third French Republic.
5
Jules François Simon was a French statesman and philosopher, and one of the leaders of the Moderate Republicans in the Third French Republic.
Paul Héroult
 5
Paul (Louis-Toussaint) Héroult was a French scientist. He was one of the inventors of the Hall-Héroult process for smelting aluminium, and developed the first successful commercial electric arc...
5
Paul (Louis-Toussaint) Héroult was a French scientist. He was one of the inventors of the Hall-Héroult process for smelting aluminium, and developed the first successful commercial electric arc...
Federico García Lorca
 5
Federico del Sagrado Corazón de Jesús García Lorca, known as Federico García Lorca, was a Spanish poet, playwright, and theatre director. García Lorca achieved international recognition as an...
5
Federico del Sagrado Corazón de Jesús García Lorca, known as Federico García Lorca, was a Spanish poet, playwright, and theatre director. García Lorca achieved international recognition as an...
Charles Dullin
 5
Charles Dullin was a French actor, theater manager and director.
5
Charles Dullin was a French actor, theater manager and director.
Henri Wallon (psychologist)
 5
Henri Paul Hyacinthe Wallon was a French philosopher, psychologist, neuropsychiatrist, teacher, and politician. He was the grandson of the historian and statesman Henri-Alexandre Wallon.
5
Henri Paul Hyacinthe Wallon was a French philosopher, psychologist, neuropsychiatrist, teacher, and politician. He was the grandson of the historian and statesman Henri-Alexandre Wallon.
Stéphane Mallarmé
 5
Stéphane Mallarmé, pen name of Étienne Mallarmé, was a French poet and critic. He was a major French symbolist poet, and his work anticipated and inspired several revolutionary artistic schools of...
5
Stéphane Mallarmé, pen name of Étienne Mallarmé, was a French poet and critic. He was a major French symbolist poet, and his work anticipated and inspired several revolutionary artistic schools of...
Henri Moissan
 5
Ferdinand Frédéric Henri Moissan was a French chemist and pharmacist who won the 1906 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work in isolating fluorine from its compounds. Moissan was one of the original...
5
Ferdinand Frédéric Henri Moissan was a French chemist and pharmacist who won the 1906 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work in isolating fluorine from its compounds. Moissan was one of the original...
Gustave Toudouze
 5
Gustave Toudouze, né le 19 mai 1847 à Paris et mort le 2 juillet 1904 dans la même ville, est un romancier, auteur dramatique et journaliste français. Il est le père de l'écrivain Georges-Gustave...
5
Gustave Toudouze, né le 19 mai 1847 à Paris et mort le 2 juillet 1904 dans la même ville, est un romancier, auteur dramatique et journaliste français. Il est le père de l'écrivain Georges-Gustave...
Berty Albrecht
 5
Berty Albrecht was a French feminist and French Resistance martyr of the Second World War.
5
Berty Albrecht was a French feminist and French Resistance martyr of the Second World War.
Vasco da Gama
 5
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira, was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
5
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira, was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
Charles Gide
 5
Charles Gide was a French economist and historian of economic thought. He was a professor at the University of Bordeaux, at Montpellier, at Université de Paris and finally at Collège de France. His...
5
Charles Gide was a French economist and historian of economic thought. He was a professor at the University of Bordeaux, at Montpellier, at Université de Paris and finally at Collège de France. His...
Darius Milhaud
 5
Darius Milhaud was a French composer, conductor, and teacher. He was a member of Les Six—also known as The Group of Six—and one of the most prolific composers of the 20th century. His compositions...
5
Darius Milhaud was a French composer, conductor, and teacher. He was a member of Les Six—also known as The Group of Six—and one of the most prolific composers of the 20th century. His compositions...
Louis Lépine
 5
Louis Jean-Baptiste Lépine was a French lawyer, politician and administrator who was Governor General of Algeria and twice Préfet de Police with the Paris Police Prefecture from 1893 to 1897 and...
5
Louis Jean-Baptiste Lépine was a French lawyer, politician and administrator who was Governor General of Algeria and twice Préfet de Police with the Paris Police Prefecture from 1893 to 1897 and...
Charles Saint-Venant (1898-1953)
 5
Charles Louis Saint-Venant, né le 7 novembre 1898 à Lille (Nord) et mort le 14 avril 1953 dans la même ville, est un homme politique français.
5
Charles Louis Saint-Venant, né le 7 novembre 1898 à Lille (Nord) et mort le 14 avril 1953 dans la même ville, est un homme politique français.
Henri Ghesquière
 5
Henri Ghesquière, né le 28 août 1863 à Lille (Nord) et décédé le 1er septembre 1918 dans la même ville, est un homme politique français.
5
Henri Ghesquière, né le 28 août 1863 à Lille (Nord) et décédé le 1er septembre 1918 dans la même ville, est un homme politique français.
Isidore Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire
 5
Isidore Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire was a French zoologist and an authority on deviation from normal structure. In 1854 he coined the term éthologie (ethology).
5
Isidore Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire was a French zoologist and an authority on deviation from normal structure. In 1854 he coined the term éthologie (ethology).
Pierre-Paul Riquet
 5
Pierre-Paul Riquet, Baron de Bonrepos was the engineer and canal-builder responsible for the construction of the Canal du Midi.
5
Pierre-Paul Riquet, Baron de Bonrepos was the engineer and canal-builder responsible for the construction of the Canal du Midi.
Diego Brosset
 5
Diego Brosset, né le 3 octobre 1898 à Buenos Aires (Argentine) et mort le 20 novembre 1944 à Champagney (Haute-Saône), est un général de division français, compagnon de la Libération.
5
Diego Brosset, né le 3 octobre 1898 à Buenos Aires (Argentine) et mort le 20 novembre 1944 à Champagney (Haute-Saône), est un général de division français, compagnon de la Libération.
Alain Savary
 5
Alain Savary was a French Socialist politician, deputy to the National Assembly of France during the Fourth and Fifth Republic, chairman of the Socialist Party (PS) and a government minister in the...
5
Alain Savary was a French Socialist politician, deputy to the National Assembly of France during the Fourth and Fifth Republic, chairman of the Socialist Party (PS) and a government minister in the...
André Maurois
 5
André Maurois was a French author.
5
André Maurois was a French author.
Gaston Defferre
 5
Gaston Defferre was a French Socialist politician. He served as mayor of Marseille for 33 years until his death in 1986. He was minister for overseas territories in Guy Mollet’s socialist government...
5
Gaston Defferre was a French Socialist politician. He served as mayor of Marseille for 33 years until his death in 1986. He was minister for overseas territories in Guy Mollet’s socialist government...
Andrée Récipon
 5
Andrée Récipon, née le 8 mai 1885 à Paris 8e et morte le 1er mars 1956 à Laillé (Ille-et-Vilaine), est une résistante française.
5
Andrée Récipon, née le 8 mai 1885 à Paris 8e et morte le 1er mars 1956 à Laillé (Ille-et-Vilaine), est une résistante française.
Rembrandt
 5
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker, and draughtsman. He is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in the...
5
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker, and draughtsman. He is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in the...
Albert Londres
 5
Albert Londres was a French journalist and writer. One of the inventors of investigative journalism, Londres not only reported news but created it, and reported it from a personal perspective. He...
5
Albert Londres was a French journalist and writer. One of the inventors of investigative journalism, Londres not only reported news but created it, and reported it from a personal perspective. He...
Albert Samain
 5
Albert Victor Samain was a French poet and writer of the Symbolist school.
5
Albert Victor Samain was a French poet and writer of the Symbolist school.
Henri Pourrat
 5
The French writer and folklore collector Henri Pourrat was born in 1887 in Ambert, a town in the mountainous Auvergne region of central France. He died near Ambert in 1959.
5
The French writer and folklore collector Henri Pourrat was born in 1887 in Ambert, a town in the mountainous Auvergne region of central France. He died near Ambert in 1959.
Arthur Honegger
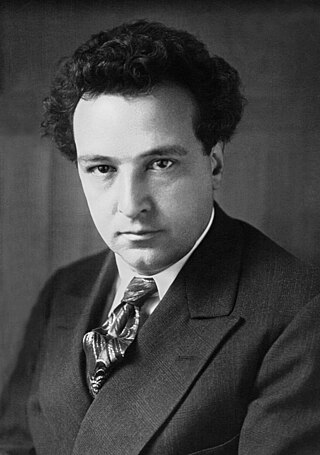 5
Arthur Honegger was a Swiss composer who was born in France and lived a large part of his life in Paris. A member of Les Six, his best known work is probably Antigone, composed between 1924 and 1927...
5
Arthur Honegger was a Swiss composer who was born in France and lived a large part of his life in Paris. A member of Les Six, his best known work is probably Antigone, composed between 1924 and 1927...
Vincent d'Indy
 5
Paul Marie Théodore Vincent d'Indy was a French composer and teacher. His influence as a teacher, in particular, was considerable. He was a co-founder of the Schola Cantorum de Paris and also taught...
5
Paul Marie Théodore Vincent d'Indy was a French composer and teacher. His influence as a teacher, in particular, was considerable. He was a co-founder of the Schola Cantorum de Paris and also taught...
Blaise Cendrars
 5
Frédéric-Louis Sauser, better known as Blaise Cendrars, was a Swiss-born novelist and poet who became a naturalized French citizen in 1916. He was a writer of considerable influence in the European...
5
Frédéric-Louis Sauser, better known as Blaise Cendrars, was a Swiss-born novelist and poet who became a naturalized French citizen in 1916. He was a writer of considerable influence in the European...
Albert Joly
 5
Albert Joly est un avocat et homme politique français né le 10 novembre 1844 à Versailles (Yvelines) et décédé le 4 décembre 1880 à Versailles.
5
Albert Joly est un avocat et homme politique français né le 10 novembre 1844 à Versailles (Yvelines) et décédé le 4 décembre 1880 à Versailles.
François Boucher
 5
François Boucher was a French painter, draughtsman and etcher, who worked in the Rococo style. Boucher is known for his idyllic and voluptuous paintings on classical themes, decorative allegories,...
5
François Boucher was a French painter, draughtsman and etcher, who worked in the Rococo style. Boucher is known for his idyllic and voluptuous paintings on classical themes, decorative allegories,...
Jean Marais
 5
Jean-Alfred Villain-Marais, known professionally as Jean Marais, was a French actor, film director, theatre director, painter, sculptor, visual artist, writer and photographer. He performed in over...
5
Jean-Alfred Villain-Marais, known professionally as Jean Marais, was a French actor, film director, theatre director, painter, sculptor, visual artist, writer and photographer. He performed in over...
Charles Dupuy
 5
Charles Alexandre Dupuy was a French statesman, three times prime minister.
5
Charles Alexandre Dupuy was a French statesman, three times prime minister.
Ernest Jacques Barbot
 5
Ernest Jacques Barbot, né le 19 août 1855 à Toulouse et mort le 10 mai 1915 Villers-Châtel, est un officier général français. C'est l'un des 42 généraux français morts au combat durant la Première...
5
Ernest Jacques Barbot, né le 19 août 1855 à Toulouse et mort le 10 mai 1915 Villers-Châtel, est un officier général français. C'est l'un des 42 généraux français morts au combat durant la Première...
Pierre Mauroy
 5
Pierre Mauroy was a French Socialist politician who was Prime Minister of France from 1981 to 1984 under President François Mitterrand. Mauroy also served as Mayor of Lille from 1973 to 2001. At the...
5
Pierre Mauroy was a French Socialist politician who was Prime Minister of France from 1981 to 1984 under President François Mitterrand. Mauroy also served as Mayor of Lille from 1973 to 2001. At the...
Albert Lebrun
 5
Albert François Lebrun was a French politician, President of France from 1932 to 1940. He was the last president of the Third Republic. He was a member of the centre-right Democratic Republican...
5
Albert François Lebrun was a French politician, President of France from 1932 to 1940. He was the last president of the Third Republic. He was a member of the centre-right Democratic Republican...
Ambrose
 5
Ambrose of Milan, venerated as Saint Ambrose, was a theologian and statesman who served as Bishop of Milan from 374 to 397. He expressed himself prominently as a public figure, fiercely promoting...
5
Ambrose of Milan, venerated as Saint Ambrose, was a theologian and statesman who served as Bishop of Milan from 374 to 397. He expressed himself prominently as a public figure, fiercely promoting...
Léopold Sédar Senghor
 5
Léopold Sédar Senghor was a Senegalese poet, politician, and cultural theorist who was the first president of Senegal (1960–1980).
5
Léopold Sédar Senghor was a Senegalese poet, politician, and cultural theorist who was the first president of Senegal (1960–1980).
Édouard Lalo
 5
Édouard-Victoire-Antoine Lalo was a French composer. His most celebrated piece is the Symphonie Espagnole, a five-movement concerto for violin and orchestra that remains a popular work in the...
5
Édouard-Victoire-Antoine Lalo was a French composer. His most celebrated piece is the Symphonie Espagnole, a five-movement concerto for violin and orchestra that remains a popular work in the...
Georges Bernanos
 5
Louis Émile Clément Georges Bernanos was a French author, and a soldier in World War I. A Catholic with monarchist leanings, he was critical of elitist thought and was opposed to what he identified...
5
Louis Émile Clément Georges Bernanos was a French author, and a soldier in World War I. A Catholic with monarchist leanings, he was critical of elitist thought and was opposed to what he identified...
René Bonpain
 5
René Bonpain, dit L'Abbé Bonpain, est un résistant et homme d'Église français né le 15 octobre 1908 à Dunkerque (Nord) et mort fusillé le 30 mars 1943 à Bondues (Nord). Il reste à ce jour le...
5
René Bonpain, dit L'Abbé Bonpain, est un résistant et homme d'Église français né le 15 octobre 1908 à Dunkerque (Nord) et mort fusillé le 30 mars 1943 à Bondues (Nord). Il reste à ce jour le...
David d'Angers
 5
Pierre-Jean David was a French sculptor, medalist and active freemason. He adopted the name David d'Angers, following his entry into the studio of the painter Jacques-Louis David in 1809 as a way of...
5
Pierre-Jean David was a French sculptor, medalist and active freemason. He adopted the name David d'Angers, following his entry into the studio of the painter Jacques-Louis David in 1809 as a way of...
Antoine Chanzy
 5
Antoine Eugène Alfred Chanzy was a French general, notable for his successes during the Franco-Prussian War and as a governor of Algeria.
5
Antoine Eugène Alfred Chanzy was a French general, notable for his successes during the Franco-Prussian War and as a governor of Algeria.
Henri Gouraud
 5
Henri Joseph Eugène Gouraud was a French general, best known for his leadership of the French Fourth Army at the end of the First World War. Following this, he became the first High Commissioner of...
5
Henri Joseph Eugène Gouraud was a French general, best known for his leadership of the French Fourth Army at the end of the First World War. Following this, he became the first High Commissioner of...
Julián Grimau
 5
Julián Grimau García was a Spanish politician, member of the Communist Party of Spain, executed during Francisco Franco's Francoist State.
5
Julián Grimau García was a Spanish politician, member of the Communist Party of Spain, executed during Francisco Franco's Francoist State.
André Theuriet
 5
Claude Adhémar André Theuriet was a 19th-century French poet and novelist.
5
Claude Adhémar André Theuriet was a 19th-century French poet and novelist.
Barthélemy Thimonnier
 5
Barthélemy Thimonnier was a French inventor, who is attributed with the invention of the first sewing machine that replicated sewing by hand. He was born in L'Arbresle, in Rhône in France.
5
Barthélemy Thimonnier was a French inventor, who is attributed with the invention of the first sewing machine that replicated sewing by hand. He was born in L'Arbresle, in Rhône in France.
Paul Le Flem
 5
Marie-Paul Achille Auguste Le Flem was a French composer and music critic.
5
Marie-Paul Achille Auguste Le Flem was a French composer and music critic.
Louis Vicat
 5
Louis Vicat was a French engineer.
5
Louis Vicat was a French engineer.
Émile Romanet
 5
Émile Romanet est un ingénieur français considéré comme un des précurseurs des caisses d'allocations familiales.
5
Émile Romanet est un ingénieur français considéré comme un des précurseurs des caisses d'allocations familiales.
Claude Nicolas Ledoux
 5
Claude-Nicolas Ledoux was one of the earliest exponents of French Neoclassical architecture. He used his knowledge of architectural theory to design not only domestic architecture but also town...
5
Claude-Nicolas Ledoux was one of the earliest exponents of French Neoclassical architecture. He used his knowledge of architectural theory to design not only domestic architecture but also town...
Suzanne Lanoy
 5
Suzanne Lanoy, née Suzanne Julie Blin le 8 juillet 1913 à Bully-en-Gohelle et morte sous la torture le 6 mars 1944 à Douai, est une enseignante et une résistante française.
5
Suzanne Lanoy, née Suzanne Julie Blin le 8 juillet 1913 à Bully-en-Gohelle et morte sous la torture le 6 mars 1944 à Douai, est une enseignante et une résistante française.
