Frequent persons on Greece's street signs
countries
242 names / 2115 streets
Eleftherios Venizelos
 84
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos was a Cretan Greek statesman and prominent leader of the Greek national liberation movement. He is noted for his contribution to the expansion of Greece and promotion...
84
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos was a Cretan Greek statesman and prominent leader of the Greek national liberation movement. He is noted for his contribution to the expansion of Greece and promotion...
Alexander the Great
 59
Alexander III of Macedon, most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20...
59
Alexander III of Macedon, most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20...
Theodoros Kolokotronis
 33
Theodoros Kolokotronis was a Greek general and the pre-eminent leader of the Greek War of Independence (1821–1829) against the Ottoman Empire.
33
Theodoros Kolokotronis was a Greek general and the pre-eminent leader of the Greek War of Independence (1821–1829) against the Ottoman Empire.
Rigas Feraios
 31
Rigas Feraios or Velestinlis ; 1757 – 24 June 1798), born as Antonios Rigas Velestinlis, was a Greek writer, political thinker and revolutionary, active in the Modern Greek Enlightenment. A victim of...
31
Rigas Feraios or Velestinlis ; 1757 – 24 June 1798), born as Antonios Rigas Velestinlis, was a Greek writer, political thinker and revolutionary, active in the Modern Greek Enlightenment. A victim of...
Chrysostomos of Smyrna
 30
Chrysostomos Kalafatis, also known as Saint Chrysostomos of Smyrna, Chrysostomos of Smyrna and Metropolitan Chrysostom, was the Greek Orthodox metropolitan bishop of Smyrna (İzmir) between 1910 and...
30
Chrysostomos Kalafatis, also known as Saint Chrysostomos of Smyrna, Chrysostomos of Smyrna and Metropolitan Chrysostom, was the Greek Orthodox metropolitan bishop of Smyrna (İzmir) between 1910 and...
Saint George
 28
Saint George, also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition, he was a soldier in the Roman army. Of Cappadocian Greek origin,...
28
Saint George, also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition, he was a soldier in the Roman army. Of Cappadocian Greek origin,...
Pavlos Melas
 27
Pavlos Melas was a Greek revolutionary and artillery officer of the Hellenic Army. He participated in the Greco-Turkish War of 1897 and was amongst the first Greek officers to join the Macedonian...
27
Pavlos Melas was a Greek revolutionary and artillery officer of the Hellenic Army. He participated in the Greco-Turkish War of 1897 and was amongst the first Greek officers to join the Macedonian...
Hermes
 27
Hermes is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, merchants, and...
27
Hermes is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, merchants, and...
Michalis Karaolis
 26
Michalis Karaolis was a Cypriot public official and revolutionary. Born in the village of Palaichori Oreinis of Pitsilia, Karaolis worked as a government clerk and a member of EOKA. He was the first...
26
Michalis Karaolis was a Cypriot public official and revolutionary. Born in the village of Palaichori Oreinis of Pitsilia, Karaolis worked as a government clerk and a member of EOKA. He was the first...
Ioannis Kapodistrias
 25
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias, sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias, was a Greek statesman who was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of 19th-century Europe.
25
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias, sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias, was a Greek statesman who was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of 19th-century Europe.
Konstantinos Kanaris
 24
Konstantinos Kanaris, also anglicised as Constantine Kanaris or Canaris, was a Greek admiral, Prime Minister, and a hero of the Greek War of Independence.
24
Konstantinos Kanaris, also anglicised as Constantine Kanaris or Canaris, was a Greek admiral, Prime Minister, and a hero of the Greek War of Independence.
Alexander Ypsilantis
 24
Alexandros Ypsilantis was a Greek nationalist politician who was member of a prominent Phanariot Greek family, a prince of the Danubian Principalities, a senior officer of the Imperial Russian...
24
Alexandros Ypsilantis was a Greek nationalist politician who was member of a prominent Phanariot Greek family, a prince of the Danubian Principalities, a senior officer of the Imperial Russian...
Aristotle
 22
Aristotle was an Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, and the...
22
Aristotle was an Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, and the...
Saint Nicholas
 22
Saint Nicholas of Myra, also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greek descent from the maritime city of Patara in Anatolia during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the...
22
Saint Nicholas of Myra, also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greek descent from the maritime city of Patara in Anatolia during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the...
Demetrius of Thessaloniki
 21
Saint Demetrius of Thessalonica, also known as the Holy Great-Martyr Demetrius the Myroblyte, was a Greek Christian martyr of the early 4th century AD.
21
Saint Demetrius of Thessalonica, also known as the Holy Great-Martyr Demetrius the Myroblyte, was a Greek Christian martyr of the early 4th century AD.
Socrates
 21
Socrates was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure,...
21
Socrates was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure,...
Andreas Papandreou
 21
Andreas Georgiou Papandreou was a Greek economist, politician, and a dominant figure in Greek politics, known for founding the political party PASOK, which he led from 1974 to 1996. He served three...
21
Andreas Georgiou Papandreou was a Greek economist, politician, and a dominant figure in Greek politics, known for founding the political party PASOK, which he led from 1974 to 1996. He served three...
Konstantinos Karamanlis
 21
Konstantinos G. Karamanlis, commonly anglicised to Constantine Karamanlis or just Caramanlis, was a four-time Prime Minister of Greece and two-term president of the Third Hellenic Republic. A...
21
Konstantinos G. Karamanlis, commonly anglicised to Constantine Karamanlis or just Caramanlis, was a four-time Prime Minister of Greece and two-term president of the Third Hellenic Republic. A...
Poseidon
 20
Poseidon is one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses. He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many...
20
Poseidon is one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses. He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many...
Georgios Papandreou
 20
Georgios Papandreou was a Greek politician, the founder of the Papandreou political dynasty. He served three terms as prime minister of Greece. He was also deputy prime minister from 1950 to 1952, in...
20
Georgios Papandreou was a Greek politician, the founder of the Papandreou political dynasty. He served three terms as prime minister of Greece. He was also deputy prime minister from 1950 to 1952, in...
Nikolaos Plastiras
 19
Nikolaos Plastiras was a Greek general and politician, who served twice as Prime Minister of Greece. A distinguished soldier known for his personal bravery, he became famous as "The Black Rider"...
19
Nikolaos Plastiras was a Greek general and politician, who served twice as Prime Minister of Greece. A distinguished soldier known for his personal bravery, he became famous as "The Black Rider"...
Georgios Karaiskakis
 19
Georgios Karaiskakis, born Georgios Karaiskos, was a Greek military commander and a leader of the Greek War of Independence.
19
Georgios Karaiskakis, born Georgios Karaiskos, was a Greek military commander and a leader of the Greek War of Independence.
Lord Byron
 19
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron was a British poet and peer. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest of English poets. Among his...
19
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron was a British poet and peer. He is one of the major figures of the Romantic movement, and is regarded as being among the greatest of English poets. Among his...
Pericles
 19
Pericles was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Ancient Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the...
19
Pericles was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Ancient Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the...
Charilaos Trikoupis
 18
Charilaos Trikoupis was a Greek politician who served as a Prime Minister of Greece seven times from 1875 until 1895.
18
Charilaos Trikoupis was a Greek politician who served as a Prime Minister of Greece seven times from 1875 until 1895.
Alexandros Papanastasiou
 18
Alexandros Papanastasiou was a Greek lawyer, sociologist and politician who served twice as the Prime Minister of Greece in the interwar period, being a pioneer in the establishment of the Second...
18
Alexandros Papanastasiou was a Greek lawyer, sociologist and politician who served twice as the Prime Minister of Greece in the interwar period, being a pioneer in the establishment of the Second...
Philip II of Macedon
 17
Philip II of Macedon was the king (basileus) of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ancient kingdom, and the...
17
Philip II of Macedon was the king (basileus) of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ancient kingdom, and the...
Andreas Miaoulis
 17
Andreas Vokos, better known by his nickname Miaoulis, was a Greek revolutionary, admiral, and politician who commanded Greek naval forces during the Greek War of Independence (1821–1829).
17
Andreas Vokos, better known by his nickname Miaoulis, was a Greek revolutionary, admiral, and politician who commanded Greek naval forces during the Greek War of Independence (1821–1829).
Homer
 17
Homer was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the most revered...
17
Homer was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the most revered...
Markos Botsaris
 17
Markos Botsaris was a Souliot chieftain, general of the Greek revolutionary army and hero of the Greek War of Independence. He played a key role in relieving the First Siege of Missolonghi in...