Richard Wagner
 5
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas. Unlike most opera composers, Wagner wrote both the libretto and the...
5
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas. Unlike most opera composers, Wagner wrote both the libretto and the...
Alexander Graham Bell
 5
Alexander Graham Bell was a Scottish-born Canadian-American inventor, scientist and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the American Telephone...
5
Alexander Graham Bell was a Scottish-born Canadian-American inventor, scientist and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the American Telephone...
Francis Jammes
 5
Francis Jammes was a French and European poet. He spent most of his life in his native region of Béarn and the Basque Country and his poems are known for their lyricism and for singing the pleasures...
5
Francis Jammes was a French and European poet. He spent most of his life in his native region of Béarn and the Basque Country and his poems are known for their lyricism and for singing the pleasures...
Henri Queffélec
 5
Henri Queffélec was a French writer and screenwriter.
5
Henri Queffélec was a French writer and screenwriter.
Gaston Ramon
 5
Gaston Ramon was a French veterinarian and biologist best known for his role in the treatment of diphtheria and tetanus.
5
Gaston Ramon was a French veterinarian and biologist best known for his role in the treatment of diphtheria and tetanus.
Roland Dorgelès
 5
Roland Dorgelès was a French novelist and a member of the Académie Goncourt.
5
Roland Dorgelès was a French novelist and a member of the Académie Goncourt.
Georges Duhamel
 5
Georges Duhamel was a French author, born in Paris. Duhamel trained as a doctor, and during World War I was attached to the French Army. In 1920, he published Confession de minuit, the first of a...
5
Georges Duhamel was a French author, born in Paris. Duhamel trained as a doctor, and during World War I was attached to the French Army. In 1920, he published Confession de minuit, the first of a...
Toussaint Louverture
 5
François-Dominique Toussaint Louverture also known as Toussaint L'Ouverture or Toussaint Bréda, was a Haitian general and the most prominent leader of the Haitian Revolution. During his life,...
5
François-Dominique Toussaint Louverture also known as Toussaint L'Ouverture or Toussaint Bréda, was a Haitian general and the most prominent leader of the Haitian Revolution. During his life,...
Jules Renard
 5
Pierre-Jules Renard was a French author and member of the Académie Goncourt, most famous for the works Poil de carotte and Les Histoires Naturelles. Among his other works are Le Plaisir de rompre and...
5
Pierre-Jules Renard was a French author and member of the Académie Goncourt, most famous for the works Poil de carotte and Les Histoires Naturelles. Among his other works are Le Plaisir de rompre and...
Léon Foucault
 5
Jean Bernard Léon Foucault was a French physicist best known for his demonstration of the Foucault pendulum, a device demonstrating the effect of Earth's rotation. He also made an early measurement...
5
Jean Bernard Léon Foucault was a French physicist best known for his demonstration of the Foucault pendulum, a device demonstrating the effect of Earth's rotation. He also made an early measurement...
Louis Hémon
 5
Louis Hémon, was a French writer, best known for his novel Maria Chapdelaine.
5
Louis Hémon, was a French writer, best known for his novel Maria Chapdelaine.
Haroun Tazieff
 5
Haroun Tazieff was a Franco-Belgian volcanologist and geologist. He was a famous cinematographer of volcanic eruptions and lava flows, and the author of several books on volcanoes. He was also a...
5
Haroun Tazieff was a Franco-Belgian volcanologist and geologist. He was a famous cinematographer of volcanic eruptions and lava flows, and the author of several books on volcanoes. He was also a...
Georges Cadoudal
 5
Georges Cadoudal, sometimes called simply Georges, was a Breton counter-revolutionary and leader of the Chouannerie during the French Revolution. He was posthumously named a Marshal of France in 1814...
5
Georges Cadoudal, sometimes called simply Georges, was a Breton counter-revolutionary and leader of the Chouannerie during the French Revolution. He was posthumously named a Marshal of France in 1814...
André Le Nôtre
 5
André Le Nôtre, originally rendered as André Le Nostre, was a French landscape architect and the principal gardener of King Louis XIV of France. He was the landscape architect who designed the...
5
André Le Nôtre, originally rendered as André Le Nostre, was a French landscape architect and the principal gardener of King Louis XIV of France. He was the landscape architect who designed the...
Serge Gainsbourg
 5
Serge Gainsbourg was a French singer-songwriter, actor, composer, and director. Regarded as one of the most important figures in French pop, he was renowned for often provocative releases which...
5
Serge Gainsbourg was a French singer-songwriter, actor, composer, and director. Regarded as one of the most important figures in French pop, he was renowned for often provocative releases which...
Django Reinhardt
 5
Jean Reinhardt, known by his Romani nickname Django, was a Romani-French jazz guitarist and composer. He was one of the first major jazz talents to emerge in Europe and has been hailed as one of its...
5
Jean Reinhardt, known by his Romani nickname Django, was a Romani-French jazz guitarist and composer. He was one of the first major jazz talents to emerge in Europe and has been hailed as one of its...
Francis Poulenc
 5
Francis Jean Marcel Poulenc was a French composer and pianist. His compositions include songs, solo piano works, chamber music, choral pieces, operas, ballets, and orchestral concert music. Among the...
5
Francis Jean Marcel Poulenc was a French composer and pianist. His compositions include songs, solo piano works, chamber music, choral pieces, operas, ballets, and orchestral concert music. Among the...
Roland Moreno
 5
Roland Moreno was a French inventor, engineer, humorist and author who was the inventor of the smart card. Moreno's smart card, or la carte à puce in French, was little known internationally....
5
Roland Moreno was a French inventor, engineer, humorist and author who was the inventor of the smart card. Moreno's smart card, or la carte à puce in French, was little known internationally....
Marcel Mérieux
 5
Marcel Mérieux, né le 16 janvier 1870 à Lyon et mort le 13 août 1937 à Collonges-au-Mont-d'Or, est un biochimiste français. Il est le fondateur de l'Institut Mérieux en 1897.
5
Marcel Mérieux, né le 16 janvier 1870 à Lyon et mort le 13 août 1937 à Collonges-au-Mont-d'Or, est un biochimiste français. Il est le fondateur de l'Institut Mérieux en 1897.
Maryse Hilsz
 5
Maryse Hilsz was a French aviator known for high altitude and endurance flights. She served with the French Resistance during World War II and died in an air crash in 1946.
5
Maryse Hilsz was a French aviator known for high altitude and endurance flights. She served with the French Resistance during World War II and died in an air crash in 1946.
Lionel Terray
 5
Lionel Terray was a French climber who made many first ascents, including on the 1955 French Makalu expedition in the Himalaya and Cerro Fitz Roy in the Patagonian Andes.
5
Lionel Terray was a French climber who made many first ascents, including on the 1955 French Makalu expedition in the Himalaya and Cerro Fitz Roy in the Patagonian Andes.
Charles Lindbergh
 5
Charles Augustus Lindbergh was an American aviator and military officer. On May 20–21, 1927, he made the first nonstop flight from New York City to Paris, a distance of 3,600 miles (5,800 km), flying...
5
Charles Augustus Lindbergh was an American aviator and military officer. On May 20–21, 1927, he made the first nonstop flight from New York City to Paris, a distance of 3,600 miles (5,800 km), flying...
Yves du Manoir
 5
Yves Frantz Loys Marie Le Pelley du Manoir, known as Yves du Manoir was a French rugby player.
5
Yves Frantz Loys Marie Le Pelley du Manoir, known as Yves du Manoir was a French rugby player.
Paul Ramadier
 5
Paul Ramadier was a French statesman.
5
Paul Ramadier was a French statesman.
Florence Arthaud
 5
Florence Arthaud, was a French sailor.
5
Florence Arthaud, was a French sailor.
James Watt
 5
James Watt was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was fundamental to the...
5
James Watt was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was fundamental to the...
Maxence Van der Meersch
 5
Maxence Van der Meersch was a French Flemish writer.
5
Maxence Van der Meersch was a French Flemish writer.
Franz Liszt
 5
Franz Liszt was a Hungarian composer, virtuoso pianist, conductor and teacher of the Romantic period. With a diverse body of work spanning more than six decades, he is considered to be one of the...
5
Franz Liszt was a Hungarian composer, virtuoso pianist, conductor and teacher of the Romantic period. With a diverse body of work spanning more than six decades, he is considered to be one of the...
Tony Garnier (architect)
 4
Tony Garnier was a noted French architect and city planner. He was most active in his home city of Lyon, where he notably designed the Halle Tony Garnier and Stade de Gerland. Garnier is considered...
4
Tony Garnier was a noted French architect and city planner. He was most active in his home city of Lyon, where he notably designed the Halle Tony Garnier and Stade de Gerland. Garnier is considered...
Armand Carrel
 4
Armand Carrel was a French journalist and political writer.
4
Armand Carrel was a French journalist and political writer.
Ferréol of Uzès
 4
Saint Ferréol (Ferreolus) of Uzès was bishop of Uzès and possibly bishop of Nîmes (553-581). His Feast Day is January 4.
4
Saint Ferréol (Ferreolus) of Uzès was bishop of Uzès and possibly bishop of Nîmes (553-581). His Feast Day is January 4.
Jules Uhry
 4
Jules Uhry est un homme politique français, né le 12 novembre 1877 à Constantine (Algérie) et décédé le 13 février 1936 à Neuilly-sur-Seine.
4
Jules Uhry est un homme politique français, né le 12 novembre 1877 à Constantine (Algérie) et décédé le 13 février 1936 à Neuilly-sur-Seine.
Pierre Lescot
 4
Pierre Lescot was a French architect active during the French Renaissance. His most notable works include the Fontaine des Innocents and the Lescot wing of the Louvre in Paris. He played an important...
4
Pierre Lescot was a French architect active during the French Renaissance. His most notable works include the Fontaine des Innocents and the Lescot wing of the Louvre in Paris. He played an important...
Michel Simon
 4
Michel Simon was a Swiss actor of German origin. He appeared in many notable French films, including La Chienne (1931), Boudu Saved from Drowning (1932), L'Atalante (1934), Port of Shadows (1938),...
4
Michel Simon was a Swiss actor of German origin. He appeared in many notable French films, including La Chienne (1931), Boudu Saved from Drowning (1932), L'Atalante (1934), Port of Shadows (1938),...
François Cuzin
 4
François Cuzin, né le 15 août 1914 à Dolomieu (Isère) et mort le 19 juillet 1944 à Signes (Var), est un enseignant et résistant français de la Seconde Guerre mondiale.
4
François Cuzin, né le 15 août 1914 à Dolomieu (Isère) et mort le 19 juillet 1944 à Signes (Var), est un enseignant et résistant français de la Seconde Guerre mondiale.
Morvan Lebesque
 4
Morvan Lebesque, was the Breton language name of Maurice Lebesque, a Breton nationalist activist and French journalist.
4
Morvan Lebesque, was the Breton language name of Maurice Lebesque, a Breton nationalist activist and French journalist.
Camille Jullian
 4
Camille Jullian was a French historian, philologist, archaeologist and historian of literature.
4
Camille Jullian was a French historian, philologist, archaeologist and historian of literature.
François Richard-Lenoir
 4
François Richard, dit Richard-Lenoir, né le 16 avril 1765 à Épinay-sur-Odon (France) et mort le 19 octobre 1839 à Paris, est un industriel manufacturier d’étoffe français qui devint l’un des...
4
François Richard, dit Richard-Lenoir, né le 16 avril 1765 à Épinay-sur-Odon (France) et mort le 19 octobre 1839 à Paris, est un industriel manufacturier d’étoffe français qui devint l’un des...
Frédéric Bastiat
 4
Claude-Frédéric Bastiat was a French economist, writer and a prominent member of the French Liberal School.
4
Claude-Frédéric Bastiat was a French economist, writer and a prominent member of the French Liberal School.
Jerome
 4
Jerome, also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian priest, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome.
4
Jerome, also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian priest, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome.
Camille Flammarion
 4
Nicolas Camille Flammarion FRAS was a French astronomer and author. He was a prolific author of more than fifty titles, including popular science works about astronomy, several notable early science...
4
Nicolas Camille Flammarion FRAS was a French astronomer and author. He was a prolific author of more than fifty titles, including popular science works about astronomy, several notable early science...
Neil Armstrong
 4
Neil Alden Armstrong was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer who in 1969 became the first person to walk on the Moon. He was also a naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor.
4
Neil Alden Armstrong was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer who in 1969 became the first person to walk on the Moon. He was also a naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor.
Daniel Balavoine
 4
Daniel Xavier-Marie Balavoine was a French singer and songwriter. He was hugely popular in the French-speaking world in the early 1980s; he inspired many singers of his generation such as...
4
Daniel Xavier-Marie Balavoine was a French singer and songwriter. He was hugely popular in the French-speaking world in the early 1980s; he inspired many singers of his generation such as...
Jules Sandeau
 4
Léonard Sylvain Julien (Jules) Sandeau was a French novelist.
4
Léonard Sylvain Julien (Jules) Sandeau was a French novelist.
François Coppée
 4
François Edouard Joachim Coppée was a French poet and novelist.
4
François Edouard Joachim Coppée was a French poet and novelist.
Edgar Allan Poe
 4
Edgar Allan Poe was an American writer, poet, author, editor, and literary critic who is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is widely...
4
Edgar Allan Poe was an American writer, poet, author, editor, and literary critic who is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is widely...
Jean Goujon
 4
Jean Goujon was a French Renaissance sculptor and architect.
4
Jean Goujon was a French Renaissance sculptor and architect.
Joseph Kessel
 4
Joseph Kessel, also known as "Jef", was a French journalist and novelist. He was a member of the Académie française and Grand Officer of the Legion of Honour.
4
Joseph Kessel, also known as "Jef", was a French journalist and novelist. He was a member of the Académie française and Grand Officer of the Legion of Honour.
Charlie Chaplin
 4
Sir Charles Spencer Chaplin was an English comic actor, filmmaker, and composer who rose to fame in the era of silent film. He became a worldwide icon through his screen persona, the Tramp, and is...
4
Sir Charles Spencer Chaplin was an English comic actor, filmmaker, and composer who rose to fame in the era of silent film. He became a worldwide icon through his screen persona, the Tramp, and is...
Caprasius of Agen
 4
Saint Caprasius of Agen is venerated as a Christian martyr and saint of the fourth century. Relics associated with him were discovered at Agen in the fifth century. Local legends dating from the 14th...
4
Saint Caprasius of Agen is venerated as a Christian martyr and saint of the fourth century. Relics associated with him were discovered at Agen in the fifth century. Local legends dating from the 14th...
François Joseph Lefebvre
 4
François Joseph Lefebvre, Duke of Danzig, was a French military commander of the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars, and one of the original eighteen Marshals of the Empire created by...
4
François Joseph Lefebvre, Duke of Danzig, was a French military commander of the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars, and one of the original eighteen Marshals of the Empire created by...
Abel Gance
 4
Abel Gance was a French film director, producer, writer and actor. A pioneer in the theory and practice of montage, he is best known for three major silent films: J'accuse (1919), La Roue (1923), and...
4
Abel Gance was a French film director, producer, writer and actor. A pioneer in the theory and practice of montage, he is best known for three major silent films: J'accuse (1919), La Roue (1923), and...
François Coli
Merlin
 4
Merlin is a mythical figure prominently featured in the legend of King Arthur and best known as a magician, with several other main roles. The familiar depiction of Merlin, based on an amalgamation...
4
Merlin is a mythical figure prominently featured in the legend of King Arthur and best known as a magician, with several other main roles. The familiar depiction of Merlin, based on an amalgamation...
Aristide Boucicaut
 4
Aristide Boucicaut was a French entrepreneur who created Le Bon Marché, the first modern department store.
4
Aristide Boucicaut was a French entrepreneur who created Le Bon Marché, the first modern department store.
Marie Louise, Duchess of Parma
 4
Marie Louise was an Austrian archduchess who reigned as Duchess of Parma from 11 April 1814 until her death in 1847. She was Napoleon's second wife and as such Empress of the French and Queen of...
4
Marie Louise was an Austrian archduchess who reigned as Duchess of Parma from 11 April 1814 until her death in 1847. She was Napoleon's second wife and as such Empress of the French and Queen of...
Jacques Cœur
 4
Jacques Cœur was a French government official and state-sponsored merchant whose personal fortune became legendary and led to his eventual disgrace. He initiated regular trade routes between France...
4
Jacques Cœur was a French government official and state-sponsored merchant whose personal fortune became legendary and led to his eventual disgrace. He initiated regular trade routes between France...
Pierre Gassendi
 4
Pierre Gassendi was a French philosopher, Catholic priest, astronomer, and mathematician. While he held a church position in south-east France, he also spent much time in Paris, where he was a leader...
4
Pierre Gassendi was a French philosopher, Catholic priest, astronomer, and mathematician. While he held a church position in south-east France, he also spent much time in Paris, where he was a leader...
Gaston Berger
 4
Gaston Berger was a French futurist but also an industrialist, a philosopher and a state manager. He is mainly known for his remarkably lucid analysis of Edmund Husserl's phenomenology and for his...
4
Gaston Berger was a French futurist but also an industrialist, a philosopher and a state manager. He is mainly known for his remarkably lucid analysis of Edmund Husserl's phenomenology and for his...
Claire Fontaine
 4
Claire Fontaine is a feminist, conceptual artist, founded in Paris in 2004 by Fulvia Carnevale and James Thornhill, an Italian-British artist duo who declared themselves her assistants. Since 2018...
4
Claire Fontaine is a feminist, conceptual artist, founded in Paris in 2004 by Fulvia Carnevale and James Thornhill, an Italian-British artist duo who declared themselves her assistants. Since 2018...
Charles Pathé
 4
Charles Morand Pathé was a pioneer of the French film and recording industries. As the founder of Pathé Frères, its roots lie in 1896 Paris, France, when Pathé and his brothers pioneered the...
4
Charles Morand Pathé was a pioneer of the French film and recording industries. As the founder of Pathé Frères, its roots lie in 1896 Paris, France, when Pathé and his brothers pioneered the...
Paul Déroulède
 4
Paul Déroulède was a French author and politician, one of the founders of the nationalist League of Patriots.
4
Paul Déroulède was a French author and politician, one of the founders of the nationalist League of Patriots.
Maximilien Robespierre
 4
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognized as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre...
4
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognized as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre...
Maurice Schumann
 4
Maurice Schumann was a French politician, journalist, writer, and hero of the Second World War who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs under Georges Pompidou from 22 June 1969 to 15 March 1973....
4
Maurice Schumann was a French politician, journalist, writer, and hero of the Second World War who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs under Georges Pompidou from 22 June 1969 to 15 March 1973....
Michael Trotobas
 4
Michael Alfred Raymond Trotobas, code named Sylvestre and known in France as Capitaine Michel, was an agent of the United Kingdom's clandestine Special Operations Executive (SOE) organization during...
4
Michael Alfred Raymond Trotobas, code named Sylvestre and known in France as Capitaine Michel, was an agent of the United Kingdom's clandestine Special Operations Executive (SOE) organization during...
Pierre Larousse
 4
Pierre Athanase Larousse was a French grammarian, lexicographer and encyclopaedist. He published many of the outstanding educational and reference works of 19th-century France, including the...
4
Pierre Athanase Larousse was a French grammarian, lexicographer and encyclopaedist. He published many of the outstanding educational and reference works of 19th-century France, including the...
Gabriel Lippmann
 4
Jonas Ferdinand Gabriel Lippmann was a Franco-Luxembourgish physicist and inventor, and Nobel laureate in physics for his method of reproducing colours photographically based on the phenomenon of...
4
Jonas Ferdinand Gabriel Lippmann was a Franco-Luxembourgish physicist and inventor, and Nobel laureate in physics for his method of reproducing colours photographically based on the phenomenon of...
Fernand David
 4
Fernand David was the French Minister of Agriculture from 21 January 1913 to 22 March 1913.
4
Fernand David was the French Minister of Agriculture from 21 January 1913 to 22 March 1913.
Victor Duruy
 4
Jean Victor Duruy was a French historian and statesman.
4
Jean Victor Duruy was a French historian and statesman.
Augustine of Hippo
 4
Augustine of Hippo, also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings influenced the...
4
Augustine of Hippo, also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings influenced the...
Théophile Roussel
 4
Jean-Baptiste Victor Théophile Roussel, né le 28 juillet 1816 à Saint-Chély-d'Apcher en Lozère, mort le 27 septembre 1903, au château d'Orfeuillette à Albaret-Sainte-Marie en Lozère, est un médecin,...
4
Jean-Baptiste Victor Théophile Roussel, né le 28 juillet 1816 à Saint-Chély-d'Apcher en Lozère, mort le 27 septembre 1903, au château d'Orfeuillette à Albaret-Sainte-Marie en Lozère, est un médecin,...
Jean Bouveri
 4
Jean Bouveri, né à Charolles en Saône-et-Loire le 18 juillet 1865 et mort le 3 juillet 1927 à Montceau-les-Mines, est un syndicaliste, député et sénateur français. Il est un des "pionniers" du...
4
Jean Bouveri, né à Charolles en Saône-et-Loire le 18 juillet 1865 et mort le 3 juillet 1927 à Montceau-les-Mines, est un syndicaliste, député et sénateur français. Il est un des "pionniers" du...
Abel Servien
 4
Abel Servien, marquis de Sablé et de Boisdauphin and Comte de La Roche des Aubiers was a French diplomat who served Cardinal Mazarin and signed for the French the Treaty of Westphalia. He was an...
4
Abel Servien, marquis de Sablé et de Boisdauphin and Comte de La Roche des Aubiers was a French diplomat who served Cardinal Mazarin and signed for the French the Treaty of Westphalia. He was an...
Nathalie Sarraute
 4
Nathalie Sarraute was a French writer and lawyer. She was nominated in 1969 for the Nobel Prize in Literature by Nobel Committee member Lars Gyllensten.
4
Nathalie Sarraute was a French writer and lawyer. She was nominated in 1969 for the Nobel Prize in Literature by Nobel Committee member Lars Gyllensten.
Alain Bombard
 4
Alain Bombard was a French biologist, physician and politician famous for sailing in a small boat across the Atlantic Ocean without provision. He theorized that a human being could very well survive...
4
Alain Bombard was a French biologist, physician and politician famous for sailing in a small boat across the Atlantic Ocean without provision. He theorized that a human being could very well survive...
Eugène Thomas
 4
Eugène Thomas was a French socialist teacher, trade unionist and politician.
He was a member of the French Resistance during World War II (1939–45).
He was Minister or Secretary of State for PTT...
4
Eugène Thomas was a French socialist teacher, trade unionist and politician.
He was a member of the French Resistance during World War II (1939–45).
He was Minister or Secretary of State for PTT...
Louis de Funès
 4
Louis Germain David de Funès de Galarza was a French actor and comedian. He is France's favourite actor, according to a series of polls conducted since the late 1960s, having played over 150 roles in...
4
Louis Germain David de Funès de Galarza was a French actor and comedian. He is France's favourite actor, according to a series of polls conducted since the late 1960s, having played over 150 roles in...
Jean Bertin
 4
Jean Henri Bertin was a French scientist, engineer and inventor. He was born in Druyes-les-Belles-Fontaines and died in Neuilly-sur-Seine. He is best known as the lead engineer for the French...
4
Jean Henri Bertin was a French scientist, engineer and inventor. He was born in Druyes-les-Belles-Fontaines and died in Neuilly-sur-Seine. He is best known as the lead engineer for the French...
Louis Delâge
 4
Louis Delâge was a French pioneer automotive engineer and manufacturer.
4
Louis Delâge was a French pioneer automotive engineer and manufacturer.
Jeanne Labourbe
 4
Jeanne Marie Labourbe was a French Bolshevik and activist who participated in the October Revolution. She died in 1919 in Odessa, executed by the police as ordered by the White Russians.
4
Jeanne Marie Labourbe was a French Bolshevik and activist who participated in the October Revolution. She died in 1919 in Odessa, executed by the police as ordered by the White Russians.
Benoît Malon
 4
Benoît Malon, was a French Socialist, writer, communard, and political leader.
4
Benoît Malon, was a French Socialist, writer, communard, and political leader.
Nathalie Lemel
 4
Nathalie Lemel, was a militant anarchist and feminist who participated on the barricades at the Commune de Paris of 1871. She was deported to Nouvelle Calédonie with Louise Michel.
4
Nathalie Lemel, was a militant anarchist and feminist who participated on the barricades at the Commune de Paris of 1871. She was deported to Nouvelle Calédonie with Louise Michel.
Joseph Bara
 4
François Joseph Bara, also written Barra, was a young French republican drummer boy at the time of the Revolution, and is known for his death and martyrdom at only 14 years old at the hands of...
4
François Joseph Bara, also written Barra, was a young French republican drummer boy at the time of the Revolution, and is known for his death and martyrdom at only 14 years old at the hands of...
Saint Martial
 4
Martial, called "the Apostle of the Gauls" or "the Apostle of Aquitaine", was the first bishop of Limoges. His feast day is 30 June.
4
Martial, called "the Apostle of the Gauls" or "the Apostle of Aquitaine", was the first bishop of Limoges. His feast day is 30 June.
Agatha of Sicily
 4
Agatha of Sicily is a Christian saint. Her feast is on 5 February. Agatha was born in Catania, part of the Roman Province of Sicily, and was martyred c. 251. She is one of several virgin martyrs who...
4
Agatha of Sicily is a Christian saint. Her feast is on 5 February. Agatha was born in Catania, part of the Roman Province of Sicily, and was martyred c. 251. She is one of several virgin martyrs who...
Michel Debré
 4
Michel Jean-Pierre Debré was the first Prime Minister of the French Fifth Republic. He is considered the "father" of the current Constitution of France. He served under President Charles de Gaulle...
4
Michel Jean-Pierre Debré was the first Prime Minister of the French Fifth Republic. He is considered the "father" of the current Constitution of France. He served under President Charles de Gaulle...
Lech Wałęsa
 4
Lech Wałęsa is a Polish statesman, dissident, and Nobel Peace Prize laureate, who served as the president of Poland between 1990 and 1995. After winning the 1990 election, Wałęsa became the first...
4
Lech Wałęsa is a Polish statesman, dissident, and Nobel Peace Prize laureate, who served as the president of Poland between 1990 and 1995. After winning the 1990 election, Wałęsa became the first...
Jean-Marie Tjibaou
 4
Jean-Marie Tjibaou was a French politician in New Caledonia and leader of the Kanak independence movement. The son of a tribal chief, Tjibaou was ordained a Catholic priest but abandoned his...
4
Jean-Marie Tjibaou was a French politician in New Caledonia and leader of the Kanak independence movement. The son of a tribal chief, Tjibaou was ordained a Catholic priest but abandoned his...
Henri Manhès
 4
Henri Manhès est un résistant français, compagnon de route du Parti communiste, né le 9 juin 1889 à Étampes et mort à Nice le 24 juin 1959.
4
Henri Manhès est un résistant français, compagnon de route du Parti communiste, né le 9 juin 1889 à Étampes et mort à Nice le 24 juin 1959.
Maturinus
 4
Maturinus, or Mathurin was a Gallo-Roman exorcist and missionary venerated as a saint.
4
Maturinus, or Mathurin was a Gallo-Roman exorcist and missionary venerated as a saint.
Clovis Hugues
 4
Clovis Hugues was a French poet, journalist, dramatist, novelist, and socialist activist. He wrote some of his works in Provençal and un 1898 was elected a majoral of the Félibrige, a society for the...
4
Clovis Hugues was a French poet, journalist, dramatist, novelist, and socialist activist. He wrote some of his works in Provençal and un 1898 was elected a majoral of the Félibrige, a society for the...
Élisabeth Boselli
 4
Élisabeth Thérèse Marie Juliette Boselli, was a French military and civilian pilot. She was the first female fighter pilot to serve in the French Air Force, and held eight world records for distance,...
4
Élisabeth Thérèse Marie Juliette Boselli, was a French military and civilian pilot. She was the first female fighter pilot to serve in the French Air Force, and held eight world records for distance,...
Jean Richepin
 4
Jean Richepin was a French poet, novelist and dramatist.
4
Jean Richepin was a French poet, novelist and dramatist.
Émile Bernard
 4
Émile Henri Bernard was a French Post-Impressionist painter and writer, who had artistic friendships with Vincent van Gogh, Paul Gauguin and Eugène Boch, and at a later time, Paul Cézanne. Most of...
4
Émile Henri Bernard was a French Post-Impressionist painter and writer, who had artistic friendships with Vincent van Gogh, Paul Gauguin and Eugène Boch, and at a later time, Paul Cézanne. Most of...
Charles-Michel de l'Épée
 4
Charles-Michel de l'Épée was a philanthropic educator of 18th-century France who has become known as the "Father of the Deaf".
4
Charles-Michel de l'Épée was a philanthropic educator of 18th-century France who has become known as the "Father of the Deaf".
Suzanne Valadon
 4
Suzanne Valadon was a French painter who was born Marie-Clémentine Valadon at Bessines-sur-Gartempe, Haute-Vienne, France. In 1894, Valadon became the first woman painter admitted to the Société...
4
Suzanne Valadon was a French painter who was born Marie-Clémentine Valadon at Bessines-sur-Gartempe, Haute-Vienne, France. In 1894, Valadon became the first woman painter admitted to the Société...
Dreyfus affair
 4
The Dreyfus affair was a political scandal that divided the Third French Republic from 1894 until its resolution in 1906. The scandal began in December 1894 when Captain Alfred Dreyfus, a 35-year-old...
4
The Dreyfus affair was a political scandal that divided the Third French Republic from 1894 until its resolution in 1906. The scandal began in December 1894 when Captain Alfred Dreyfus, a 35-year-old...
Francisco Goya
 4
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His paintings,...
4
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His paintings,...
Lou Martin
 4
Louis Michael Martin was a piano and organ player from Belfast, Northern Ireland. He was an original member of the London-based band Killing Floor, and also worked with fellow Irish musician Rory...
4
Louis Michael Martin was a piano and organ player from Belfast, Northern Ireland. He was an original member of the London-based band Killing Floor, and also worked with fellow Irish musician Rory...
Pierre Benoit (novelist)
 4
Pierre Benoit was a French novelist, screenwriter and member of the Académie française. He is perhaps best known for his second novel L'Atlantide (1919) that has been filmed several times.
4
Pierre Benoit was a French novelist, screenwriter and member of the Académie française. He is perhaps best known for his second novel L'Atlantide (1919) that has been filmed several times.
Marion du Faouët
 4
Marie-Louise Tromel, better known as Marion du Faouët or Marie Finefont, born on May 6, 1717, was the leader of a group of highwaymen who were active near Le Faouët, Morbihan, Brittany. She was...
4
Marie-Louise Tromel, better known as Marion du Faouët or Marie Finefont, born on May 6, 1717, was the leader of a group of highwaymen who were active near Le Faouët, Morbihan, Brittany. She was...
Tudwal
 4
Saint Tudwal, also known as Tual, Tudgual, Tugdual, Tugual, Pabu, Papu, or Tugdualus (Latin), was a Breton monk, considered to be one of the seven founder saints of Brittany.
4
Saint Tudwal, also known as Tual, Tudgual, Tugdual, Tugual, Pabu, Papu, or Tugdualus (Latin), was a Breton monk, considered to be one of the seven founder saints of Brittany.
Eugène de Mazenod
 4
Eugène de Mazenod, OMI was a French aristocrat and Catholic bishop. Mazenod founded the congregation of the Missionary Oblates of Mary Immaculate.
4
Eugène de Mazenod, OMI was a French aristocrat and Catholic bishop. Mazenod founded the congregation of the Missionary Oblates of Mary Immaculate.
René Goscinny
 4
René Goscinny was a French comic editor and writer, who created the Astérix comic book series with illustrator Albert Uderzo. He was raised primarily in Buenos Aires, Argentina, where he attended...
4
René Goscinny was a French comic editor and writer, who created the Astérix comic book series with illustrator Albert Uderzo. He was raised primarily in Buenos Aires, Argentina, where he attended...
René Bazin
 4
René François Nicolas Marie Bazin was a French novelist.
4
René François Nicolas Marie Bazin was a French novelist.
Andrei Sakharov
 4
Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov was a Soviet physicist and a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, which he was awarded in 1975 for emphasizing human rights around the world.
4
Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov was a Soviet physicist and a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, which he was awarded in 1975 for emphasizing human rights around the world.
Charles VII of France
 4
Charles VII, called the Victorious or the Well-Served, was King of France from 1422 to his death in 1461. His reign saw the end of the Hundred Years' War and a de facto end of the English claims to...
4
Charles VII, called the Victorious or the Well-Served, was King of France from 1422 to his death in 1461. His reign saw the end of the Hundred Years' War and a de facto end of the English claims to...
Octave Mirbeau
 4
Octave Mirbeau was a French novelist, art critic, travel writer, pamphleteer, journalist and playwright, who achieved celebrity in Europe and great success among the public, whilst still appealing to...
4
Octave Mirbeau was a French novelist, art critic, travel writer, pamphleteer, journalist and playwright, who achieved celebrity in Europe and great success among the public, whilst still appealing to...
Maximilien Sébastien Foy
 4
Maximilien Sébastien Foy was a French military leader, statesman and writer.
4
Maximilien Sébastien Foy was a French military leader, statesman and writer.
Michel Gérard
 4
Michel Gérard est un réalisateur français, né le 28 avril 1933 à Nancy (France).
4
Michel Gérard est un réalisateur français, né le 28 avril 1933 à Nancy (France).