17
Markos Botsaris was a Souliot chieftain, general of the Greek revolutionary army and hero of the Greek War of Independence. He played a key role in relieving the First Siege of Missolonghi in...
Kostis Palamas
 16
Kostis Palamas was a Greek poet who wrote the words to the Olympic Hymn. He was a central figure of the Greek literary generation of the 1880s and one of the cofounders of the so-called New Athenian...
16
Kostis Palamas was a Greek poet who wrote the words to the Olympic Hymn. He was a central figure of the Greek literary generation of the 1880s and one of the cofounders of the so-called New Athenian...
Artemis
 15
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Artemis is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, nature, vegetation, childbirth, care of children, and chastity. In later times, she was...
15
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Artemis is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, nature, vegetation, childbirth, care of children, and chastity. In later times, she was...
Xenophon
 15
Xenophon of Athens was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies of the...
15
Xenophon of Athens was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies of the...
Achilles
 15
In Greek mythology, Achilles or Achilleus was a hero of the Trojan War who was known as being the greatest of all the Greek warriors. A central character in Homer's Iliad, he was the son of the...
15
In Greek mythology, Achilles or Achilleus was a hero of the Trojan War who was known as being the greatest of all the Greek warriors. A central character in Homer's Iliad, he was the son of the...
Laskarina Bouboulina
 15
Laskarina Pinotsi, commonly known as Bouboulina, was a Greek naval commander, heroine of the Greek War of Independence in 1821, and considered perhaps the first woman to attain the rank of admiral.
15
Laskarina Pinotsi, commonly known as Bouboulina, was a Greek naval commander, heroine of the Greek War of Independence in 1821, and considered perhaps the first woman to attain the rank of admiral.
Constantine the Great
 14
Constantine I, also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a pivotal role in elevating the status of...
14
Constantine I, also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a pivotal role in elevating the status of...
Dionysios Solomos
 14
Dionysios Solomos was a Greek poet from Zakynthos, who is considered to be Greece's national poet. He is best known for writing the Hymn to Liberty, which was set to music by Nikolaos Mantzaros and...
14
Dionysios Solomos was a Greek poet from Zakynthos, who is considered to be Greece's national poet. He is best known for writing the Hymn to Liberty, which was set to music by Nikolaos Mantzaros and...
Panagis Tsaldaris
 14
Panagis Tsaldaris was a Greek politician who served as Prime Minister of Greece twice. He was a revered conservative politician and leader for many years (1922–1936) of the conservative People's...
14
Panagis Tsaldaris was a Greek politician who served as Prime Minister of Greece twice. He was a revered conservative politician and leader for many years (1922–1936) of the conservative People's...
Komnenos
 14
The House of Komnenos, Latinized as Comnenus, was a Byzantine Greek noble family who ruled the Byzantine Empire in the 11th and 12th centuries. The first reigning member, Isaac I Komnenos, ruled from...
14
The House of Komnenos, Latinized as Comnenus, was a Byzantine Greek noble family who ruled the Byzantine Empire in the 11th and 12th centuries. The first reigning member, Isaac I Komnenos, ruled from...
Thucydides
 14
Thucydides was an Athenian historian and general. His History of the Peloponnesian War recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed...
14
Thucydides was an Athenian historian and general. His History of the Peloponnesian War recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed...
Justinian I
 14
Justinian I, also known as Justinian the Great, was the Eastern Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
14
Justinian I, also known as Justinian the Great, was the Eastern Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
Yannis Makriyannis
 14
Yiannis Makriyiannis, born Ioannis Triantaphyllou, was a Greek merchant, military officer, politician and author, best known today for his Memoirs. Starting from humble origins, he joined the Greek...
14
Yiannis Makriyiannis, born Ioannis Triantaphyllou, was a Greek merchant, military officer, politician and author, best known today for his Memoirs. Starting from humble origins, he joined the Greek...
Constantine I of Greece
 14
Constantine I was King of Greece from 18 March 1913 to 11 June 1917 and from 19 December 1920 to 27 September 1922. He was commander-in-chief of the Hellenic Army during the unsuccessful...
14
Constantine I was King of Greece from 18 March 1913 to 11 June 1917 and from 19 December 1920 to 27 September 1922. He was commander-in-chief of the Hellenic Army during the unsuccessful...
Grigoris Lambrakis
 14
Grigoris Lambrakis was a Greek politician, physician, athlete, and lecturer. He participated in track and field sports and was a member of the faculty of the School of Medicine at the University of...
14
Grigoris Lambrakis was a Greek politician, physician, athlete, and lecturer. He participated in track and field sports and was a member of the faculty of the School of Medicine at the University of...
Athanasios Diakos
 14
Athanasios Nikolaos Massavetas
or Grammatikos also known as Athanasios Diakos was a Greek military commander during the Greek War of Independence, considered a venerable national hero in Greece.
14
Athanasios Nikolaos Massavetas
or Grammatikos also known as Athanasios Diakos was a Greek military commander during the Greek War of Independence, considered a venerable national hero in Greece.
Apollo
 14
Apollo is one of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing...
14
Apollo is one of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing...
Constantine XI Palaiologos
 13
Constantine XI Dragases Palaiologos or Dragaš Palaeologus was the last Roman (Byzantine) emperor, reigning from 1449 until his death in battle at the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. Constantine's...
13
Constantine XI Dragases Palaiologos or Dragaš Palaeologus was the last Roman (Byzantine) emperor, reigning from 1449 until his death in battle at the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. Constantine's...
Alexandros Panagoulis
 13
Alexandros Panagoulis was a Greek politician and poet. He took an active role in the fight against the Regime of the Colonels (1967–1974) in Greece. He became famous for his attempt to assassinate...
13
Alexandros Panagoulis was a Greek politician and poet. He took an active role in the fight against the Regime of the Colonels (1967–1974) in Greece. He became famous for his attempt to assassinate...
Gregory V of Constantinople
 13
Gregory V, born Georgios Angelopoulos, was Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 1797 to 1798, from 1806 to 1808, and from 1818 to 1821. He was responsible for much restoration work to the...
13
Gregory V, born Georgios Angelopoulos, was Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 1797 to 1798, from 1806 to 1808, and from 1818 to 1821. He was responsible for much restoration work to the...
Adamantios Korais
 13
Adamantios Korais or Koraïs was a Greek scholar credited with laying the foundations of modern Greek literature and a major figure in the Greek Enlightenment. His activities paved the way for the...
13
Adamantios Korais or Koraïs was a Greek scholar credited with laying the foundations of modern Greek literature and a major figure in the Greek Enlightenment. His activities paved the way for the...
Asclepius
 13
Asclepius is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Greek religion and mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis, or Arsinoe, or of Apollo alone. Asclepius represents the healing aspect of the...
13
Asclepius is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Greek religion and mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis, or Arsinoe, or of Apollo alone. Asclepius represents the healing aspect of the...
Paraskeva of the Balkans
Plato
 13
Plato, born Aristocles, was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the written dialogue and dialectic...
13
Plato, born Aristocles, was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the written dialogue and dialectic...
George Averoff
 12
George M. Averoff, alternately Jorgos Averof or Georgios Averof, was a Greek businessman and philanthropist. He is one of the great national benefactors of Greece. Born in the town of Metsovo,...
12
George M. Averoff, alternately Jorgos Averof or Georgios Averof, was a Greek businessman and philanthropist. He is one of the great national benefactors of Greece. Born in the town of Metsovo,...
Herodotus
 12
Herodotus was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He is known for having written...
12
Herodotus was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He is known for having written...
Aphrodite
 12
Aphrodite is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, procreation, and as her syncretized Roman goddess counterpart Venus, desire, sex, fertility, prosperity,...
12
Aphrodite is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, procreation, and as her syncretized Roman goddess counterpart Venus, desire, sex, fertility, prosperity,...
Democritus
 12
Democritus was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe.
12
Democritus was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe.
Solon
 12
Solon was an archaic Athenian statesman, lawmaker, political philosopher, and poet. He is one of the Seven Sages of Greece and credited with laying the foundations for Athenian democracy. Solon's...
12
Solon was an archaic Athenian statesman, lawmaker, political philosopher, and poet. He is one of the Seven Sages of Greece and credited with laying the foundations for Athenian democracy. Solon's...
Lycurgus (lawgiver)
 11
Lycurgus was the legendary lawgiver of Sparta. He is credited with establishing the military-oriented reformation of Spartan society in accordance with the Oracle of Apollo at Delphi. All his reforms...