Danielle Mitterrand
 4
Danielle Émilienne Isabelle Mitterrand was the wife of French President François Mitterrand, and president of the Fondation Danielle-Mitterrand - France Libertés.
4
Danielle Émilienne Isabelle Mitterrand was the wife of French President François Mitterrand, and president of the Fondation Danielle-Mitterrand - France Libertés.
Philibert of Jumièges
 4
Philibert of Jumièges was an abbot and monastic founder, particularly associated with Jumièges Abbey.
4
Philibert of Jumièges was an abbot and monastic founder, particularly associated with Jumièges Abbey.
Nina Simone
 4
Nina Simone was an American singer, songwriter, pianist, composer, arranger and civil rights activist. Her music spanned styles including classical, folk, gospel, blues, jazz, R&B, and pop. In 2023...
4
Nina Simone was an American singer, songwriter, pianist, composer, arranger and civil rights activist. Her music spanned styles including classical, folk, gospel, blues, jazz, R&B, and pop. In 2023...
Fernand Braudel
 4
Fernand Paul Achille Braudel was a French historian. His scholarship focused on three main projects: The Mediterranean, Civilization and Capitalism (1955–79), and the unfinished Identity of France...
4
Fernand Paul Achille Braudel was a French historian. His scholarship focused on three main projects: The Mediterranean, Civilization and Capitalism (1955–79), and the unfinished Identity of France...
Émile Souvestre
 4
Émile Souvestre was a Breton novelist who was a native of Morlaix, Brittany. Initially unsuccessful as a writer of drama, he fared better as a novelist and as a researcher and writer of Breton...
4
Émile Souvestre was a Breton novelist who was a native of Morlaix, Brittany. Initially unsuccessful as a writer of drama, he fared better as a novelist and as a researcher and writer of Breton...
Camille Pissarro
 4
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro was a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painter born on the island of St Thomas. His importance resides in his contributions to both Impressionism and...
4
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro was a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painter born on the island of St Thomas. His importance resides in his contributions to both Impressionism and...
Alcide De Gasperi
 4
Alcide Amedeo Francesco De Gasperi was an Italian politician who founded the Christian Democracy party and served as prime minister of Italy in eight successive coalition governments from 1945 to...
4
Alcide Amedeo Francesco De Gasperi was an Italian politician who founded the Christian Democracy party and served as prime minister of Italy in eight successive coalition governments from 1945 to...
Gustave Charpentier
 4
Gustave Charpentier was a French composer, best known for his opera Louise.
4
Gustave Charpentier was a French composer, best known for his opera Louise.
Jules Barbey d'Aurevilly
 4
Jules-Amédée Barbey d'Aurevilly was a French novelist, poet, short story writer, and literary critic. He specialised in mystery tales that explored hidden motivation and hinted at evil without being...
4
Jules-Amédée Barbey d'Aurevilly was a French novelist, poet, short story writer, and literary critic. He specialised in mystery tales that explored hidden motivation and hinted at evil without being...
Micheline Ostermeyer
 4
Micheline Ostermeyer was a French athlete and concert pianist. She won three medals at the 1948 Summer Olympics in shot put, discus throw, and high jump. After retiring from sports in 1950, she...
4
Micheline Ostermeyer was a French athlete and concert pianist. She won three medals at the 1948 Summer Olympics in shot put, discus throw, and high jump. After retiring from sports in 1950, she...
Philippe Séguin
 4
Philippe Séguin was a French political figure who was President of the National Assembly from 1993 to 1997 and President of the Cour des Comptes of France from 2004 to 2010.
4
Philippe Séguin was a French political figure who was President of the National Assembly from 1993 to 1997 and President of the Cour des Comptes of France from 2004 to 2010.
Henri Rol-Tanguy
 4
Henri Rol-Tanguy was a French communist and a leader in the Resistance during World War II. At his death The New York Times called him "one of France's most decorated Resistance heroes".
4
Henri Rol-Tanguy was a French communist and a leader in the Resistance during World War II. At his death The New York Times called him "one of France's most decorated Resistance heroes".
Charles Tellier
 4
Charles Tellier was a French engineer, born in Amiens. He early made a study of motors and compressed air. In 1868, he began experiments in refrigeration, which resulted ultimately in the...
4
Charles Tellier was a French engineer, born in Amiens. He early made a study of motors and compressed air. In 1868, he began experiments in refrigeration, which resulted ultimately in the...
Gaston III, Count of Foix
 4
Gaston III, known as Gaston Phoebus or Fébus, was the eleventh Count of Foix and twenty-fourth Viscount of Béarn from 1343 until his death.
4
Gaston III, known as Gaston Phoebus or Fébus, was the eleventh Count of Foix and twenty-fourth Viscount of Béarn from 1343 until his death.
François Cevert
 4
Albert François Cevert was a French racing driver who took part in the Formula One World Championship. He competed in 48 World Championship Grands Prix, achieving one win, 13 podium finishes and 89...
4
Albert François Cevert was a French racing driver who took part in the Formula One World Championship. He competed in 48 World Championship Grands Prix, achieving one win, 13 podium finishes and 89...
Albert Sorel
 4
Albert Sorel was a French historian. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature nine times.
4
Albert Sorel was a French historian. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature nine times.
Jean Prévost
 4
Jean Prévost was a French writer, journalist, and Resistance fighter.
4
Jean Prévost was a French writer, journalist, and Resistance fighter.
Henri Regnault
 4
Alexandre Georges Henri Regnault was a French painter.
4
Alexandre Georges Henri Regnault was a French painter.
Philippe Kieffer
 4
Philippe Kieffer, né le 24 octobre 1899 à Port-au-Prince (Haïti) et mort le 20 novembre 1962 à Cormeilles-en-Parisis, est un officier de marine français nommé compagnon de la Libération. Durant la...
4
Philippe Kieffer, né le 24 octobre 1899 à Port-au-Prince (Haïti) et mort le 20 novembre 1962 à Cormeilles-en-Parisis, est un officier de marine français nommé compagnon de la Libération. Durant la...
Aignan of Orleans
 4
Aignan or Agnan (358–453), seventh Bishop of Orléans, France, assisted Roman general Flavius Aetius in the defense of the city against Attila the Hun in 451. He is known as Saint Aignan.
4
Aignan or Agnan (358–453), seventh Bishop of Orléans, France, assisted Roman general Flavius Aetius in the defense of the city against Attila the Hun in 451. He is known as Saint Aignan.
François Billoux
 4
François Billoux was a French communist politician.
4
François Billoux was a French communist politician.
Michel Rondet (syndicaliste)
 4
Michel Rondet est un syndicaliste français né le 17 août 1841 au Chambon-Feugerolles et mort le 21 septembre 1908 à Pont de l’Enceinte à Grazac, vers Yssingeaux (Haute-Loire).
4
Michel Rondet est un syndicaliste français né le 17 août 1841 au Chambon-Feugerolles et mort le 21 septembre 1908 à Pont de l’Enceinte à Grazac, vers Yssingeaux (Haute-Loire).
Joseph Fontaine
 4
Joseph Louis-Rosario Fontaine was a Liberal party member of the House of Commons of Canada. He was born at Saint-Damase, Quebec. He was a master butcher, meat cutter, farmer and merchant by career.
4
Joseph Louis-Rosario Fontaine was a Liberal party member of the House of Commons of Canada. He was born at Saint-Damase, Quebec. He was a master butcher, meat cutter, farmer and merchant by career.
Alexis Maneyrol
 4
Alexis Maneyrol, né le 26 août 1891 à Frossay (Loire-Atlantique) et mort le 13 octobre 1923 à Lympne (Royaume-Uni), est l'un des pionniers français de l'aviation.
4
Alexis Maneyrol, né le 26 août 1891 à Frossay (Loire-Atlantique) et mort le 13 octobre 1923 à Lympne (Royaume-Uni), est l'un des pionniers français de l'aviation.
Romy Schneider
 4
Romy Schneider was a German-French actress. She is regarded as one of the greatest screen actresses of all time and became a cult figure due to her role as Empress Elisabeth of Austria in the Sissi...
4
Romy Schneider was a German-French actress. She is regarded as one of the greatest screen actresses of all time and became a cult figure due to her role as Empress Elisabeth of Austria in the Sissi...
François Jacob
 4
François Jacob was a French biologist who, together with Jacques Monod, originated the idea that control of enzyme levels in all cells occurs through regulation of transcription. He shared the 1965...
4
François Jacob was a French biologist who, together with Jacques Monod, originated the idea that control of enzyme levels in all cells occurs through regulation of transcription. He shared the 1965...
Maurice Rollinat
 4
Maurice Rollinat was a French poet and musician.
4
Maurice Rollinat was a French poet and musician.
Daniel Mayer
 4
Daniel Raphaël Mayer was a French politician and a member of the French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO) and president of the Ligue des droits de l'homme from 1958 to 1975. He founded the...
4
Daniel Raphaël Mayer was a French politician and a member of the French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO) and president of the Ligue des droits de l'homme from 1958 to 1975. He founded the...
Évariste Galois
 4
Évariste Galois was a French mathematician and political activist. While still in his teens, he was able to determine a necessary and sufficient condition for a polynomial to be solvable by radicals,...
4
Évariste Galois was a French mathematician and political activist. While still in his teens, he was able to determine a necessary and sufficient condition for a polynomial to be solvable by radicals,...
Jacques Chirac
 4
Jacques René Chirac was a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. He was previously Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and 1986 to 1988, as well as Mayor of...
4
Jacques René Chirac was a French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. He was previously Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and 1986 to 1988, as well as Mayor of...
Maurice de Vlaminck
 4
Maurice de Vlaminck was a French painter. Along with André Derain and Henri Matisse, he is considered one of the principal figures in the Fauve movement, a group of modern artists who from 1904 to...
4
Maurice de Vlaminck was a French painter. Along with André Derain and Henri Matisse, he is considered one of the principal figures in the Fauve movement, a group of modern artists who from 1904 to...
Charles Nodier
 4
Jean Charles Emmanuel Nodier was a French author and librarian who introduced a younger generation of Romanticists to the conte fantastique, gothic literature, and vampire tales. His dream related...
4
Jean Charles Emmanuel Nodier was a French author and librarian who introduced a younger generation of Romanticists to the conte fantastique, gothic literature, and vampire tales. His dream related...
André Pantigny
 4
André Pantigny est connu en tant que militant socialiste et résistant français de la Seconde Guerre mondiale ; il est né à Oignies dans le Pas-de-Calais, le 3 juin 1900, et mort le 4 décembre 1944 au...
4
André Pantigny est connu en tant que militant socialiste et résistant français de la Seconde Guerre mondiale ; il est né à Oignies dans le Pas-de-Calais, le 3 juin 1900, et mort le 4 décembre 1944 au...
René Fonck
 4
Colonel René Paul Fonck was a French aviator who ended the First World War as the top Entente fighter ace and, when all succeeding aerial conflicts of the 20th and 21st centuries are also considered,...
4
Colonel René Paul Fonck was a French aviator who ended the First World War as the top Entente fighter ace and, when all succeeding aerial conflicts of the 20th and 21st centuries are also considered,...
Pierre Bonnard
 4
Pierre Bonnard was a French painter, illustrator and printmaker, known especially for the stylized decorative qualities of his paintings and his bold use of color. A founding member of the...
4
Pierre Bonnard was a French painter, illustrator and printmaker, known especially for the stylized decorative qualities of his paintings and his bold use of color. A founding member of the...
Bourvil
 4
André Robert Raimbourg, better known as André Bourvil, and mononymously as Bourvil, was a French actor and singer best known for his roles in comedy films, most notably in his collaboration with...
4
André Robert Raimbourg, better known as André Bourvil, and mononymously as Bourvil, was a French actor and singer best known for his roles in comedy films, most notably in his collaboration with...
Auguste Delaune
 3
Auguste Delaune, né le 26 septembre 1908 à Graville-Sainte-Honorine, est un secrétaire général de la Fédération sportive et gymnique du travail. Membre du Parti communiste français, dirigeant...
3
Auguste Delaune, né le 26 septembre 1908 à Graville-Sainte-Honorine, est un secrétaire général de la Fédération sportive et gymnique du travail. Membre du Parti communiste français, dirigeant...
Pierre Leroux
 3
Pierre Henri Leroux was a French philosopher and political economist. He was born at Bercy, now a part of Paris, the son of an artisan.
3
Pierre Henri Leroux was a French philosopher and political economist. He was born at Bercy, now a part of Paris, the son of an artisan.
Juliette Récamier
 3
Jeanne Françoise Julie Adélaïde Récamier, known as Juliette, was a French socialite whose salon drew people from the leading literary and political circles of early 19th-century Paris. An icon of...
3
Jeanne Françoise Julie Adélaïde Récamier, known as Juliette, was a French socialite whose salon drew people from the leading literary and political circles of early 19th-century Paris. An icon of...
Alberto Giacometti
 3
Alberto Giacometti was a Swiss sculptor, painter, draftsman and printmaker. Beginning in 1922, he lived and worked mainly in Paris but regularly visited his hometown Borgonovo to see his family and...
3
Alberto Giacometti was a Swiss sculptor, painter, draftsman and printmaker. Beginning in 1922, he lived and worked mainly in Paris but regularly visited his hometown Borgonovo to see his family and...
Paul Demange (actor)
 3
Paul Demange was a French film actor who had roles in over 200 films from 1933 to 1977.
3
Paul Demange was a French film actor who had roles in over 200 films from 1933 to 1977.
Jean Froissart
 3
Jean Froissart was a French-speaking medieval author and court historian from the Low Countries who wrote several works, including Chronicles and Meliador, a long Arthurian romance, and a large body...
3
Jean Froissart was a French-speaking medieval author and court historian from the Low Countries who wrote several works, including Chronicles and Meliador, a long Arthurian romance, and a large body...
Victorien Sardou
 3
Victorien Sardou was a French dramatist. He is best remembered today for his development, along with Eugène Scribe, of the well-made play. He also wrote several plays that were made into popular...
3
Victorien Sardou was a French dramatist. He is best remembered today for his development, along with Eugène Scribe, of the well-made play. He also wrote several plays that were made into popular...
Déodat de Séverac
 3
Marie-Joseph Alexandre Déodat de Séverac was a French composer.
3
Marie-Joseph Alexandre Déodat de Séverac was a French composer.
Aristide Aubert du Petit-Thouars
 3
Aristide Aubert du Petit-Thouars was a French naval officer, and participant of the French defeat at the Battle of the Nile, where he was killed in action.
3
Aristide Aubert du Petit-Thouars was a French naval officer, and participant of the French defeat at the Battle of the Nile, where he was killed in action.
Émile Jamais
 3
Émile Jamais, né à Aigues-Vives dans le Gard le 10 décembre 1856 et mort dans la même ville le 10 novembre 1893, est un homme politique français.
3
Émile Jamais, né à Aigues-Vives dans le Gard le 10 décembre 1856 et mort dans la même ville le 10 novembre 1893, est un homme politique français.
Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza
 3
Pierre Paul François Camille Savorgnan de Brazza was an Italian-French explorer. With his family's financial help, he explored the Ogooué region of Central Africa, and later with the backing of the...
3
Pierre Paul François Camille Savorgnan de Brazza was an Italian-French explorer. With his family's financial help, he explored the Ogooué region of Central Africa, and later with the backing of the...
Peter Abelard
 3
Peter Abelard was a medieval French scholastic philosopher, leading logician, theologian, poet, composer and musician.
3
Peter Abelard was a medieval French scholastic philosopher, leading logician, theologian, poet, composer and musician.
Philippe de Girard
 3
Philippe Henri de Girard was a French engineer and inventor of the first flax spinning frame in 1810, and the person after whom the town of Żyrardów in Poland was named. He was also the uncredited...
3
Philippe Henri de Girard was a French engineer and inventor of the first flax spinning frame in 1810, and the person after whom the town of Żyrardów in Poland was named. He was also the uncredited...
Gabriel Voisin
 3
Gabriel Voisin was a French aviation pioneer and the creator of Europe's first manned, engine-powered, heavier-than-air aircraft capable of a sustained (1 km), circular, controlled flight, which was...
3
Gabriel Voisin was a French aviation pioneer and the creator of Europe's first manned, engine-powered, heavier-than-air aircraft capable of a sustained (1 km), circular, controlled flight, which was...
Henri Frenay
 3
Henri Frenay Sandoval was a French military officer and French Resistance member, who served as minister of prisoners, refugees and deportees in Charles de Gaulle's Provisional Government of the...
3
Henri Frenay Sandoval was a French military officer and French Resistance member, who served as minister of prisoners, refugees and deportees in Charles de Gaulle's Provisional Government of the...
Louis de Foix (ingénieur)
 3
Louis de Foix, né vers 1535 à Paris et mort vers 1604, est un horloger, ingénieur et architecte français.
3
Louis de Foix, né vers 1535 à Paris et mort vers 1604, est un horloger, ingénieur et architecte français.
Louis Tiercelin
 3
Louis Tiercelin, was a French writer, poet and playwright associated with the Breton cultural renaissance of the early 20th century.
3
Louis Tiercelin, was a French writer, poet and playwright associated with the Breton cultural renaissance of the early 20th century.
Bernard Délicieux
 3
Bernard Délicieux was a Spiritual Franciscan friar who resisted the Inquisition in Carcassonne and Languedoc region of southern France.
3
Bernard Délicieux was a Spiritual Franciscan friar who resisted the Inquisition in Carcassonne and Languedoc region of southern France.
Marie-Louis-Antoine-Gaston Boissier
 3
Marie-Louis-Antoine-Gaston Boissier, French classical scholar, and secretary of the Académie française, was born at Nîmes.
3
Marie-Louis-Antoine-Gaston Boissier, French classical scholar, and secretary of the Académie française, was born at Nîmes.
Jean-Baptiste Alphonse Karr
 3
Jean-Baptiste Alphonse Karr was a French critic, journalist, and novelist.
3
Jean-Baptiste Alphonse Karr was a French critic, journalist, and novelist.
Charles Grad
 3
Charles Grad, né le 8 décembre 1842 à Turckheim et mort le 3 juillet 1890 à Wintzenheim-Logelbach, est un homme politique catholique – député protestataire – et écrivain scientifique alsacien, auteur...
3
Charles Grad, né le 8 décembre 1842 à Turckheim et mort le 3 juillet 1890 à Wintzenheim-Logelbach, est un homme politique catholique – député protestataire – et écrivain scientifique alsacien, auteur...
Queen Mathilde of Belgium
 3
Mathilde is Queen of the Belgians as the wife of King Philippe. She is the first native-born Belgian queen. She has founded and assisted charities to decrease poverty in the country.
3
Mathilde is Queen of the Belgians as the wife of King Philippe. She is the first native-born Belgian queen. She has founded and assisted charities to decrease poverty in the country.
Nicolas Poussin
 3
Nicolas Poussin was a French painter who was a leading painter of the classical French Baroque style, although he spent most of his working life in Rome. Most of his works were on religious and...
3
Nicolas Poussin was a French painter who was a leading painter of the classical French Baroque style, although he spent most of his working life in Rome. Most of his works were on religious and...
Fermin
 3
Fermin was a legendary holy man and martyr, traditionally venerated as the co-patron saint of Navarre, Spain. His death may be associated with either the Decian persecution (250) or Diocletianic...
3
Fermin was a legendary holy man and martyr, traditionally venerated as the co-patron saint of Navarre, Spain. His death may be associated with either the Decian persecution (250) or Diocletianic...
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
 3
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel was a German philosopher and one of the most influential figures of German idealism and 19th-century philosophy. His influence extends across the entire range of...
3
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel was a German philosopher and one of the most influential figures of German idealism and 19th-century philosophy. His influence extends across the entire range of...
Olivier Messiaen
 3
Olivier Eugène Prosper Charles Messiaen was a French composer, organist, and ornithologist who was one of the major composers of the 20th century. His music is rhythmically complex. Harmonically and...
3
Olivier Eugène Prosper Charles Messiaen was a French composer, organist, and ornithologist who was one of the major composers of the 20th century. His music is rhythmically complex. Harmonically and...
Nicolas Leblanc
 3
Nicolas Leblanc was a French chemist and surgeon who discovered how to manufacture soda ash from common salt.
3
Nicolas Leblanc was a French chemist and surgeon who discovered how to manufacture soda ash from common salt.
Ambroise Thomas
 3
Charles Louis Ambroise Thomas was a French composer and teacher, best known for his operas Mignon (1866) and Hamlet (1868).
3
Charles Louis Ambroise Thomas was a French composer and teacher, best known for his operas Mignon (1866) and Hamlet (1868).
René Schmitt
 3
René Jean Schmitt est un homme politique français, né le 17 mars 1907 à Cormeilles (Eure) et mort le 14 mars 1968 à Équeurdreville-Hainneville (Manche).
3
René Jean Schmitt est un homme politique français, né le 17 mars 1907 à Cormeilles (Eure) et mort le 14 mars 1968 à Équeurdreville-Hainneville (Manche).
Commandant Dumont
 3
Paul Héraud, né le 25 mai 1906 à Saint-Victor-la-Coste (Gard) et mort le 9 août 1944 à Tallard, est un résistant français, Compagnon de la Libération à titre posthume par décret du 19 octobre 1945.
3
Paul Héraud, né le 25 mai 1906 à Saint-Victor-la-Coste (Gard) et mort le 9 août 1944 à Tallard, est un résistant français, Compagnon de la Libération à titre posthume par décret du 19 octobre 1945.
Joseph d'Arbaud
 3
Joseph d'Arbaud was a French poet and writer from Provence. He was a leading figure in the Provençal Revival, a literary movement of the nineteenth century.
3
Joseph d'Arbaud was a French poet and writer from Provence. He was a leading figure in the Provençal Revival, a literary movement of the nineteenth century.
Clémence Isaure
 3
Clémence Isaure is a quasi-legendary Occitan medieval figure credited with founding or restoring the Acadèmia dels Jòcs Florals or Academy of the Floral Games. She is supposed to have left a legacy...
3
Clémence Isaure is a quasi-legendary Occitan medieval figure credited with founding or restoring the Acadèmia dels Jòcs Florals or Academy of the Floral Games. She is supposed to have left a legacy...
Robert of Arbrissel
 3
Robert of Arbrissel was an itinerant preacher, and founder of Fontevraud Abbey. He was born at Arbrissel and died at Orsan Priory in the present department of Cher.
3
Robert of Arbrissel was an itinerant preacher, and founder of Fontevraud Abbey. He was born at Arbrissel and died at Orsan Priory in the present department of Cher.
Agrippa d'Aubigné
 3
Théodore-Agrippa d'Aubigné was a French poet, soldier, propagandist and chronicler. His epic poem Les Tragiques (1616) is widely regarded as his masterpiece. In a book about his Catholic contemporary...
3
Théodore-Agrippa d'Aubigné was a French poet, soldier, propagandist and chronicler. His epic poem Les Tragiques (1616) is widely regarded as his masterpiece. In a book about his Catholic contemporary...
Quiteria
 3
Quiteria was a second-century virgin martyr and saint about whom nothing is certain except her name and her cult. She appears in the Roman Martyrology, but not in any other ancient calendars.
3
Quiteria was a second-century virgin martyr and saint about whom nothing is certain except her name and her cult. She appears in the Roman Martyrology, but not in any other ancient calendars.
Dante Alighieri
 3
Dante Alighieri, most likely baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante, was an Italian poet, writer, and philosopher. His Divine Comedy, originally called Comedìa...
3
Dante Alighieri, most likely baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante, was an Italian poet, writer, and philosopher. His Divine Comedy, originally called Comedìa...
Zénaïde Fleuriot
 3
Zénaïde-Marie-Anne Fleuriot, was a French novelist. She wrote eighty three novels, all aimed at young women, most of which were published in the series Bibliothèque rose and Bibliothèque bleue. Her...
3
Zénaïde-Marie-Anne Fleuriot, was a French novelist. She wrote eighty three novels, all aimed at young women, most of which were published in the series Bibliothèque rose and Bibliothèque bleue. Her...
Albert Caquot
 3
Albert Irénée Caquot was a French engineer. He received the “Croix de Guerre 1914–1918 (France)” and was Grand-croix of the Légion d’Honneur (1951). In 1962, he was awarded the Wilhelm Exner Medal....
3
Albert Irénée Caquot was a French engineer. He received the “Croix de Guerre 1914–1918 (France)” and was Grand-croix of the Légion d’Honneur (1951). In 1962, he was awarded the Wilhelm Exner Medal....
Sylvain Eugène Raynal
 3
Sylvain Eugène Raynal was a French military officer.
3
Sylvain Eugène Raynal was a French military officer.
Guillaume Fichet
 3
Guillaume Fichet was a French scholar, who cooperated with Johann Heynlin to establish the first printing press in France (Paris) in 1470.
3
Guillaume Fichet was a French scholar, who cooperated with Johann Heynlin to establish the first printing press in France (Paris) in 1470.
Agnès Sorel
 3
Agnès Sorel, known by the sobriquet Dame de beauté, was a favourite and chief mistress of King Charles VII of France, by whom she bore four daughters. She is considered the first officially...
3
Agnès Sorel, known by the sobriquet Dame de beauté, was a favourite and chief mistress of King Charles VII of France, by whom she bore four daughters. She is considered the first officially...
Anna Politkovskaya
 3
Anna Stepanovna Politkovskaya was an American-Russian journalist and human rights activist, who reported on political and social events in Russia, in particular, the Second Chechen War (1999–2005).
3
Anna Stepanovna Politkovskaya was an American-Russian journalist and human rights activist, who reported on political and social events in Russia, in particular, the Second Chechen War (1999–2005).
Philip the Apostle
 3
Philip the Apostle was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Later Christian traditions describe Philip as the apostle who preached in Greece, Syria, and Asia-Minor.
3
Philip the Apostle was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. Later Christian traditions describe Philip as the apostle who preached in Greece, Syria, and Asia-Minor.
Jean Wiener
 3
Jean Wiener was a French pianist and composer.
3
Jean Wiener was a French pianist and composer.
Marcel Brindejonc des Moulinais
 3
Marcel-Georges Brindejonc des Moulinais was a French aviator best known for long-distance flights, including crossing the Baltic Sea. He also flew as an exhibition and racing pilot. He flew...
3
Marcel-Georges Brindejonc des Moulinais was a French aviator best known for long-distance flights, including crossing the Baltic Sea. He also flew as an exhibition and racing pilot. He flew...
François Rude
 3
François Rude was a French sculptor, best known for the Departure of the Volunteers, also known as La Marseillaise on the Arc de Triomphe in Paris. (1835–36). His work often expressed patriotic...
3
François Rude was a French sculptor, best known for the Departure of the Volunteers, also known as La Marseillaise on the Arc de Triomphe in Paris. (1835–36). His work often expressed patriotic...
Alberto Santos-Dumont
 3
Alberto Santos-Dumont, self-stylized as Alberto Santos=Dumont, was a Brazilian aeronaut, sportsman, inventor, and one of the few people to have contributed significantly to the early development of...
3
Alberto Santos-Dumont, self-stylized as Alberto Santos=Dumont, was a Brazilian aeronaut, sportsman, inventor, and one of the few people to have contributed significantly to the early development of...
Étienne Billières
 3
Étienne Billières, né le 21 mars 1876 à Toulouse (Haute-Garonne) et mort le 3 février 1935 à Alger, est un homme politique français. Il est élu maire socialiste de Toulouse en 1925, fonction qu'il...
3
Étienne Billières, né le 21 mars 1876 à Toulouse (Haute-Garonne) et mort le 3 février 1935 à Alger, est un homme politique français. Il est élu maire socialiste de Toulouse en 1925, fonction qu'il...
Alexandre Cabanel
 3
Alexandre Cabanel was a French painter. He painted historical, classical and religious subjects in the academic style. He was also well known as a portrait painter. According to Diccionario...
3
Alexandre Cabanel was a French painter. He painted historical, classical and religious subjects in the academic style. He was also well known as a portrait painter. According to Diccionario...
Pierre Lefaucheux
 3
Pierre-André Lefaucheux was a leading French industrialist and recipient of the Order of Liberation, awarded to heroes of France's Liberation during World War II.
3
Pierre-André Lefaucheux was a leading French industrialist and recipient of the Order of Liberation, awarded to heroes of France's Liberation during World War II.
Poniatowski
 3
The House of Poniatowski is a prominent Polish family that was part of the nobility of Poland. A member of this family, Stanisław Poniatowski, was elected as King of Poland and reigned from 1764...
3
The House of Poniatowski is a prominent Polish family that was part of the nobility of Poland. A member of this family, Stanisław Poniatowski, was elected as King of Poland and reigned from 1764...
Claude Farrère
 3
Claude Farrère, pseudonym of Frédéric-Charles Bargone, was a French Navy officer and writer. Many of his novels are based in exotic locations such as Istanbul, Saigon, or Nagasaki.
3
Claude Farrère, pseudonym of Frédéric-Charles Bargone, was a French Navy officer and writer. Many of his novels are based in exotic locations such as Istanbul, Saigon, or Nagasaki.
Valentin Haüy
 3
Valentin Haüy was the founder, in 1785, of the first school for the blind, the Institute for Blind Youth in Paris. In 1819, Louis Braille entered this school.
3
Valentin Haüy was the founder, in 1785, of the first school for the blind, the Institute for Blind Youth in Paris. In 1819, Louis Braille entered this school.
Sacha Guitry
 3
Alexandre-Pierre Georges "Sacha" Guitry was a French stage actor, film actor, director, screenwriter, and playwright of the boulevard theatre. He was the son of a leading French actor, Lucien Guitry,...
3
Alexandre-Pierre Georges "Sacha" Guitry was a French stage actor, film actor, director, screenwriter, and playwright of the boulevard theatre. He was the son of a leading French actor, Lucien Guitry,...
Gaston Doumergue
 3
Pierre Paul Henri Gaston Doumergue was a French politician of the Third Republic. He served as President of France from 1924 to 1931, succeeding Alexandre Millerand, who had resigned.
3
Pierre Paul Henri Gaston Doumergue was a French politician of the Third Republic. He served as President of France from 1924 to 1931, succeeding Alexandre Millerand, who had resigned.
Fabre d'Églantine
 3
Philippe François Nazaire Fabre d'Églantine, commonly known as Fabre d'Églantine, was a French actor, dramatist, poet, and politician of the French Revolution.
3
Philippe François Nazaire Fabre d'Églantine, commonly known as Fabre d'Églantine, was a French actor, dramatist, poet, and politician of the French Revolution.
Gustave Nadaud
 3
Gustave Nadaud was a French composer and chansonnier.
3
Gustave Nadaud was a French composer and chansonnier.
Lucien Bossoutrot
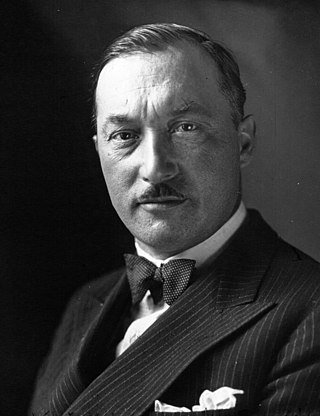 3
Jean Baptiste Lucien Bossoutrot est un aviateur et homme politique français, né le 16 mai 1890 à Tulle (Corrèze) au 42, rue de la Barrière et mort le 1er septembre 1958 à Viry-Châtillon...
3
Jean Baptiste Lucien Bossoutrot est un aviateur et homme politique français, né le 16 mai 1890 à Tulle (Corrèze) au 42, rue de la Barrière et mort le 1er septembre 1958 à Viry-Châtillon...
Francisque Sarcey
 3
Francisque Sarcey was a French journalist and dramatic critic.
3
Francisque Sarcey was a French journalist and dramatic critic.
Alexis Carrel
 3
Alexis Carrel was a French surgeon and biologist who spent most of his scientific career in the United States. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1912 for pioneering vascular...
3
Alexis Carrel was a French surgeon and biologist who spent most of his scientific career in the United States. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1912 for pioneering vascular...
Henri Moll
 3
Alexandre Marie Frédéric Henry Moll dit Henri Moll, né le 17 mars 1871 à Saulx de Vesoul (Haute-Saône) et tombé au champ d'honneur le 9 novembre 1910 au Tchad au cours du combat de Doroté, était un...
3
Alexandre Marie Frédéric Henry Moll dit Henri Moll, né le 17 mars 1871 à Saulx de Vesoul (Haute-Saône) et tombé au champ d'honneur le 9 novembre 1910 au Tchad au cours du combat de Doroté, était un...
Jacques Bingen
 3
Jacques Bingen was a high-ranking member of the French Resistance during World War II who, when captured by the Gestapo, chose to commit suicide rather than risk divulging what he knew under torture.
3
Jacques Bingen was a high-ranking member of the French Resistance during World War II who, when captured by the Gestapo, chose to commit suicide rather than risk divulging what he knew under torture.
Eugène Adrien Ducretet
 3
Eugène Adrien Ducretet was a French scientific instrument manufacturer, who performed some of the first experiments on wireless telegraphy in France. His father, Louis Joseph Ducretet, was a Savoy...
3
Eugène Adrien Ducretet was a French scientific instrument manufacturer, who performed some of the first experiments on wireless telegraphy in France. His father, Louis Joseph Ducretet, was a Savoy...
Antoine Brun
 3
Anthoine Brun (1599–1654), baron d'Aspremont, was a Burgundian (Franche-Comté) diplomat in the service of Philip IV of Spain.
3
Anthoine Brun (1599–1654), baron d'Aspremont, was a Burgundian (Franche-Comté) diplomat in the service of Philip IV of Spain.