11
Lycurgus was the legendary lawgiver of Sparta. He is credited with establishing the military-oriented reformation of Spartan society in accordance with the Oracle of Apollo at Delphi. All his reforms...
Hephaestus
 11
Hephaestus is the Greek god of artisans, blacksmiths, carpenters, craftsmen, fire, metallurgy, metalworking, sculpture and volcanoes. Hephaestus's Roman counterpart is Vulcan. In Greek mythology,...
11
Hephaestus is the Greek god of artisans, blacksmiths, carpenters, craftsmen, fire, metallurgy, metalworking, sculpture and volcanoes. Hephaestus's Roman counterpart is Vulcan. In Greek mythology,...
George I of Greece
 11
George I was King of Greece from 30 March 1863 until his assassination in 1913.
11
George I was King of Greece from 30 March 1863 until his assassination in 1913.
Konstantinos Davakis
 11
Konstantinos Davakis was a Greek military officer in World War II. He organized the Greek defensive lines during the Battle of Pindus that led to Italian defeat in the first stage of the...
11
Konstantinos Davakis was a Greek military officer in World War II. He organized the Greek defensive lines during the Battle of Pindus that led to Italian defeat in the first stage of the...
Alexandros Papadiamantis
 11
Alexandros Papadiamantis was an influential Greek novelist, short-story writer and poet.
11
Alexandros Papadiamantis was an influential Greek novelist, short-story writer and poet.
Alexander Fleming
 11
Sir Alexander Fleming was a Scottish physician and microbiologist, best known for discovering the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance, which he named penicillin. His discovery in...
11
Sir Alexander Fleming was a Scottish physician and microbiologist, best known for discovering the world's first broadly effective antibiotic substance, which he named penicillin. His discovery in...
Nikos Kazantzakis
 11
Nikos Kazantzakis was a Greek writer, journalist, politician, poet and philosopher. Widely considered a giant of modern Greek literature, he was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in nine...
11
Nikos Kazantzakis was a Greek writer, journalist, politician, poet and philosopher. Widely considered a giant of modern Greek literature, he was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in nine...
Themistocles
 11
Themistocles was an Athenian politician and general. He was one of a new breed of non-aristocratic politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy. As a politician,...
11
Themistocles was an Athenian politician and general. He was one of a new breed of non-aristocratic politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy. As a politician,...
Dimitrios Gounaris
 10
Dimitrios Gounaris was a Greek politician who served as the prime minister of Greece from 25 February to 10 August 1915 and 26 March 1921 to 3 May 1922. The leader of the People's Party, he was the...
10
Dimitrios Gounaris was a Greek politician who served as the prime minister of Greece from 25 February to 10 August 1915 and 26 March 1921 to 3 May 1922. The leader of the People's Party, he was the...
Germanos III of Old Patras
 10
Germanos III of Old Patras, born Georgios Kontzias, was an Orthodox Metropolitan of Patras. He played an important role in the Greek Revolution of 1821, having diplomatic and political activity.
10
Germanos III of Old Patras, born Georgios Kontzias, was an Orthodox Metropolitan of Patras. He played an important role in the Greek Revolution of 1821, having diplomatic and political activity.
Odysseas Androutsos
 10
Odysseas Androutsos was a Greek armatolos in eastern continental Greece and a prominent figure of the Greek War of Independence.
10
Odysseas Androutsos was a Greek armatolos in eastern continental Greece and a prominent figure of the Greek War of Independence.
Euripides
 10
Euripides was a tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars...
10
Euripides was a tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars...
Demosthenes
 10
Demosthenes was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual prowess and provide insight into the politics...
10
Demosthenes was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual prowess and provide insight into the politics...
Athanasius of Alexandria
 10
Athanasius I of Alexandria, also called Athanasius the Great, Athanasius the Confessor, or, among Coptic Christians, Athanasius the Apostolic, was a Christian theologian and the 20th pope of...
10
Athanasius I of Alexandria, also called Athanasius the Great, Athanasius the Confessor, or, among Coptic Christians, Athanasius the Apostolic, was a Christian theologian and the 20th pope of...
Theseus
 10
Theseus was a divine hero and the founder of Athens from Greek mythology. The myths surrounding Theseus, his journeys, exploits, and friends, have provided material for storytelling throughout the...
10
Theseus was a divine hero and the founder of Athens from Greek mythology. The myths surrounding Theseus, his journeys, exploits, and friends, have provided material for storytelling throughout the...
Heracles
 10
Heracles, born Alcaeus or Alcides, was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon. He was a descendant and half-brother of Perseus. He was the...
10
Heracles, born Alcaeus or Alcides, was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon. He was a descendant and half-brother of Perseus. He was the...
Hippocrates
 9
Hippocrates of Kos, also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally...
9
Hippocrates of Kos, also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally...
Ion Dragoumis
 9
Ion Dragoumis was a Greek diplomat, philosopher, writer and revolutionary.
9
Ion Dragoumis was a Greek diplomat, philosopher, writer and revolutionary.
Kostas Krystallis
 9
Kostas Krystallis was an Aromanian ethnic, Greek author and poet, representative of 19th century Greek pastoral literature. He was born an Ottoman subject in Epirus, but escaped to Greece after being...
9
Kostas Krystallis was an Aromanian ethnic, Greek author and poet, representative of 19th century Greek pastoral literature. He was born an Ottoman subject in Epirus, but escaped to Greece after being...
Diogenes
 9
Diogenes, also known as Diogenes the Cynic or Diogenes of Sinope, was a Greek philosopher and one of the founders of Cynicism. He was born in Sinope, an Ionian colony on the Black Sea coast of...
9
Diogenes, also known as Diogenes the Cynic or Diogenes of Sinope, was a Greek philosopher and one of the founders of Cynicism. He was born in Sinope, an Ionian colony on the Black Sea coast of...
Hera
 9
In ancient Greek religion, Hera is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount...
9
In ancient Greek religion, Hera is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount...
Sophocles
 9
Sophocles was an ancient Greek tragedian, known as one of three from whom at least one play has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or contemporary with, those of Aeschylus;...
9
Sophocles was an ancient Greek tragedian, known as one of three from whom at least one play has survived in full. His first plays were written later than, or contemporary with, those of Aeschylus;...
Aeschylus
 9
Aeschylus was an ancient Greek tragedian often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is largely based on...
9
Aeschylus was an ancient Greek tragedian often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is largely based on...
Marinos Antypas
 9
Marinos Antypas was a Greek lawyer, journalist, and critic who was one of the country's first socialists. He founded publications who were shuttered, was repeatedly arrested for his social criticism,...
9
Marinos Antypas was a Greek lawyer, journalist, and critic who was one of the country's first socialists. He founded publications who were shuttered, was repeatedly arrested for his social criticism,...
Sofoklis Venizelos
 9
Sofoklis Venizelos was a Greek politician who served three times as Prime Minister of Greece: in 1944, 1950 and 1950–1951.
9
Sofoklis Venizelos was a Greek politician who served three times as Prime Minister of Greece: in 1944, 1950 and 1950–1951.
George II of Greece
 8
George II was King of Greece from 27 September 1922 until 25 March 1924, and again from 25 November 1935 until his death on 1 April 1947.
8
George II was King of Greece from 27 September 1922 until 25 March 1924, and again from 25 November 1935 until his death on 1 April 1947.
Joachim II of Constantinople
 8
Joachim II was Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 1860 to 1863 and from 1873 to 1878.
8
Joachim II was Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 1860 to 1863 and from 1873 to 1878.
Papaflessas
 8
Grigorios Dimitrios Dikaios-Flessas, popularly known as Papaflessas was a Greek priest and government official who became one of the most influential figures during the Greek War of Independence. The...
8
Grigorios Dimitrios Dikaios-Flessas, popularly known as Papaflessas was a Greek priest and government official who became one of the most influential figures during the Greek War of Independence. The...
Andreas Syggros
 8
Andreas Syggros was a Greek banker from Istanbul, at the time known internationally as Constantinople, and a philanthropist.
Born in Istanbul to Chiot parents who left the island due to the Massacre...
8
Andreas Syggros was a Greek banker from Istanbul, at the time known internationally as Constantinople, and a philanthropist.
Born in Istanbul to Chiot parents who left the island due to the Massacre...
Cimon
 8
Cimon or Kimon was an Athenian strategos and politician.