Henry Chéron
 3
Henry Frédéric Chéron was a French lawyer and politician who became active in local politics in the Calvados department of Normandy while still a young man, and always maintained his roots in...
3
Henry Frédéric Chéron was a French lawyer and politician who became active in local politics in the Calvados department of Normandy while still a young man, and always maintained his roots in...
Victor Massé
 3
Victor Massé was a French composer.
3
Victor Massé was a French composer.
Cécile Brunschvicg
 3
Cécile Brunschvicg, born Cécile Kahn, was a French feminist politician. From the 1920s until her death she was regarded as "the grande dame of the feminist movement" in France.
3
Cécile Brunschvicg, born Cécile Kahn, was a French feminist politician. From the 1920s until her death she was regarded as "the grande dame of the feminist movement" in France.
Raymond Sommer
 3
Pierre Raymond Sommer was a French racing driver. He raced both before and after WWII with some success, particularly in endurance racing. He won the 24 Hours of Le Mans endurance race in both 1932...
3
Pierre Raymond Sommer was a French racing driver. He raced both before and after WWII with some success, particularly in endurance racing. He won the 24 Hours of Le Mans endurance race in both 1932...
Paul Machy
 3
Paul, Emile Amand Machy, né le 17 octobre 1887 à Oye-Plage (Pas-de-Calais) et Mort pour la France fin mars 1945 lors de son transfert à Buchenwald (Allemagne), est un homme politique français.
3
Paul, Emile Amand Machy, né le 17 octobre 1887 à Oye-Plage (Pas-de-Calais) et Mort pour la France fin mars 1945 lors de son transfert à Buchenwald (Allemagne), est un homme politique français.
Jan Masaryk
 3
Jan Garrigue Masaryk was a Czech diplomat and politician who served as the Foreign Minister of Czechoslovakia from 1940 to 1948. American journalist John Gunther described Masaryk as "a brave,...
3
Jan Garrigue Masaryk was a Czech diplomat and politician who served as the Foreign Minister of Czechoslovakia from 1940 to 1948. American journalist John Gunther described Masaryk as "a brave,...
Jacques-Henri Bernardin de Saint-Pierre
 3
Jacques-Henri Bernardin de Saint-Pierre was a French writer and botanist. He is best known for his 1788 novel, Paul et Virginie, a very popular 18th-century classic of French literature.
3
Jacques-Henri Bernardin de Saint-Pierre was a French writer and botanist. He is best known for his 1788 novel, Paul et Virginie, a very popular 18th-century classic of French literature.
Louis XIV
 3
Louis XIV, also known as Louis the Great or the Sun King, was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any sovereign. Although...
3
Louis XIV, also known as Louis the Great or the Sun King, was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any sovereign. Although...
Jean-François Champollion
 3
Jean-François Champollion, also known as Champollion le jeune, was a French philologist and orientalist, known primarily as the decipherer of Egyptian hieroglyphs and a founding figure in the field...
3
Jean-François Champollion, also known as Champollion le jeune, was a French philologist and orientalist, known primarily as the decipherer of Egyptian hieroglyphs and a founding figure in the field...
Niki de Saint Phalle
 3
Niki de Saint Phalle was a French-American sculptor, painter, filmmaker, and author of colorful hand-illustrated books. Widely noted as one of the few female monumental sculptors, Saint Phalle was...
3
Niki de Saint Phalle was a French-American sculptor, painter, filmmaker, and author of colorful hand-illustrated books. Widely noted as one of the few female monumental sculptors, Saint Phalle was...
François-Joseph-Victor Broussais
 3
François-Joseph-Victor Broussais was a French physician.
3
François-Joseph-Victor Broussais was a French physician.
Georges Carpentier
 3
Georges Carpentier was a French boxer, actor and World War I pilot.
A precocious pugilist, Carpentier fought in numerous categories. He fought mainly as a light heavyweight and heavyweight in a...
3
Georges Carpentier was a French boxer, actor and World War I pilot.
A precocious pugilist, Carpentier fought in numerous categories. He fought mainly as a light heavyweight and heavyweight in a...
Ernest Pérochon
 3
Ernest Pérochon (1885–1942) was a French writer who won the Prix Goncourt in 1920 for his novel Nêne. Initially a teacher, he left his career in education in 1921 to pursue writing. He wrote poems,...
3
Ernest Pérochon (1885–1942) was a French writer who won the Prix Goncourt in 1920 for his novel Nêne. Initially a teacher, he left his career in education in 1921 to pursue writing. He wrote poems,...
Louis Comte
 3
Louis Apollinaire Christien Emmanuel Comte "The King's Conjurer", also known simply as Comte, was a celebrated nineteenth-century Parisian magician, greatly admired by Robert-Houdin.
3
Louis Apollinaire Christien Emmanuel Comte "The King's Conjurer", also known simply as Comte, was a celebrated nineteenth-century Parisian magician, greatly admired by Robert-Houdin.
Jules Siegfried
 3
Jules Siegfried was a French politician. He served as a member of the Chamber of Deputies from 1885 to 1897, and from 1902 to 1922.
3
Jules Siegfried was a French politician. He served as a member of the Chamber of Deputies from 1885 to 1897, and from 1902 to 1922.
Guy Bouriat
 3
Guy Bouriat est un pilote automobile français.
3
Guy Bouriat est un pilote automobile français.
François de Tessan
 3
François de Tessan, issu d'une famille de l'aristocratie cévenole, du Vigan, est un journaliste, homme de lettres et homme politique radical-socialiste français, né le 16 février 1883 à...
3
François de Tessan, issu d'une famille de l'aristocratie cévenole, du Vigan, est un journaliste, homme de lettres et homme politique radical-socialiste français, né le 16 février 1883 à...
Louis Daquin
 3
Louis Daquin was a French film director, screenwriter and actor. He directed 14 films between 1938 and 1963. He also appeared in 11 films between 1937 and 1979.
3
Louis Daquin was a French film director, screenwriter and actor. He directed 14 films between 1938 and 1963. He also appeared in 11 films between 1937 and 1979.
Emmanuel Vitria
 3
Emmanuel Vitria, né le 24 janvier 1920 et mort le 11 mai 1987 à Marseille, est un des premiers hommes à bénéficier d'une transplantation cardiaque. Il détient pendant de nombreuses années le record...
3
Emmanuel Vitria, né le 24 janvier 1920 et mort le 11 mai 1987 à Marseille, est un des premiers hommes à bénéficier d'une transplantation cardiaque. Il détient pendant de nombreuses années le record...
René Gasnier
 3
René Gasnier, né le 24 mars 1874 à Quimperlé (Finistère) et mort le 3 octobre 1913 à Bouchemaine (Maine-et-Loire), né dans une vieille famille angevine, est un sportif français, un des principaux...
3
René Gasnier, né le 24 mars 1874 à Quimperlé (Finistère) et mort le 3 octobre 1913 à Bouchemaine (Maine-et-Loire), né dans une vieille famille angevine, est un sportif français, un des principaux...
Victor Segalen
 3
Victor Segalen was a French naval doctor, ethnographer, archeologist, writer, poet, explorer, art-theorist, linguist and literary critic.
3
Victor Segalen was a French naval doctor, ethnographer, archeologist, writer, poet, explorer, art-theorist, linguist and literary critic.
Michael Strogoff
 3
Michael Strogoff: The Courier of the Czar is a novel written by Jules Verne in 1876. Critic Leonard S. Davidow, considers it one of Verne's best books. Davidow wrote, "Jules Verne has written no...
3
Michael Strogoff: The Courier of the Czar is a novel written by Jules Verne in 1876. Critic Leonard S. Davidow, considers it one of Verne's best books. Davidow wrote, "Jules Verne has written no...
Georges Mandel
 3
Georges Mandel was a French Jewish journalist, and politician.
3
Georges Mandel was a French Jewish journalist, and politician.
Jules Méline
 3
Félix Jules Méline was a French statesman, Prime Minister of France from 1896 to 1898.
3
Félix Jules Méline was a French statesman, Prime Minister of France from 1896 to 1898.
Robert Buron
 3
Robert Buron was a French politician. Buron represented Mayenne as a deputy in the French National Assembly from 1945 to 1958 and was a minister in several French governments during France’s Fourth...
3
Robert Buron was a French politician. Buron represented Mayenne as a deputy in the French National Assembly from 1945 to 1958 and was a minister in several French governments during France’s Fourth...
Émile Durkheim
 3
David Émile Durkheim was a French sociologist. Durkheim formally established the academic discipline of sociology and is commonly cited as one of the principal architects of modern social science,...
3
David Émile Durkheim was a French sociologist. Durkheim formally established the academic discipline of sociology and is commonly cited as one of the principal architects of modern social science,...
Gaston Monmousseau
 3
Gaston René Léon Monmousseau was a French railway worker, trade union leader, politician and author, from a rural working-class background. He became an anarcho-syndicalist, then a communist, and...
3
Gaston René Léon Monmousseau was a French railway worker, trade union leader, politician and author, from a rural working-class background. He became an anarcho-syndicalist, then a communist, and...
Hyacinthe Rigaud
 3
Jacint Rigau-Ros i Serra, known in French as Hyacinthe Rigaud, was a Spanish-French baroque painter most famous for his portraits of Louis XIV and other members of the French nobility.
3
Jacint Rigau-Ros i Serra, known in French as Hyacinthe Rigaud, was a Spanish-French baroque painter most famous for his portraits of Louis XIV and other members of the French nobility.
Oscar Niemeyer
 3
Oscar Ribeiro de Almeida Niemeyer Soares Filho, known as Oscar Niemeyer, was a Brazilian architect considered to be one of the key figures in the development of modern architecture. Niemeyer was best...
3
Oscar Ribeiro de Almeida Niemeyer Soares Filho, known as Oscar Niemeyer, was a Brazilian architect considered to be one of the key figures in the development of modern architecture. Niemeyer was best...
François Camel
 3
François Camel est un homme politique socialiste français, instituteur de profession, syndicaliste, résistant, né le 3 mai 1893 à Esplas-de-Sérou (Ariège) et mort le 1er mai 1941 à Lasserre (Ariège).
3
François Camel est un homme politique socialiste français, instituteur de profession, syndicaliste, résistant, né le 3 mai 1893 à Esplas-de-Sérou (Ariège) et mort le 1er mai 1941 à Lasserre (Ariège).
Jacqueline de Romilly
 3
Jacqueline Worms de Romilly was a French philologist, classical scholar and fiction writer. She was the first woman nominated to the Collège de France, and in 1988, the second woman to enter the...
3
Jacqueline Worms de Romilly was a French philologist, classical scholar and fiction writer. She was the first woman nominated to the Collège de France, and in 1988, the second woman to enter the...
Gilles Gahinet
 3
Gilles Gahinet est un navigateur et architecte naval français, né le 25 août 1947 à Larmor-Baden, et mort le 10 octobre 1984 à Nantes.
3
Gilles Gahinet est un navigateur et architecte naval français, né le 25 août 1947 à Larmor-Baden, et mort le 10 octobre 1984 à Nantes.
Émile Fayolle
 3
Marie Émile Fayolle was a French general during World War I and a diplomat, elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France.
3
Marie Émile Fayolle was a French general during World War I and a diplomat, elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France.
Bertran de Born
 3
Bertran de Born was a baron from the Limousin in France, and one of the major Occitan troubadours of the 12th-13th century. He composed love songs (cansos) but was better known for his political...
3
Bertran de Born was a baron from the Limousin in France, and one of the major Occitan troubadours of the 12th-13th century. He composed love songs (cansos) but was better known for his political...
Joseph Fourier
 3
Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier was a French mathematician and physicist born in Auxerre and best known for initiating the investigation of Fourier series, which eventually developed into Fourier...
3
Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier was a French mathematician and physicist born in Auxerre and best known for initiating the investigation of Fourier series, which eventually developed into Fourier...
Jean Auguste Margueritte
 3
Jean Auguste Margueritte, French General, father of Victor Margueritte and Paul Margueritte.
3
Jean Auguste Margueritte, French General, father of Victor Margueritte and Paul Margueritte.
François Joseph Paul de Grasse
 3
François Joseph Paul, Comte de Grasse, Marquis of Grasse-Tilly SMOM was a career French officer who achieved the rank of admiral. He is best known for his command of the French fleet at the Battle of...
3
François Joseph Paul, Comte de Grasse, Marquis of Grasse-Tilly SMOM was a career French officer who achieved the rank of admiral. He is best known for his command of the French fleet at the Battle of...
Bertrand d'Argentré
 3
Bertrand d'Argentré was a Breton jurist and historian.
3
Bertrand d'Argentré was a Breton jurist and historian.
Étienne Méhul
 3
Étienne Nicolas Méhul was a French composer of the late classical and early romantic periods. He was known as "the most important opera composer in France during the Revolution". He was also the...
3
Étienne Nicolas Méhul was a French composer of the late classical and early romantic periods. He was known as "the most important opera composer in France during the Revolution". He was also the...
Gabriel Deshayes
 3
Gabriel Deshayes, né le 4 décembre 1767 à Beignon et mort le 28 décembre 1841 à Saint-Laurent-sur-Sèvre, est un prêtre catholique français, supérieur général et fondateur de plusieurs congrégations.
3
Gabriel Deshayes, né le 4 décembre 1767 à Beignon et mort le 28 décembre 1841 à Saint-Laurent-sur-Sèvre, est un prêtre catholique français, supérieur général et fondateur de plusieurs congrégations.
Albert Christophle
 3
Albert Christophle, né à Domfront le 13 juillet 1830 et mort à Paris 16e le 23 janvier 1904, est un avocat, jurisconsulte et homme politique français, son fils George est le gendre d'Émile de Marcère.
3
Albert Christophle, né à Domfront le 13 juillet 1830 et mort à Paris 16e le 23 janvier 1904, est un avocat, jurisconsulte et homme politique français, son fils George est le gendre d'Émile de Marcère.
Roger Martin du Gard
 3
Roger Martin du Gard was a French novelist, winner of the 1937 Nobel Prize in Literature.
3
Roger Martin du Gard was a French novelist, winner of the 1937 Nobel Prize in Literature.
Georges Simenon
 3
Georges Joseph Christian Simenon was a Belgian writer, most famous for his fictional detective Jules Maigret. One of the most popular authors of the 20th century, he published around 400 novels, 21...
3
Georges Joseph Christian Simenon was a Belgian writer, most famous for his fictional detective Jules Maigret. One of the most popular authors of the 20th century, he published around 400 novels, 21...
Albin Roussin
 3
Albin Reine Roussin was a French admiral and statesman.
3
Albin Reine Roussin was a French admiral and statesman.
Gustave Caillebotte
 3
Gustave Caillebotte was a French painter who was a member and patron of the Impressionists, although he painted in a more realistic manner than many others in the group. Caillebotte was known for his...
3
Gustave Caillebotte was a French painter who was a member and patron of the Impressionists, although he painted in a more realistic manner than many others in the group. Caillebotte was known for his...
Marie Pape-Carpantier
 3
Marie Pape-Carpantier (1815–1878) was a French educator born on 11 September 1815 in Sarthe, France and died in Villiers-le-Bel (Val-d'Oise) on 31 July 1878. She grew to play a major part in...
3
Marie Pape-Carpantier (1815–1878) was a French educator born on 11 September 1815 in Sarthe, France and died in Villiers-le-Bel (Val-d'Oise) on 31 July 1878. She grew to play a major part in...
Alain de Boissieu
 3
Alain de Boissieu Déan de Luigné was a French general who served in the Free French Forces during World War II, later becoming Army chief of staff (1971–1975). He was the son-in-law of General...
3
Alain de Boissieu Déan de Luigné was a French general who served in the Free French Forces during World War II, later becoming Army chief of staff (1971–1975). He was the son-in-law of General...
Isabelle Romée
 3
Isabelle Romée, also known as Isabelle de Vouthon and Isabelle d'Arc (1377–1458) and Ysabeau Romee, was the mother of Joan of Arc. She grew up in Vouthon-Bas and later married Jacques d'Arc. The...
3
Isabelle Romée, also known as Isabelle de Vouthon and Isabelle d'Arc (1377–1458) and Ysabeau Romee, was the mother of Joan of Arc. She grew up in Vouthon-Bas and later married Jacques d'Arc. The...
René-Marie Madec
 3
René-Marie Madec, called Medoc in Anglo-Indian writings, was a French adventurer in India.
3
René-Marie Madec, called Medoc in Anglo-Indian writings, was a French adventurer in India.
Maurice Denis
 3
Maurice Denis was a French painter, decorative artist, and writer. An important figure in the transitional period between impressionism and modern art, he is associated with Les Nabis, symbolism, and...
3
Maurice Denis was a French painter, decorative artist, and writer. An important figure in the transitional period between impressionism and modern art, he is associated with Les Nabis, symbolism, and...
Victor Petit
 3
Victor Petit est un dessinateur d'architecture, lithographe et écrivain français né en 1817 à Troyes (Aube) et mort en 1871 à Aix-les-Bains.