8
Cimon or Kimon was an Athenian strategos and politician.
Athanasios Tsakalov
 8
Athanasios Tsakalov was a member of the Filiki Eteria, or a Greek patriotic organization against Ottoman rule.
8
Athanasios Tsakalov was a member of the Filiki Eteria, or a Greek patriotic organization against Ottoman rule.
Georgios Gennimatas
 8
Georgios Gennimatas was a Greek politician and founding member of the Panhellenic Socialist Movement (PASOK). He studied civil engineering at the National Technical University of Athens. He occupied...
8
Georgios Gennimatas was a Greek politician and founding member of the Panhellenic Socialist Movement (PASOK). He studied civil engineering at the National Technical University of Athens. He occupied...
Agesilaus II
 8
Agesilaus II was king of Sparta from c. 400 to c. 360 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony...
8
Agesilaus II was king of Sparta from c. 400 to c. 360 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony...
Orpheus
 8
In Greek mythology, Orpheus was a Thracian bard, legendary musician and prophet. He was also a renowned poet and, according to the legend, travelled with Jason and the Argonauts in search of the...
8
In Greek mythology, Orpheus was a Thracian bard, legendary musician and prophet. He was also a renowned poet and, according to the legend, travelled with Jason and the Argonauts in search of the...
Nikitaras
 8
Nikitaras was the nom de guerre of Nikitas Stamatelopoulos, a Greek revolutionary in the Greek War of Independence. Due to his fighting prowess, he was known as Turkofagos or Turkophagos, literally...
8
Nikitaras was the nom de guerre of Nikitas Stamatelopoulos, a Greek revolutionary in the Greek War of Independence. Due to his fighting prowess, he was known as Turkofagos or Turkophagos, literally...
Archimedes
 7
Archimedes of Syracuse was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is...
7
Archimedes of Syracuse was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is...
Olof Palme
 7
Sven Olof Joachim Palme was a Swedish politician and statesman who served as Prime Minister of Sweden from 1969 to 1976 and 1982 to 1986. Palme led the Swedish Social Democratic Party from 1969 until...
7
Sven Olof Joachim Palme was a Swedish politician and statesman who served as Prime Minister of Sweden from 1969 to 1976 and 1982 to 1986. Palme led the Swedish Social Democratic Party from 1969 until...
Praxiteles
 7
Praxiteles of Athens, the son of Cephisodotus the Elder, was the most renowned of the Attica sculptors of the 4th century BC. He was the first to sculpt the nude female form in a life-size statue....
7
Praxiteles of Athens, the son of Cephisodotus the Elder, was the most renowned of the Attica sculptors of the 4th century BC. He was the first to sculpt the nude female form in a life-size statue....
Melina Mercouri
 7
Maria Amalia "Melina" Mercouri was a Greek actress, singer, activist, and politician. She came from a political family that was prominent over multiple generations. She received an Academy Award...
7
Maria Amalia "Melina" Mercouri was a Greek actress, singer, activist, and politician. She came from a political family that was prominent over multiple generations. She received an Academy Award...
Themistoklis Sofoulis
 7
Themistoklis Sofoulis or Sophoulis was a prominent centrist and liberal Greek politician from Samos Island, who served three times as Prime Minister of Greece, with the Liberal Party, which he led...
7
Themistoklis Sofoulis or Sophoulis was a prominent centrist and liberal Greek politician from Samos Island, who served three times as Prime Minister of Greece, with the Liberal Party, which he led...
Aristophanes
 7
Aristophanes was an Ancient Greek comic playwright from Athens and a poet of Old Attic Comedy. He wrote in total forty plays, of which eleven survive virtually complete today. These provide the most...
7
Aristophanes was an Ancient Greek comic playwright from Athens and a poet of Old Attic Comedy. He wrote in total forty plays, of which eleven survive virtually complete today. These provide the most...
Antigone
 7
In Greek mythology, Antigone is a Theban princess, and a character in several ancient Greek tragedies. She is the daughter of Oedipus, king of Thebes. Her mother is Jocasta. In another variation of...
7
In Greek mythology, Antigone is a Theban princess, and a character in several ancient Greek tragedies. She is the daughter of Oedipus, king of Thebes. Her mother is Jocasta. In another variation of...
Charles Nicolas Fabvier
 7
Charles Nicolas Fabvier was an ambassador, general and French member of parliament who played a distinguished role in the Greek War of Independence.
7
Charles Nicolas Fabvier was an ambassador, general and French member of parliament who played a distinguished role in the Greek War of Independence.
Patroclus
 7
In Greek mythology, Patroclus was a Greek hero of the Trojan War and an important character in Homer's Iliad. Born in Opus, Patroclus was the son of the Argonaut Menoetius. When he was a child, he...
7
In Greek mythology, Patroclus was a Greek hero of the Trojan War and an important character in Homer's Iliad. Born in Opus, Patroclus was the son of the Argonaut Menoetius. When he was a child, he...
Dionysus
 7
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also...
7
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also...
Nikolaos Skoufas
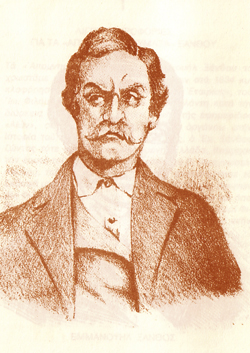 7
Nikolaos Skoufas was a founding member of the Filiki Eteria, a Greek conspiratorial organization against the Ottoman Empire.
7
Nikolaos Skoufas was a founding member of the Filiki Eteria, a Greek conspiratorial organization against the Ottoman Empire.
Nikolaos Votsis
 7
Nikolaos Votsis was a Greek naval officer who distinguished himself during the Balkan Wars and rose to the rank of Rear Admiral.
7
Nikolaos Votsis was a Greek naval officer who distinguished himself during the Balkan Wars and rose to the rank of Rear Admiral.
Kostas Varnalis
 7
Kostas Varnalis was a Greek poet.
7
Kostas Varnalis was a Greek poet.
Lambros Katsonis
 7
Lambros Katsonis was a Greek privateer of the 18th century who would ultimately sail under the Russian flag with the rank of colonel. He became a knight of the Russian Empire and was awarded the...
7
Lambros Katsonis was a Greek privateer of the 18th century who would ultimately sail under the Russian flag with the rank of colonel. He became a knight of the Russian Empire and was awarded the...
Ptolemy
 7
Claudius Ptolemy was an Alexandrian mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later...
7
Claudius Ptolemy was an Alexandrian mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later...
Dimitrios Papanikolis
 7
Dimitrios Papanikolis (1790–1855) was a naval hero of the Greek Revolution, famous for being the first to successfully employ a fireship to destroy an Ottoman ship of the line.
7
Dimitrios Papanikolis (1790–1855) was a naval hero of the Greek Revolution, famous for being the first to successfully employ a fireship to destroy an Ottoman ship of the line.
Jason
 6
Jason was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece is featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He...
6
Jason was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece is featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He...
Basil of Caesarea
 6
Basil of Caesarea, also called Saint Basil the Great, was a bishop of Caesarea Mazaca in Cappadocia, Asia Minor. He was an influential theologian who supported the Nicene Creed and opposed the...
6
Basil of Caesarea, also called Saint Basil the Great, was a bishop of Caesarea Mazaca in Cappadocia, Asia Minor. He was an influential theologian who supported the Nicene Creed and opposed the...
Nikolaos Kriezotis
 6
Nikolaos Kriezotis was a Greek soldier who served as a leader during the Greek War of Independence in Euboea.
6
Nikolaos Kriezotis was a Greek soldier who served as a leader during the Greek War of Independence in Euboea.
Olga Constantinovna of Russia
 6
Olga Constantinovna of Russia was Queen of Greece as the wife of King George I. She was briefly the regent of Greece in 1920.
6
Olga Constantinovna of Russia was Queen of Greece as the wife of King George I. She was briefly the regent of Greece in 1920.
Giorgos Seferis
 6
Giorgos or George Seferis, the pen name of Georgios Seferiadis, was a Greek poet and diplomat. He was one of the most important Greek poets of the 20th century, and a Nobel laureate.
6
Giorgos or George Seferis, the pen name of Georgios Seferiadis, was a Greek poet and diplomat. He was one of the most important Greek poets of the 20th century, and a Nobel laureate.
Iphigenia
 6
In Greek mythology, Iphigenia was a daughter of King Agamemnon and Queen Clytemnestra, and thus a princess of Mycenae.
6
In Greek mythology, Iphigenia was a daughter of King Agamemnon and Queen Clytemnestra, and thus a princess of Mycenae.
Cybele
 6
Cybele is an Anatolian mother goddess; she may have a possible forerunner in the earliest neolithic at Çatalhöyük. She is Phrygia's only known goddess, and was probably its national deity. Greek...
6
Cybele is an Anatolian mother goddess; she may have a possible forerunner in the earliest neolithic at Çatalhöyük. She is Phrygia's only known goddess, and was probably its national deity. Greek...
Paul the Apostle
 6
Paul, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is...
6
Paul, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Christian apostle who spread the teachings of Jesus in the first-century world. For his contributions towards the New Testament, he is...
Grigoris Afxentiou
 6
Grigoris Pieris Afxentiou was a Greek-Cypriot insurgent leader who led campaigns against the British colonial government as a member of EOKA. He was second-in-command to general Georgios Grivas and...
6
Grigoris Pieris Afxentiou was a Greek-Cypriot insurgent leader who led campaigns against the British colonial government as a member of EOKA. He was second-in-command to general Georgios Grivas and...
Gregory Orologas
 6
Saint Gregory (Orologas) of Kydonies the Ethno-Hieromartyr, also Gregory of Cydoniae, 1864–1922, was a Greek Orthodox metropolitan bishop in the early 20th century in northwest Anatolia, in the...
6
Saint Gregory (Orologas) of Kydonies the Ethno-Hieromartyr, also Gregory of Cydoniae, 1864–1922, was a Greek Orthodox metropolitan bishop in the early 20th century in northwest Anatolia, in the...
Amalia of Oldenburg
 6
Amalia of Oldenburg was a Oldenburg princess who became Queen of Greece from 1836 to 1862 as the wife of King Otto Friedrich Ludwig. She was loved widely by the Greeks due to her patriotic love for...
6
Amalia of Oldenburg was a Oldenburg princess who became Queen of Greece from 1836 to 1862 as the wife of King Otto Friedrich Ludwig. She was loved widely by the Greeks due to her patriotic love for...
Hadrian
 6
Hadrian was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, the Aeli Hadriani,...
6
Hadrian was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, the Aeli Hadriani,...
Saint Barbara
 6
Saint Barbara, known in the Eastern Orthodox Church as the Great Martyr Barbara, was an early Christian Greek saint and martyr.
6
Saint Barbara, known in the Eastern Orthodox Church as the Great Martyr Barbara, was an early Christian Greek saint and martyr.
Paul of Greece
 6
Paul was King of Greece, reigning from 1 April 1947 until his death on 6 March 1964.
6
Paul was King of Greece, reigning from 1 April 1947 until his death on 6 March 1964.
Priam
 5
In Greek mythology, Priam was the legendary and last king of Troy during the Trojan War. He was the son of Laomedon. His many children included notable characters such as Hector, Paris, and Cassandra.
5
In Greek mythology, Priam was the legendary and last king of Troy during the Trojan War. He was the son of Laomedon. His many children included notable characters such as Hector, Paris, and Cassandra.
Alexandros Papagos
 5
Alexandros Papagos was a Greek army officer who led the Hellenic Army in World War II and the later stages of the subsequent Greek Civil War. The only Greek career officer to rise to the rank of...
5
Alexandros Papagos was a Greek army officer who led the Hellenic Army in World War II and the later stages of the subsequent Greek Civil War. The only Greek career officer to rise to the rank of...
Emmanouel Pappas
 5
Emmanouel Pappas was a prominent member of Filiki Eteria and leader of the Greek War of Independence in Macedonia.
5
Emmanouel Pappas was a prominent member of Filiki Eteria and leader of the Greek War of Independence in Macedonia.
Lucian
 5
Lucian of Samosata was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer who is best known for his characteristic tongue-in-cheek style, with which he frequently ridiculed superstition,...
5
Lucian of Samosata was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer who is best known for his characteristic tongue-in-cheek style, with which he frequently ridiculed superstition,...
John I Tzimiskes
 5
John I Tzimiskes was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general who married into the influential Skleros family, he strengthened and expanded the Byzantine...
5
John I Tzimiskes was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general who married into the influential Skleros family, he strengthened and expanded the Byzantine...
Plutarch
 5
Plutarch was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his Parallel Lives, a series of biographies...
5
Plutarch was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his Parallel Lives, a series of biographies...
Prometheus
 5
In Greek mythology, Prometheus is one of the Titans and a god of fire. Prometheus is best known for defying the Olympian gods by stealing fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of...
5
In Greek mythology, Prometheus is one of the Titans and a god of fire. Prometheus is best known for defying the Olympian gods by stealing fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of...
Basil II
 5
Basil II Porphyrogenitus, nicknamed the Bulgar Slayer, was the senior Byzantine emperor from 976 to 1025. He and his brother Constantine VIII were crowned before their father Romanos II died in 963,...
5
Basil II Porphyrogenitus, nicknamed the Bulgar Slayer, was the senior Byzantine emperor from 976 to 1025. He and his brother Constantine VIII were crowned before their father Romanos II died in 963,...
Eusebius
 5
Eusebius of Caesarea, also known as Eusebius Pamphilus, was a Greek Syro-Palestinian historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea...
5
Eusebius of Caesarea, also known as Eusebius Pamphilus, was a Greek Syro-Palestinian historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea...
Angelos Sikelianos
 5
Angelos Sikelianos was a Greek lyric poet and playwright. His themes include Greek history, religious symbolism as well as universal harmony in poems such as The Moonstruck, Prologue to Life, Mother...
5
Angelos Sikelianos was a Greek lyric poet and playwright. His themes include Greek history, religious symbolism as well as universal harmony in poems such as The Moonstruck, Prologue to Life, Mother...
Odysseus
 5
In Greek and Roman mythology, Odysseus, also known by the Latin variant Ulysses, is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the Odyssey. Odysseus also plays a key role in...
5
In Greek and Roman mythology, Odysseus, also known by the Latin variant Ulysses, is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the Odyssey. Odysseus also plays a key role in...
Petros Protopapadakis
 5
Petros Protopapadakis was a politician and Prime Minister of Greece from May to September 1922.
5
Petros Protopapadakis was a politician and Prime Minister of Greece from May to September 1922.
John the Apostle
 5
John the Apostle, also known as Saint John the Beloved and, in Eastern Orthodox Christianity, Saint John the Theologian, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament....
5
John the Apostle, also known as Saint John the Beloved and, in Eastern Orthodox Christianity, Saint John the Theologian, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament....
Anaxagoras
 5
Anaxagoras was a Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. Born in Clazomenae at a time when Asia Minor was under the control of the Persian Empire, Anaxagoras came to Athens. In later life he was charged with...
5
Anaxagoras was a Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. Born in Clazomenae at a time when Asia Minor was under the control of the Persian Empire, Anaxagoras came to Athens. In later life he was charged with...
Demeter
 5
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although Demeter is mostly...
5
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although Demeter is mostly...
Μαριανίνα Κριεζή
 5
Η Μαριανίνα Κριεζή (1947-2022) ήταν Ελληνίδα στιχουργός, παραγωγός του ραδιοφώνου, συγγραφέας και μεταφράστρια.
5
Η Μαριανίνα Κριεζή (1947-2022) ήταν Ελληνίδα στιχουργός, παραγωγός του ραδιοφώνου, συγγραφέας και μεταφράστρια.
Nikephoros II Phokas
 5
Nikephoros II Phokas, Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless greatly contributed...
5
Nikephoros II Phokas, Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless greatly contributed...
Otto of Greece
 5
Otto was a Bavarian prince who ruled as King of Greece from the establishment of the Kingdom of Greece on 27 May 1832, under the Convention of London, until he was deposed in October 1862.
5
Otto was a Bavarian prince who ruled as King of Greece from the establishment of the Kingdom of Greece on 27 May 1832, under the Convention of London, until he was deposed in October 1862.
Saint Spyridon
Pluto (mythology)
 5
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Pluto was the ruler of the Greek underworld. The earlier name for the god was Hades, which became more common as the name of the underworld itself. Pluto...
5
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Pluto was the ruler of the Greek underworld. The earlier name for the god was Hades, which became more common as the name of the underworld itself. Pluto...
Pythagoras
 5
Pythagoras of Samos was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and...
5
Pythagoras of Samos was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and...
Theodoros Diligiannis
 5
Theodoros Deligiannis was a Greek politician, minister and member of the Greek Parliament, who served as Prime Minister of Greece five times from 1885 until his assassination.