3
Victor Petit est un dessinateur d'architecture, lithographe et écrivain français né en 1817 à Troyes (Aube) et mort en 1871 à Aix-les-Bains.
Raymonde de Laroche
 3
Raymonde de Laroche was a French pilot, thought to be the first woman to pilot a plane. She became the world's first licensed female pilot on 8 March 1910.
3
Raymonde de Laroche was a French pilot, thought to be the first woman to pilot a plane. She became the world's first licensed female pilot on 8 March 1910.
Émile Guépratte
 3
Émile Paul Aimable Guépratte was a French admiral.
3
Émile Paul Aimable Guépratte was a French admiral.
Jacques de Thézac
 3
Jacques de Thézac est un yachtman, ethnologue, photographe et philanthrope français, fondateur de l'Œuvre des Abris du marin.
3
Jacques de Thézac est un yachtman, ethnologue, photographe et philanthrope français, fondateur de l'Œuvre des Abris du marin.
Jules Romains
 3
Jules Romains was a French poet and writer and the founder of the Unanimism literary movement. His works include the play Knock ou le Triomphe de la médecine, and a cycle of works called Les Hommes...
3
Jules Romains was a French poet and writer and the founder of the Unanimism literary movement. His works include the play Knock ou le Triomphe de la médecine, and a cycle of works called Les Hommes...
Eugène Guillevic
 3
Eugène Guillevic was a French poet. Professionally, he went by the single name Guillevic.
3
Eugène Guillevic was a French poet. Professionally, he went by the single name Guillevic.
Maurice Noguès
 3
Maurice Noguès was a French aviator from Brittany.
3
Maurice Noguès was a French aviator from Brittany.
Frédéric Le Guyader
 3
Frédéric Le Guyader, né le 14 mars 1847 à Brasparts et mort le 24 novembre 1926 à Kerfeunteun, est un écrivain français.
3
Frédéric Le Guyader, né le 14 mars 1847 à Brasparts et mort le 24 novembre 1926 à Kerfeunteun, est un écrivain français.
Paul Sébillot
 3
Paul Sébillot was a French folklorist, painter, and writer. Many of his works are about his native province, Brittany.
3
Paul Sébillot was a French folklorist, painter, and writer. Many of his works are about his native province, Brittany.
Samson of Dol
 3
Samson of Dol was a Welsh saint, who is also counted among the seven founder saints of Brittany with Pol Aurelian, Tugdual or Tudwal, Brieuc, Malo, Patern (Paternus) and Corentin. Born in southern...
3
Samson of Dol was a Welsh saint, who is also counted among the seven founder saints of Brittany with Pol Aurelian, Tugdual or Tudwal, Brieuc, Malo, Patern (Paternus) and Corentin. Born in southern...
Jacques Chaban-Delmas
 3
Jacques Chaban-Delmas was a French Gaullist politician. He served as Prime Minister under Georges Pompidou from 1969 to 1972. He was the Mayor of Bordeaux from 1947 to 1995 and a deputy for the...
3
Jacques Chaban-Delmas was a French Gaullist politician. He served as Prime Minister under Georges Pompidou from 1969 to 1972. He was the Mayor of Bordeaux from 1947 to 1995 and a deputy for the...
Paulin Talabot
 3
Paulin Talabot was a French railway and canal engineer. Educated at the École Polytechnique, Talabot started his career building canals. Inspired by George and Robert Stephenson's steam railways in...
3
Paulin Talabot was a French railway and canal engineer. Educated at the École Polytechnique, Talabot started his career building canals. Inspired by George and Robert Stephenson's steam railways in...
Henri Rivière (naval officer)
 3
Henri Laurent Rivière (1827–1883) was a French naval officer and a writer who is chiefly remembered today for advancing the French conquest of Tonkin in the 1880s. Rivière's seizure of the citadel of...
3
Henri Laurent Rivière (1827–1883) was a French naval officer and a writer who is chiefly remembered today for advancing the French conquest of Tonkin in the 1880s. Rivière's seizure of the citadel of...
Charles Robin
 3
Charles Robin was an entrepreneur from the Isle of Jersey who traded between the maritime region of Canada and the British Isles.
3
Charles Robin was an entrepreneur from the Isle of Jersey who traded between the maritime region of Canada and the British Isles.
Victor Baltard
 3
Victor Baltard was a French architect famed for work in Paris including designing Les Halles market and the Saint-Augustin church.
3
Victor Baltard was a French architect famed for work in Paris including designing Les Halles market and the Saint-Augustin church.
Émile Dewoitine
 3
Émile Dewoitine was a French aviation industrialist.
3
Émile Dewoitine was a French aviation industrialist.
Jean Marie Le Bris
 3
Jean Marie Le Bris was a French aviator, born in Concarneau, Brittany who built two glider aircraft and performed at least one flight on board of his first machine in late 1856. His name is sometimes...
3
Jean Marie Le Bris was a French aviator, born in Concarneau, Brittany who built two glider aircraft and performed at least one flight on board of his first machine in late 1856. His name is sometimes...
Maurice Bellonte
 3
Maurice Bellonte was a French aviator who set flight distance records.
3
Maurice Bellonte was a French aviator who set flight distance records.
Christine de Pizan
 3
Christine de Pizan or Pisan, was an Italian-born French poet and court writer for King Charles VI of France and several French dukes.
3
Christine de Pizan or Pisan, was an Italian-born French poet and court writer for King Charles VI of France and several French dukes.
Jean Nicot
 3
Jean Nicot de Villemain was a French diplomat and scholar. He is famous for being the first to bring tobacco to France, including snuff tobacco. Nicotine is named after the tobacco plant Nicotiana...
3
Jean Nicot de Villemain was a French diplomat and scholar. He is famous for being the first to bring tobacco to France, including snuff tobacco. Nicotine is named after the tobacco plant Nicotiana...
François Antoine de Boissy d'Anglas
 3
François-Antoine, Count of the Empire (1756–1826) was a French writer, lawyer and politician during the Revolution and the Empire.
3
François-Antoine, Count of the Empire (1756–1826) was a French writer, lawyer and politician during the Revolution and the Empire.
Marcel Bernard
 3
Marcel Bernard was a French tennis player. He is best remembered for having won the French Championships in 1946. Bernard initially intended to play only in the doubles event but was persuaded to...
3
Marcel Bernard was a French tennis player. He is best remembered for having won the French Championships in 1946. Bernard initially intended to play only in the doubles event but was persuaded to...
Pierre de Fermat
 3
Pierre de Fermat was a French mathematician who is given credit for early developments that led to infinitesimal calculus, including his technique of adequality. In particular, he is recognized for...
3
Pierre de Fermat was a French mathematician who is given credit for early developments that led to infinitesimal calculus, including his technique of adequality. In particular, he is recognized for...
Marcel Callo
 3
Marcel Callo was a French Roman Catholic from Rennes who served in Catholic organizations – in particular the Young Christian Workers (Jocists) – devoted to charitable works to the poor and to...
3
Marcel Callo was a French Roman Catholic from Rennes who served in Catholic organizations – in particular the Young Christian Workers (Jocists) – devoted to charitable works to the poor and to...
Frida Kahlo
 3
Magdalena Carmen Frida Kahlo y Calderón was a Mexican painter known for her many portraits, self-portraits, and works inspired by the nature and artifacts of Mexico. Inspired by the country's popular...
3
Magdalena Carmen Frida Kahlo y Calderón was a Mexican painter known for her many portraits, self-portraits, and works inspired by the nature and artifacts of Mexico. Inspired by the country's popular...
Laurent Fignon
 3
Laurent Patrick Fignon was a French professional road bicycle racer who won the Tour de France in 1983 and 1984 and the Giro d'Italia in 1989. He is former FICP World No. 1 in 1989. He nearly...
3
Laurent Patrick Fignon was a French professional road bicycle racer who won the Tour de France in 1983 and 1984 and the Giro d'Italia in 1989. He is former FICP World No. 1 in 1989. He nearly...
Alain Mimoun
 3
Alain Mimoun, born Ali Mimoun Ould Kacha, was a French long-distance runner who competed in track events, cross-country running and the marathon. He was the 1956 Olympic champion in the marathon. He...
3
Alain Mimoun, born Ali Mimoun Ould Kacha, was a French long-distance runner who competed in track events, cross-country running and the marathon. He was the 1956 Olympic champion in the marathon. He...
Germaine de Staël
 3
Anne Louise Germaine de Staël-Holstein, commonly known as Madame de Staël, was a prominent philosopher, woman of letters, and political theorist in both Parisian and Genevan intellectual circles. She...
3
Anne Louise Germaine de Staël-Holstein, commonly known as Madame de Staël, was a prominent philosopher, woman of letters, and political theorist in both Parisian and Genevan intellectual circles. She...
Yvonne Jean-Haffen
 3
Yvonne Jean-Haffen, née à Paris le 27 octobre 1895 et morte à Dinan le 24 novembre 1993, est une artiste peintre, dessinatrice, graveuse et céramiste française.
3
Yvonne Jean-Haffen, née à Paris le 27 octobre 1895 et morte à Dinan le 24 novembre 1993, est une artiste peintre, dessinatrice, graveuse et céramiste française.
Félix Leclerc
 3
Félix Leclerc, was a French-Canadian singer-songwriter, poet, writer, actor and Québécois political activist. He was made an Officer of the Order of Canada on December 20, 1968. Leclerc was...
3
Félix Leclerc, was a French-Canadian singer-songwriter, poet, writer, actor and Québécois political activist. He was made an Officer of the Order of Canada on December 20, 1968. Leclerc was...
Théophile Briant
 3
Théophile Briant, né le 2 août 1891 à Douai, et mort le 5 août 1956 à Paramé, est un poète français.
3
Théophile Briant, né le 2 août 1891 à Douai, et mort le 5 août 1956 à Paramé, est un poète français.
Louis Rossel
 3
Louis-Nathaniel Rossel was a French army officer and a politician. On 19 March 1871, he became the only senior French officer to join up with the Paris Commune, playing an important role as Minister...
3
Louis-Nathaniel Rossel was a French army officer and a politician. On 19 March 1871, he became the only senior French officer to join up with the Paris Commune, playing an important role as Minister...
Ella Fitzgerald
 3
Ella Jane Fitzgerald was an American jazz singer, sometimes referred to as the "First Lady of Song", "Queen of Jazz", and "Lady Ella". She was noted for her purity of tone, impeccable diction,...
3
Ella Jane Fitzgerald was an American jazz singer, sometimes referred to as the "First Lady of Song", "Queen of Jazz", and "Lady Ella". She was noted for her purity of tone, impeccable diction,...
Georges de La Tour
 3
Georges de La Tour was a French Baroque painter, who spent most of his working life in the Duchy of Lorraine, which was temporarily absorbed into France between 1641 and 1648. He painted mostly...
3
Georges de La Tour was a French Baroque painter, who spent most of his working life in the Duchy of Lorraine, which was temporarily absorbed into France between 1641 and 1648. He painted mostly...
Amédée Guillotin de Corson
 3
L'abbé Amédée-Aimé Guillotin de Corson, né à Nozay (Loire-Atlantique) le 26 mai 1837 et mort à Bain-de-Bretagne (Ille-et-Vilaine) le 7 août 1905, est un prêtre et historien français, spécialiste de...
3
L'abbé Amédée-Aimé Guillotin de Corson, né à Nozay (Loire-Atlantique) le 26 mai 1837 et mort à Bain-de-Bretagne (Ille-et-Vilaine) le 7 août 1905, est un prêtre et historien français, spécialiste de...
Charlotte Perriand
 3
Charlotte Perriand was a French architect and designer. Her work aimed to create functional living spaces in the belief that better design helps in creating a better society. In her article "L'Art de...
3
Charlotte Perriand was a French architect and designer. Her work aimed to create functional living spaces in the belief that better design helps in creating a better society. In her article "L'Art de...
Étienne Lenoir
 3
Jean Joseph Étienne Lenoir, also known as Jean J. Lenoir, was a Belgian-French engineer who developed the internal combustion engine in 1858. Prior designs for such engines were patented as early as...
3
Jean Joseph Étienne Lenoir, also known as Jean J. Lenoir, was a Belgian-French engineer who developed the internal combustion engine in 1858. Prior designs for such engines were patented as early as...
Auguste Pavie
 3
Auguste Jean-Marie Pavie was a French colonial civil servant, explorer and diplomat who was instrumental in establishing French control over Laos in the last two decades of the 19th century. After a...
3
Auguste Jean-Marie Pavie was a French colonial civil servant, explorer and diplomat who was instrumental in establishing French control over Laos in the last two decades of the 19th century. After a...
Jean Coquelin
 3
Jean Coquelin (1865–1944) was a French film and stage actor and the son of Benoît-Constant Coquelin.
3
Jean Coquelin (1865–1944) was a French film and stage actor and the son of Benoît-Constant Coquelin.
Vincent Ferrer
 3
Vincent Ferrer, OP was a Valencian Dominican friar and preacher, who gained acclaim as a missionary and a logician. He is honored as a saint of the Catholic Church and other churches of Catholic...
3
Vincent Ferrer, OP was a Valencian Dominican friar and preacher, who gained acclaim as a missionary and a logician. He is honored as a saint of the Catholic Church and other churches of Catholic...
Conwoïon
 3
Saint Conwoïon was a Breton saint and abbot. He was probably born around 800 at Comblessac (Ille-et-Vilaine) into a Gallo-Roman family descended, or claiming descent, from Roman senators.
3
Saint Conwoïon was a Breton saint and abbot. He was probably born around 800 at Comblessac (Ille-et-Vilaine) into a Gallo-Roman family descended, or claiming descent, from Roman senators.
John James Audubon
 3
John James Audubon was a French-American self-trained artist, naturalist, and ornithologist. His combined interests in art and ornithology turned into a plan to make a complete pictorial record of...
3
John James Audubon was a French-American self-trained artist, naturalist, and ornithologist. His combined interests in art and ornithology turned into a plan to make a complete pictorial record of...
Jacques Offenbach
 3
Jacques Offenbach 20 June 1819 – 5 October 1880) was a German-born French composer, cellist and impresario. He is remembered for his nearly 100 operettas of the 1850s to the 1870s, and his...
3
Jacques Offenbach 20 June 1819 – 5 October 1880) was a German-born French composer, cellist and impresario. He is remembered for his nearly 100 operettas of the 1850s to the 1870s, and his...
Albert Bayet
 3
Albert Pierre Jules Joseph Bayet was a French sociologist, professor at both the Sorbonne and the École pratique des hautes études.
3
Albert Pierre Jules Joseph Bayet was a French sociologist, professor at both the Sorbonne and the École pratique des hautes études.
Alexandra David-Néel
 3
Alexandra David-Néel was a Belgian–French explorer, spiritualist, Buddhist, anarchist, opera singer, and writer. She is most known for her 1924 visit to Lhasa, Tibet, when it was forbidden to...
3
Alexandra David-Néel was a Belgian–French explorer, spiritualist, Buddhist, anarchist, opera singer, and writer. She is most known for her 1924 visit to Lhasa, Tibet, when it was forbidden to...
Marie Durand
 3
Marie Durand (1711–1776), was a French Protestant. She was famously imprisoned in the Tour de Constance (Aigues-Mortes) from 25 August 1730 for attending a Huguenot assembly with her mother, or...
3
Marie Durand (1711–1776), was a French Protestant. She was famously imprisoned in the Tour de Constance (Aigues-Mortes) from 25 August 1730 for attending a Huguenot assembly with her mother, or...
Paul Séramy
 3
Paul Séramy, né le 4 février 1920 à Saint-Voir (Allier) et mort le 23 février 1992 à Villejuif (Val-de-Marne), est un ancien sénateur de Seine-et-Marne et maire de Fontainebleau.
3
Paul Séramy, né le 4 février 1920 à Saint-Voir (Allier) et mort le 23 février 1992 à Villejuif (Val-de-Marne), est un ancien sénateur de Seine-et-Marne et maire de Fontainebleau.
Jean Lamy
 3
Jean Lamy is a former French slalom canoeist who competed from the late 1970s to the early 1980s. He won a silver medal in the C-2 team event at the 1979 ICF Canoe Slalom World Championships in...
3
Jean Lamy is a former French slalom canoeist who competed from the late 1970s to the early 1980s. He won a silver medal in the C-2 team event at the 1979 ICF Canoe Slalom World Championships in...
Jules Lemaître
 3
François Élie Jules Lemaître was a French critic and dramatist.
3
François Élie Jules Lemaître was a French critic and dramatist.
Fanfonne Guillierme
 3
Fanfonne Guillierme born Antoinette Guillierme was a French manadière. She is known as "the Grande Dame of the Camargue".
3
Fanfonne Guillierme born Antoinette Guillierme was a French manadière. She is known as "the Grande Dame of the Camargue".