5
Theodoros Deligiannis was a Greek politician, minister and member of the Greek Parliament, who served as Prime Minister of Greece five times from 1885 until his assassination.
Theophrastus
 5
Theophrastus was a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos. His given name was Τύρταμος (Túrtamos); his nickname Θεόφραστος...
5
Theophrastus was a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos. His given name was Τύρταμος (Túrtamos); his nickname Θεόφραστος...
El Greco
 4
Doménikos Theotokópoulos, most widely known as El Greco, was a Greek painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. El Greco was a nickname, and the artist normally signed his paintings...
4
Doménikos Theotokópoulos, most widely known as El Greco, was a Greek painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. El Greco was a nickname, and the artist normally signed his paintings...
Menelaus
 4
In Greek mythology, Menelaus was a Greek king of Mycenaean (pre-Dorian) Sparta. According to the Iliad, the Trojan war began as a result of Menelaus’s wife, Helen, fleeing to Troy with the Trojan...
4
In Greek mythology, Menelaus was a Greek king of Mycenaean (pre-Dorian) Sparta. According to the Iliad, the Trojan war began as a result of Menelaus’s wife, Helen, fleeing to Troy with the Trojan...
Cassander
 4
Cassander was king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 305 BC until 297 BC, and de facto ruler of southern Greece from 317 BC until his death.
4
Cassander was king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 305 BC until 297 BC, and de facto ruler of southern Greece from 317 BC until his death.
Helena, mother of Constantine I
 4
Flavia Julia Helena, also known as Helena of Constantinople and in Christianity as Saint Helena, was an Augusta of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine the Great. She was born in the...
4
Flavia Julia Helena, also known as Helena of Constantinople and in Christianity as Saint Helena, was an Augusta of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine the Great. She was born in the...
Αθανάσιος Νικομηδείας
 4
Ο Αθανάσιος Νικομηδείας, ή Αθανάσιος ο του Καρύδη, ήταν Κύπριος επίσκοπος αρχικά Λιβύης, αργότερα μητροπολίτης Νικομηδείας και εθνομάρτυρας του 1821.
4
Ο Αθανάσιος Νικομηδείας, ή Αθανάσιος ο του Καρύδη, ήταν Κύπριος επίσκοπος αρχικά Λιβύης, αργότερα μητροπολίτης Νικομηδείας και εθνομάρτυρας του 1821.
Thetis
 4
Thetis is a figure from Greek mythology with varying mythological roles. She mainly appears as a sea nymph, a goddess of water, and one of the 50 Nereids, daughters of the ancient sea god Nereus.
4
Thetis is a figure from Greek mythology with varying mythological roles. She mainly appears as a sea nymph, a goddess of water, and one of the 50 Nereids, daughters of the ancient sea god Nereus.
Γεώργιος Σουρής
 4
Ο Γεώργιος Σουρής ήταν Έλληνας σατιρικός ποιητής και ένας από τους σπουδαιότερους της νεότερης Ελλάδας, έχοντας χαρακτηριστεί ως «σύγχρονος Αριστοφάνης». Κατά τη διάρκεια της ζωής του προτάθηκε για...
4
Ο Γεώργιος Σουρής ήταν Έλληνας σατιρικός ποιητής και ένας από τους σπουδαιότερους της νεότερης Ελλάδας, έχοντας χαρακτηριστεί ως «σύγχρονος Αριστοφάνης». Κατά τη διάρκεια της ζωής του προτάθηκε για...
Ajax the Great
 4
Ajax or Aias is a Greek mythological hero, the son of King Telamon and Periboea, and the half-brother of Teucer. He plays an important role in the Trojan War, and is portrayed as a towering figure...
4
Ajax or Aias is a Greek mythological hero, the son of King Telamon and Periboea, and the half-brother of Teucer. He plays an important role in the Trojan War, and is portrayed as a towering figure...
Hector
 4
In Greek mythology, Hector is a Trojan prince, and one of four sons to the King of Troy, he was a hero and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. He is a major character in Homer's...
4
In Greek mythology, Hector is a Trojan prince, and one of four sons to the King of Troy, he was a hero and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. He is a major character in Homer's...
Spyridon Louis
 4
Spyridon Louis, commonly known as Spyros Louis, was a Greek water carrier who won the first modern-day Olympic marathon at the 1896 Summer Olympics. Following his victory, he was celebrated as a...
4
Spyridon Louis, commonly known as Spyros Louis, was a Greek water carrier who won the first modern-day Olympic marathon at the 1896 Summer Olympics. Following his victory, he was celebrated as a...
Electra
 4
Electra, also spelt Elektra, is one of the most popular mythological characters in tragedies. She is the main character in two Greek tragedies, Electra by Sophocles and Electra by Euripides. She is...
4
Electra, also spelt Elektra, is one of the most popular mythological characters in tragedies. She is the main character in two Greek tragedies, Electra by Sophocles and Electra by Euripides. She is...
Alcibiades
 4
Alcibiades was an Athenian statesman and general. The last of the Alcmaeonidae, he played a major role in the second half of the Peloponnesian War as a strategic advisor, military commander, and...
4
Alcibiades was an Athenian statesman and general. The last of the Alcmaeonidae, he played a major role in the second half of the Peloponnesian War as a strategic advisor, military commander, and...
Pausanias
 4
Pausanias may refer to:Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
Pausanias of Sicily, physician of the 5th century BC, who was a friend of Empedocles
Pausanias of Athens,...
4
Pausanias may refer to:Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
Pausanias of Sicily, physician of the 5th century BC, who was a friend of Empedocles
Pausanias of Athens,...
Heraclitus
 4
Heraclitus was an ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from the city of Ephesus, which was then part of the Persian Empire.
4
Heraclitus was an ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from the city of Ephesus, which was then part of the Persian Empire.
Hesperides
 4
In Greek mythology, the Hesperides are the nymphs of evening and golden light of sunsets, who were the "Daughters of the Evening" or "Nymphs of the West". They were also called the Atlantides from...
4
In Greek mythology, the Hesperides are the nymphs of evening and golden light of sunsets, who were the "Daughters of the Evening" or "Nymphs of the West". They were also called the Atlantides from...
Dimitris Plapoutas
 4
Dimitris 'Koliopoulos' Plapoutas was a Greek general who fought during the Greek War of Independence against the rule of the Ottoman Empire.
4
Dimitris 'Koliopoulos' Plapoutas was a Greek general who fought during the Greek War of Independence against the rule of the Ottoman Empire.
Daedalus
 4
In Greek mythology, Daedalus was a skillful architect and craftsman, seen as a symbol of wisdom, knowledge and power. He is the father of Icarus, the uncle of Perdix, and possibly also the father of...
4
In Greek mythology, Daedalus was a skillful architect and craftsman, seen as a symbol of wisdom, knowledge and power. He is the father of Icarus, the uncle of Perdix, and possibly also the father of...
Epimenides
 4
Epimenides of Knossos was a semi-mythical 7th or 6th century BC Greek seer and philosopher-poet, from Knossos or Phaistos.
4
Epimenides of Knossos was a semi-mythical 7th or 6th century BC Greek seer and philosopher-poet, from Knossos or Phaistos.
Saint Phanourios
 4
Saint Phanourios also known as St. Phanourios the Newly-Manifest is recognized as a saint by the Eastern Orthodox Church. He is commemorated on August 27.
4
Saint Phanourios also known as St. Phanourios the Newly-Manifest is recognized as a saint by the Eastern Orthodox Church. He is commemorated on August 27.
Miltos Sachtouris
 4
Miltos Sachtouris was a Greek poet. He was a descendant of Georgios Sachtouris, whose origins were the Island of Ydra. When he was young he abandoned his law studies to follow his real passion,...
4
Miltos Sachtouris was a Greek poet. He was a descendant of Georgios Sachtouris, whose origins were the Island of Ydra. When he was young he abandoned his law studies to follow his real passion,...
Georgios Papanikolaou
 4
Georgios Nikolaou Papanikolaou was a Greek physician, zoologist and microscopist who was a pioneer in cytopathology and early cancer detection, and inventor of the "Pap smear".
4
Georgios Nikolaou Papanikolaou was a Greek physician, zoologist and microscopist who was a pioneer in cytopathology and early cancer detection, and inventor of the "Pap smear".
Medea
 4
In Greek mythology, Medea is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis.
In the myth of Jason and the Argonauts, she aids Jason in his search for the Golden Fleece. She later marries him, but eventually...
4
In Greek mythology, Medea is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis.
In the myth of Jason and the Argonauts, she aids Jason in his search for the Golden Fleece. She later marries him, but eventually...
Saint Pantaleon
 4
Saint Pantaleon, counted in Western Christianity as among the Fourteen Holy Helpers of the Late Middle Ages, and in Eastern Christianity as one of the Holy Unmercenary Healers, was a martyr of...
4
Saint Pantaleon, counted in Western Christianity as among the Fourteen Holy Helpers of the Late Middle Ages, and in Eastern Christianity as one of the Holy Unmercenary Healers, was a martyr of...
Οικογένεια Παπαστράτου
 4
Η Οικογένεια Παπαστράτου είναι παλιά οικογένεια βιομηχάνων της Ελλάδας, και μεγάλοι ευεργέτες του Αγρινίου, της Αθήνας και του Πειραιά όπου και η ιδιαίτερη συνοικία.
4
Η Οικογένεια Παπαστράτου είναι παλιά οικογένεια βιομηχάνων της Ελλάδας, και μεγάλοι ευεργέτες του Αγρινίου, της Αθήνας και του Πειραιά όπου και η ιδιαίτερη συνοικία.
Phocion
 4
Phocion, nicknamed The Good (ὁ χρηστός, was an Athenian statesman and strategos, and the subject of one of Plutarch's Parallel Lives.
4
Phocion, nicknamed The Good (ὁ χρηστός, was an Athenian statesman and strategos, and the subject of one of Plutarch's Parallel Lives.
Persephone
 4
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone, also called Kore or Cora, is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after her abduction by her uncle Hades, the...
4
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone, also called Kore or Cora, is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after her abduction by her uncle Hades, the...
Cleanthes
 4
Cleanthes, of Assos, was a Greek Stoic philosopher and boxer who was the successor to Zeno of Citium as the second head (scholarch) of the Stoic school in Athens. Originally a boxer, he came to...
4
Cleanthes, of Assos, was a Greek Stoic philosopher and boxer who was the successor to Zeno of Citium as the second head (scholarch) of the Stoic school in Athens. Originally a boxer, he came to...
Pindar
 4
Pindar was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar is by far...
4
Pindar was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar is by far...
Manto Mavrogenous
 4
Manto Mavrogenous was a Greek princess and heroine of the Greek War of Independence. An extremely wealthy aristocrat, she contributed her fortune for the Hellenic cause. Under her encouragement, her...
4
Manto Mavrogenous was a Greek princess and heroine of the Greek War of Independence. An extremely wealthy aristocrat, she contributed her fortune for the Hellenic cause. Under her encouragement, her...
Isocrates
 4
Isocrates was an ancient Greek rhetorician, one of the ten Attic orators. Among the most influential Greek rhetoricians of his time, Isocrates made many contributions to rhetoric and education...
4
Isocrates was an ancient Greek rhetorician, one of the ten Attic orators. Among the most influential Greek rhetoricians of his time, Isocrates made many contributions to rhetoric and education...
Epameinondas Zymvrakakis
 4
Epameinondas Zymbrakakis or Pamikos Zymbrakakis was a Greek Lieutenant General who fought in World War I.
4
Epameinondas Zymbrakakis or Pamikos Zymbrakakis was a Greek Lieutenant General who fought in World War I.
Aspasia
 4
Aspasia was a metic woman in Classical Athens. Born in Miletus, she moved to Athens and began a relationship with the statesman Pericles, with whom she had a son, Pericles the Younger. According to...
4
Aspasia was a metic woman in Classical Athens. Born in Miletus, she moved to Athens and began a relationship with the statesman Pericles, with whom she had a son, Pericles the Younger. According to...
Tantalus
 4
Tantalus, also called Atys, was a Greek mythological figure, most famous for his punishment in Tartarus: for trying to trick the gods into eating his son, he was made to stand in a pool of water...
4
Tantalus, also called Atys, was a Greek mythological figure, most famous for his punishment in Tartarus: for trying to trick the gods into eating his son, he was made to stand in a pool of water...
Amphitrite
 4
In ancient Greek mythology, Amphitrite was the goddess of the sea, the queen of the sea, and her consort is Poseidon. She was a daughter of Nereus and Doris. Under the influence of the Olympian...
4
In ancient Greek mythology, Amphitrite was the goddess of the sea, the queen of the sea, and her consort is Poseidon. She was a daughter of Nereus and Doris. Under the influence of the Olympian...
Anthony the Great
 4
Anthony the Great was a Christian monk from Egypt, revered since his death as a saint. He is distinguished from other saints named Anthony, such as Anthony of Padua, by various epithets: Anthony of...
4
Anthony the Great was a Christian monk from Egypt, revered since his death as a saint. He is distinguished from other saints named Anthony, such as Anthony of Padua, by various epithets: Anthony of...
Asimakis Fotilas
 4
Asimakis Fotilas (1761–1835) was a Greek politician and a revolutionary leader.
4
Asimakis Fotilas (1761–1835) was a Greek politician and a revolutionary leader.
Telemachus
 4
Telemachus, in Greek mythology, is the son of Odysseus and Penelope, who is a central character in Homer's Odyssey. When Telemachus reached manhood, he visited Pylos and Sparta in search of his...
4
Telemachus, in Greek mythology, is the son of Odysseus and Penelope, who is a central character in Homer's Odyssey. When Telemachus reached manhood, he visited Pylos and Sparta in search of his...
Nectarios of Aegina
Kosmas the Aetolian
 4
Kosmas the Aetolian, sometimes Cosmas the Aetolian or Patrokosmas "Father Kosmas", was a monk in the Greek Orthodox Church. He is recognized as one of the originators of the twentieth-century...
4
Kosmas the Aetolian, sometimes Cosmas the Aetolian or Patrokosmas "Father Kosmas", was a monk in the Greek Orthodox Church. He is recognized as one of the originators of the twentieth-century...
Codrus
 4
Codrus was the last of the semi-mythical Kings of Athens. He was an ancient exemplar of patriotism and self-sacrifice. He was succeeded by his son Medon, who it is claimed ruled not as king but as...
4
Codrus was the last of the semi-mythical Kings of Athens. He was an ancient exemplar of patriotism and self-sacrifice. He was succeeded by his son Medon, who it is claimed ruled not as king but as...
Napoleon Zervas
 3
Napoleon Zervas was a Hellenic Army officer and resistance leader during World War II. He organized and led the National Republican Greek League (EDES), the second most significant, in terms of size...
3
Napoleon Zervas was a Hellenic Army officer and resistance leader during World War II. He organized and led the National Republican Greek League (EDES), the second most significant, in terms of size...
Aikaterini Laskaridou
 3
Aikaterini Laskaridou (1842–1916) was a Greek feminist and educator who created the kindergarten system in Greece and introduced physical exercise into the girls' schools.
3
Aikaterini Laskaridou (1842–1916) was a Greek feminist and educator who created the kindergarten system in Greece and introduced physical exercise into the girls' schools.
Zeno of Elea
 3
Zeno of Elea was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. He was a student of Parmenides and one of the Eleatics. Born in Elea, Zeno defended his instructor's belief in monism, the idea that only one single...
3
Zeno of Elea was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. He was a student of Parmenides and one of the Eleatics. Born in Elea, Zeno defended his instructor's belief in monism, the idea that only one single...
Galen
 3
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus, often anglicized as Galen or Galen of Pergamon, was a Roman and Greek physician, surgeon, and philosopher. Considered to be one of the most accomplished of all...
3
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus, often anglicized as Galen or Galen of Pergamon, was a Roman and Greek physician, surgeon, and philosopher. Considered to be one of the most accomplished of all...
Νίκος Σβορώνος
 3
Ο Νίκος Σβορώνος ήταν σημαντικός Έλληνας ιστορικός με ιδιαίτερη επιρροή στη σύγχρονη ιστοριογραφία στην Ελλάδα.
3
Ο Νίκος Σβορώνος ήταν σημαντικός Έλληνας ιστορικός με ιδιαίτερη επιρροή στη σύγχρονη ιστοριογραφία στην Ελλάδα.
Antigonus I Monophthalmus
 3
Antigonus I Monophthalmus was a Macedonian Greek general and successor of Alexander the Great. A prominent military leader in Alexander's army, he went on to control large parts of Alexander's former...
3
Antigonus I Monophthalmus was a Macedonian Greek general and successor of Alexander the Great. A prominent military leader in Alexander's army, he went on to control large parts of Alexander's former...