Charlotte Delbo
 3
Charlotte Delbo was a French writer chiefly known for her haunting memoirs of her time as a prisoner in Auschwitz, where she was sent for her activities as a member of the French Resistance.
3
Charlotte Delbo was a French writer chiefly known for her haunting memoirs of her time as a prisoner in Auschwitz, where she was sent for her activities as a member of the French Resistance.
Marcellin Champagnat
 3
Marcellin Joseph Benedict Champagnat, FMS was a French Catholic religious born in Le Rosey, village of Marlhes, near St. Etienne (Loire), France. He was the founder of the Marist Brothers, a...
3
Marcellin Joseph Benedict Champagnat, FMS was a French Catholic religious born in Le Rosey, village of Marlhes, near St. Etienne (Loire), France. He was the founder of the Marist Brothers, a...
Gustave Zédé
 3
Gustave Zédé (1825-1891) was a French naval engineer and pioneering designer of submarines.
3
Gustave Zédé (1825-1891) was a French naval engineer and pioneering designer of submarines.
Eugène Labiche
 3
Eugène Marin Labiche was a French dramatist. He remains famous for his contribution to the vaudeville genre and his passionate and domestic pochads.
3
Eugène Marin Labiche was a French dramatist. He remains famous for his contribution to the vaudeville genre and his passionate and domestic pochads.
Philibert de l'Orme
 3
Philibert de l'Orme was a French architect and writer, and one of the great masters of French Renaissance architecture. His surname is also written De l'Orme, de L'Orme, or Delorme.
3
Philibert de l'Orme was a French architect and writer, and one of the great masters of French Renaissance architecture. His surname is also written De l'Orme, de L'Orme, or Delorme.
Jean-Loup Chrétien
 3
Jean-Loup Jacques Marie Chrétien is a French retired Général de Brigade in the Armée de l'Air, and a former CNES spationaut. He flew on two Franco-Soviet space missions and a NASA Space Shuttle...
3
Jean-Loup Jacques Marie Chrétien is a French retired Général de Brigade in the Armée de l'Air, and a former CNES spationaut. He flew on two Franco-Soviet space missions and a NASA Space Shuttle...
Joseph Claussat
 3
Pierre Clovis François Joseph Claussat was a French politician. He served as the mayor of Châteldon from 1908 until his death in 1925. He also served as a member of the Chamber of Deputies from 1911...
3
Pierre Clovis François Joseph Claussat was a French politician. He served as the mayor of Châteldon from 1908 until his death in 1925. He also served as a member of the Chamber of Deputies from 1911...
Louis Gallouédec
 3
Louis Gallouédec was a French geographer.
3
Louis Gallouédec was a French geographer.
Antoine Pinay
 3
Antoine Pinay was a French conservative politician who served as Prime Minister of France from 1952 to 1953.
3
Antoine Pinay was a French conservative politician who served as Prime Minister of France from 1952 to 1953.
Jules Grévy
 3
François Judith Paul Grévy, known as Jules Grévy, was a French lawyer and politician who served as President of France from 1879 to 1887. He was a leader of the Moderate Republicans, and given that...
3
François Judith Paul Grévy, known as Jules Grévy, was a French lawyer and politician who served as President of France from 1879 to 1887. He was a leader of the Moderate Republicans, and given that...
Hubert Dubedout
 3
Hubert Dubedout, né le 9 décembre 1922 à Paris et mort le 25 juillet 1986 à Chamonix-Mont-Blanc, est un homme politique français.
3
Hubert Dubedout, né le 9 décembre 1922 à Paris et mort le 25 juillet 1986 à Chamonix-Mont-Blanc, est un homme politique français.
Alphonse Beau de Rochas
 3
Alphonse Eugène Beau de Rochas was a French engineer. He was the first to patent the four-stroke engine in 1862, but he did not build one and the idea was subsequently developed by Nicolaus Otto and...
3
Alphonse Eugène Beau de Rochas was a French engineer. He was the first to patent the four-stroke engine in 1862, but he did not build one and the idea was subsequently developed by Nicolaus Otto and...
Paul-Henri Spaak
 3
Paul-Henri Charles Spaak was an influential Belgian Socialist politician, diplomat and statesman. Along with Robert Schuman, Alcide De Gasperi and Konrad Adenauer he was a leader in the formation of...
3
Paul-Henri Charles Spaak was an influential Belgian Socialist politician, diplomat and statesman. Along with Robert Schuman, Alcide De Gasperi and Konrad Adenauer he was a leader in the formation of...
Pauline Kergomard
 3
Pauline Kergomard was a French educator. She is known as the founder of the nursery school in France.
3
Pauline Kergomard was a French educator. She is known as the founder of the nursery school in France.
François Fabié
 3
François Fabié, né au Moulin de Roupeyrac à Durenque (Aveyron) le 3 novembre 1846 et mort le 18 juillet 1928 à La Valette-du-Var (Var), est un poète régionaliste français. Le Moulin de Roupeyrac, sa...
3
François Fabié, né au Moulin de Roupeyrac à Durenque (Aveyron) le 3 novembre 1846 et mort le 18 juillet 1928 à La Valette-du-Var (Var), est un poète régionaliste français. Le Moulin de Roupeyrac, sa...
René Payot
 3
René Payot, né le 11 août 1894 à Monthey (Valais) et mort le 15 mai 1970 à Genève, est un journaliste suisse.
3
René Payot, né le 11 août 1894 à Monthey (Valais) et mort le 15 mai 1970 à Genève, est un journaliste suisse.
Anatole de Monzie
 3
Anatole de Monzie was a French administrator, encyclopaedist, political figure and scholar. His father was a tax collector in Bazas, Gironde where Anatole – a name he disliked from an early age – was...
3
Anatole de Monzie was a French administrator, encyclopaedist, political figure and scholar. His father was a tax collector in Bazas, Gironde where Anatole – a name he disliked from an early age – was...
Louise Labé
 3
Louise Charlin Perrin Labé,, also identified as La Belle Cordière, was a French poet of the Renaissance born in Lyon, the daughter of wealthy ropemaker Pierre Charly and his second wife, Etiennette...
3
Louise Charlin Perrin Labé,, also identified as La Belle Cordière, was a French poet of the Renaissance born in Lyon, the daughter of wealthy ropemaker Pierre Charly and his second wife, Etiennette...
Eugène Pelletan
 3
Pierre Clément Eugène Pelletan was a French writer, journalist and politician.
3
Pierre Clément Eugène Pelletan was a French writer, journalist and politician.
Julius and Ethel Rosenberg
 3
Julius Rosenberg and Ethel Rosenberg were an American married couple who were convicted of spying for the Soviet Union, including providing top-secret information about American radar, sonar, jet...
3
Julius Rosenberg and Ethel Rosenberg were an American married couple who were convicted of spying for the Soviet Union, including providing top-secret information about American radar, sonar, jet...
William of St-Thierry
 3
William of Saint-Thierry, O. Cist was a twelfth-century Benedictine, theologian and mystic from Liège who became abbot of Saint-Thierry in France, and later joined the Cistercian Order.
3
William of Saint-Thierry, O. Cist was a twelfth-century Benedictine, theologian and mystic from Liège who became abbot of Saint-Thierry in France, and later joined the Cistercian Order.
Sébastienne Guyot
 3
Sébastienne Marie Henriette Guyot was a French engineer who specialised in aerodynamic flying. A top athlete, she participated in the 1928 Summer Olympics in Amsterdam in the 800 meters and was...
3
Sébastienne Marie Henriette Guyot was a French engineer who specialised in aerodynamic flying. A top athlete, she participated in the 1928 Summer Olympics in Amsterdam in the 800 meters and was...
Marie Mauron
 3
Marie Mauron, née Marie-Antoinette Roumanille le 5 avril 1896 à Saint-Rémy-de-Provence, dans les Bouches-du-Rhône et morte le 31 octobre 1986 dans la même ville, dans son Mas d'Angirany, est une...
3
Marie Mauron, née Marie-Antoinette Roumanille le 5 avril 1896 à Saint-Rémy-de-Provence, dans les Bouches-du-Rhône et morte le 31 octobre 1986 dans la même ville, dans son Mas d'Angirany, est une...
Pierre Bachelet
 3
Pierre Bachelet was a French singer-songwriter and film score composer. He was also known as Andrew Bacson.
3
Pierre Bachelet was a French singer-songwriter and film score composer. He was also known as Andrew Bacson.
Michel Berger
 3
Michel Jean Hamburger, known professionally as Michel Berger, was a French singer and songwriter. He was a leading figure of France's pop music scene for two decades as a singer; as a songwriter, he...
3
Michel Jean Hamburger, known professionally as Michel Berger, was a French singer and songwriter. He was a leading figure of France's pop music scene for two decades as a singer; as a songwriter, he...
Jacques Simon (cyclist)
 3
Jacques Simon was a French cyclist. He competed at the 1960 Summer Olympics in the 100 km team time trial and finished in seventh place. Between 1961 and 1977 he won at least 14 one-day races.
3
Jacques Simon was a French cyclist. He competed at the 1960 Summer Olympics in the 100 km team time trial and finished in seventh place. Between 1961 and 1977 he won at least 14 one-day races.
Charles Debarge
 3
Charles Debarge, né le 12 février 1909 à Harnes (Pas-de-Calais) et mort de ses blessures le 23 septembre 1942 à la prison d’Arras (Pas-de-Calais), est l'un des héros de la Résistance communiste dans...
3
Charles Debarge, né le 12 février 1909 à Harnes (Pas-de-Calais) et mort de ses blessures le 23 septembre 1942 à la prison d’Arras (Pas-de-Calais), est l'un des héros de la Résistance communiste dans...
Uriane Sorriaux
 3
Uriane Sorriaux, né le 12 juillet 1859 à Bouchain et mort le 26 juillet 1918 à Vilvorde, est un homme politique français.
3
Uriane Sorriaux, né le 12 juillet 1859 à Bouchain et mort le 26 juillet 1918 à Vilvorde, est un homme politique français.
Marius Berliet
 3
Marius Berliet, né le 21 janvier 1866 à Lyon 1er et mort le 17 mai 1949 à Cannes, est le fondateur de la société des Automobiles Marius Berliet, constructeur automobile de voitures et camions...
3
Marius Berliet, né le 21 janvier 1866 à Lyon 1er et mort le 17 mai 1949 à Cannes, est le fondateur de la société des Automobiles Marius Berliet, constructeur automobile de voitures et camions...
Lazare Ponticelli
 3
Lazare Ponticelli, Knight of Vittorio Veneto, was at 110, the last surviving officially recognized veteran of the First World War from France and the last poilu of its trenches to die.
3
Lazare Ponticelli, Knight of Vittorio Veneto, was at 110, the last surviving officially recognized veteran of the First World War from France and the last poilu of its trenches to die.
Ferdinand Fabre
 3
Ferdinand Simon Fabre was a French novelist whose novels depict the life of the peasants and clergy of his native region, the upper valley of the river Orb, in the département of Hérault.
3
Ferdinand Simon Fabre was a French novelist whose novels depict the life of the peasants and clergy of his native region, the upper valley of the river Orb, in the département of Hérault.
Casimir Delavigne
Antonio Machado
 3
Antonio Cipriano José María y Francisco de Santa Ana Machado y Ruiz, known as Antonio Machado, was a Spanish poet and one of the leading figures of the Spanish literary movement known as the...
3
Antonio Cipriano José María y Francisco de Santa Ana Machado y Ruiz, known as Antonio Machado, was a Spanish poet and one of the leading figures of the Spanish literary movement known as the...
Pierre Sauvaigo
 3
Pierre Sauvaigo est un homme politique français, né le 3 mai 1921 à Paris et décédé le 28 février 1983 à Cagnes-sur-Mer.
3
Pierre Sauvaigo est un homme politique français, né le 3 mai 1921 à Paris et décédé le 28 février 1983 à Cagnes-sur-Mer.
Rudolf Diesel
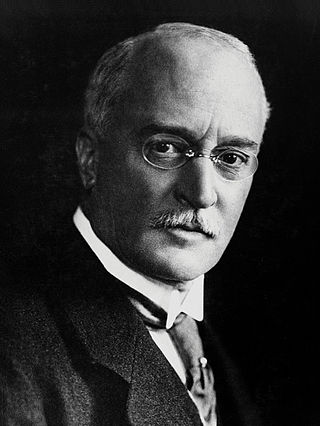 3
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who is famous for having invented the Diesel engine, which burns Diesel fuel; both are named after him.
3
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who is famous for having invented the Diesel engine, which burns Diesel fuel; both are named after him.
Emma Calvé
 3
Emma Calvé, born Rosa Emma Calvet was a French operatic dramatic soprano.
3
Emma Calvé, born Rosa Emma Calvet was a French operatic dramatic soprano.
Jean-Raymond Guyon
 3
Jean-Raymond Guyon, né le 2 avril 1900 à Libourne (Gironde) et mort le 26 mars 1961 à Tonneins (Lot-et-Garonne), est un homme politique et économiste français.
3
Jean-Raymond Guyon, né le 2 avril 1900 à Libourne (Gironde) et mort le 26 mars 1961 à Tonneins (Lot-et-Garonne), est un homme politique et économiste français.
George Washington
 3
George Washington was an American Founding Father, military officer, and politician who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Second Continental...
3
George Washington was an American Founding Father, military officer, and politician who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Second Continental...
René Crabos
 3
René Crabos was a French rugby union player and administrator who represented the France national team 17 times between 1920 and 1924, and went on to be president of the Fédération Française de Rugby...
3
René Crabos was a French rugby union player and administrator who represented the France national team 17 times between 1920 and 1924, and went on to be president of the Fédération Française de Rugby...
Yitzhak Rabin
 3
Yitzhak Rabin was an Israeli politician, statesman and general. He was the fifth prime minister of Israel, serving two terms in office, 1974–1977, and from 1992 until his assassination in 1995.
3
Yitzhak Rabin was an Israeli politician, statesman and general. He was the fifth prime minister of Israel, serving two terms in office, 1974–1977, and from 1992 until his assassination in 1995.
Thales of Miletus
 3
Thales of Miletus was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. Thales was one of the Seven Sages, founding figures of Ancient Greece.
3
Thales of Miletus was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. Thales was one of the Seven Sages, founding figures of Ancient Greece.
Michel Foucault
 3
Paul-Michel Foucault was a French philosopher, historian of ideas, writer, political activist, and literary critic. Foucault's theories primarily address the relationships between power and...
3
Paul-Michel Foucault was a French philosopher, historian of ideas, writer, political activist, and literary critic. Foucault's theories primarily address the relationships between power and...
Crispin and Crispinian
 3
Saints Crispin and Crispinian are the Christian patron saints of cobblers, curriers, tanners, and leather workers. They were beheaded during the reign of Diocletian; the date of their execution is...
3
Saints Crispin and Crispinian are the Christian patron saints of cobblers, curriers, tanners, and leather workers. They were beheaded during the reign of Diocletian; the date of their execution is...
Paul Devaux
 3
Paul Devaux was a liberal Belgian revolutionary politician and historian.
3
Paul Devaux was a liberal Belgian revolutionary politician and historian.
Fernand Darchicourt
 3
Fernand Darchicourt, né le 26 septembre 1917 à Saint-Étienne (Loire) et mort le 23 décembre 1968 à Gasville (Eure-et-Loir), est un homme politique français.
3
Fernand Darchicourt, né le 26 septembre 1917 à Saint-Étienne (Loire) et mort le 23 décembre 1968 à Gasville (Eure-et-Loir), est un homme politique français.
Camille Blanc
 3
Camille Blanc, was a French municipal leader, with many interests in Monaco. From 1904 to 1925, he was founding mayor of Beausoleil, a town adjacent to Monte Carlo, which had previously formed part...
3
Camille Blanc, was a French municipal leader, with many interests in Monaco. From 1904 to 1925, he was founding mayor of Beausoleil, a town adjacent to Monte Carlo, which had previously formed part...
Antoine Bourdelle
 3
Antoine Bourdelle, born Émile Antoine Bordelles, was an influential and prolific French sculptor and teacher. He was a student of Auguste Rodin, a teacher of Giacometti and Henri Matisse, and an...
3
Antoine Bourdelle, born Émile Antoine Bordelles, was an influential and prolific French sculptor and teacher. He was a student of Auguste Rodin, a teacher of Giacometti and Henri Matisse, and an...
Palisot de Beauvois
 3
Ambroise Marie François Joseph Palisot, Baron de Beauvois was a French naturalist and zoologist.
3
Ambroise Marie François Joseph Palisot, Baron de Beauvois was a French naturalist and zoologist.
Marie Marvingt
 3
Marie Marvingt was a French athlete, mountaineer, aviator, and journalist. She won numerous prizes for her sporting achievements including those of swimming, cycling, mountain climbing, winter...
3
Marie Marvingt was a French athlete, mountaineer, aviator, and journalist. She won numerous prizes for her sporting achievements including those of swimming, cycling, mountain climbing, winter...