Saint Stephen
 3
Stephen is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first martyr of Christianity. According to the Acts of the Apostles, he was a deacon in the early church at Jerusalem who angered members of...
3
Stephen is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first martyr of Christianity. According to the Acts of the Apostles, he was a deacon in the early church at Jerusalem who angered members of...
Polybius
 3
Polybius was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work The Histories, a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second...
3
Polybius was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work The Histories, a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second...
Zeus
 3
Zeus is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus. His name is cognate with the first syllable of his Roman equivalent Jupiter.
3
Zeus is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus. His name is cognate with the first syllable of his Roman equivalent Jupiter.
Georgios Drossinis
 3
Georgios Drosinis was a Greek author, poet, scholar and an editor. He is considered to be a co-founder of the New Athenian School.
3
Georgios Drosinis was a Greek author, poet, scholar and an editor. He is considered to be a co-founder of the New Athenian School.
Antonis Katsantonis
 3
Antonis Katsantonis was a notable Greek klepht who lived in the era before the Greek War of Independence.
3
Antonis Katsantonis was a notable Greek klepht who lived in the era before the Greek War of Independence.
Alexandros Mavrokordatos
 3
Alexandros Mavrokordatos was a Greek statesman, diplomat, politician and member of the Mavrocordatos family of Phanariotes.
3
Alexandros Mavrokordatos was a Greek statesman, diplomat, politician and member of the Mavrocordatos family of Phanariotes.
Δημήτριος Μπισκίνης
 3
Ο Δημήτριος Α. Μπισκίνης ήταν Έλληνας ζωγράφος της ακαδημαϊκής σχολής.
3
Ο Δημήτριος Α. Μπισκίνης ήταν Έλληνας ζωγράφος της ακαδημαϊκής σχολής.
Sophie de Marbois-Lebrun, Duchess of Plaisance
 3
Sophie de Marbois-Lebrun, Duchess of Plaisance (1785–1854) was a French noblewoman, known as an important figure in Greek high society the first decades after Greek independence. She was born in...
3
Sophie de Marbois-Lebrun, Duchess of Plaisance (1785–1854) was a French noblewoman, known as an important figure in Greek high society the first decades after Greek independence. She was born in...
Aesop
 3
Aesop was a Greek fabulist and storyteller credited with a number of fables now collectively known as Aesop's Fables. Although his existence remains unclear and no writings by him survive, numerous...
3
Aesop was a Greek fabulist and storyteller credited with a number of fables now collectively known as Aesop's Fables. Although his existence remains unclear and no writings by him survive, numerous...
Pandora
 3
In Greek mythology, Pandora was the first human woman created by Hephaestus on the instructions of Zeus. As Hesiod related it, each god cooperated by giving her unique gifts. Her other name—inscribed...
3
In Greek mythology, Pandora was the first human woman created by Hephaestus on the instructions of Zeus. As Hesiod related it, each god cooperated by giving her unique gifts. Her other name—inscribed...
Alcyone and Ceyx
 3
In Greek mythology, Alcyone and Ceyx were a wife and husband who incurred the wrath of the god Zeus for their romantic hubris.
3
In Greek mythology, Alcyone and Ceyx were a wife and husband who incurred the wrath of the god Zeus for their romantic hubris.
Georgios Grivas
 3
Georgios Grivas, also known by his nickname Digenis, was the Cypriot founder and leader of the Greek and Greek Cypriot paramilitary organisations Organization X (1942–1949), EOKA (1955–1959) and EOKA...
3
Georgios Grivas, also known by his nickname Digenis, was the Cypriot founder and leader of the Greek and Greek Cypriot paramilitary organisations Organization X (1942–1949), EOKA (1955–1959) and EOKA...
Constantine Paparrigopoulos
 3
Constantine Paparrigopoulos was a Greek historian, who is considered the founder of modern Greek historiography. He is the founder of the concept of historical continuity of Greece from antiquity to...
3
Constantine Paparrigopoulos was a Greek historian, who is considered the founder of modern Greek historiography. He is the founder of the concept of historical continuity of Greece from antiquity to...
Odysseas Elytis
 3
Odysseas Elytis was a Greek poet, man of letters, essayist and translator, regarded as the definitive exponent of romantic modernism in Greece and the world. He is one of the most praised poets of...
3
Odysseas Elytis was a Greek poet, man of letters, essayist and translator, regarded as the definitive exponent of romantic modernism in Greece and the world. He is one of the most praised poets of...
Νικηφόρος Μανδηλαράς
 3
Ο Νικηφόρος Μανδηλαράς ήταν Έλληνας νομικός, δημοσιογράφος και εκδότης εφημερίδας. Είναι περισσότερο γνωστός ως δικηγόρος υπερασπίσεως στη δίκη για την υπόθεση ΑΣΠΙΔΑ που ποτέ δεν ολοκληρώθηκε....
3
Ο Νικηφόρος Μανδηλαράς ήταν Έλληνας νομικός, δημοσιογράφος και εκδότης εφημερίδας. Είναι περισσότερο γνωστός ως δικηγόρος υπερασπίσεως στη δίκη για την υπόθεση ΑΣΠΙΔΑ που ποτέ δεν ολοκληρώθηκε....
Menas of Egypt
 3
Menas of Egypt, a martyr and wonder-worker, is one of the most well-known Coptic saints in the East and the West, due to the many miracles that are attributed to his intercession and prayers. Menas...
3
Menas of Egypt, a martyr and wonder-worker, is one of the most well-known Coptic saints in the East and the West, due to the many miracles that are attributed to his intercession and prayers. Menas...
Saint Kyriaki
Ambrosios Pleianthidis
 3
Ambrosios Pleiathidis also known as Ambrosios of Moschonisia was the Greek Orthodox metropolitan bishop of Moschonisia, in modern Turkey, from February to September 1922. He was executed by the...
3
Ambrosios Pleiathidis also known as Ambrosios of Moschonisia was the Greek Orthodox metropolitan bishop of Moschonisia, in modern Turkey, from February to September 1922. He was executed by the...
Mary, mother of Jesus
 3
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under various titles such as virgin or queen, many of...
3
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under various titles such as virgin or queen, many of...
Agamemnon
 3
In Greek mythology, Agamemnon was a king of Mycenae who commanded the Achaeans during the Trojan War. He was the son of King Atreus and Queen Aerope, the brother of Menelaus, the husband of...
3
In Greek mythology, Agamemnon was a king of Mycenae who commanded the Achaeans during the Trojan War. He was the son of King Atreus and Queen Aerope, the brother of Menelaus, the husband of...
Diagoras of Rhodes
 3
Diagoras of Rhodes was an Ancient Greek boxer from the 5th century BC, who was celebrated for his own victories, as well as the victories of his sons and grandsons. He was a member of the Eratidea...
3
Diagoras of Rhodes was an Ancient Greek boxer from the 5th century BC, who was celebrated for his own victories, as well as the victories of his sons and grandsons. He was a member of the Eratidea...
Emmanouil Benakis
 3
Emmanouil Benakis was a Greek merchant and politician, considered a national benefactor of Greece.
3
Emmanouil Benakis was a Greek merchant and politician, considered a national benefactor of Greece.
Periander
 3
Periander was the second tyrant of the Cypselid dynasty that ruled over ancient Corinth. Periander's rule brought about a prosperous time in Corinth's history, as his administrative skill made...
3
Periander was the second tyrant of the Cypselid dynasty that ruled over ancient Corinth. Periander's rule brought about a prosperous time in Corinth's history, as his administrative skill made...
Dionysios of Zakynthos
 3
Saint Dionysios of Zakynthos was a 16th-century Orthodox Christian Archbishop of Aegina. He was born on the Greek island of Zakynthos in 1547. He is the patron saint of Zakynthos and is celebrated on...
3
Saint Dionysios of Zakynthos was a 16th-century Orthodox Christian Archbishop of Aegina. He was born on the Greek island of Zakynthos in 1547. He is the patron saint of Zakynthos and is celebrated on...
Romanos the Melodist
 3
Romanos the Melodist was a Byzantine hymnographer and composer, who is a central early figure in the history of Byzantine music. Called "the Pindar of rhythmic poetry", he flourished during the sixth...
3
Romanos the Melodist was a Byzantine hymnographer and composer, who is a central early figure in the history of Byzantine music. Called "the Pindar of rhythmic poetry", he flourished during the sixth...
Panagiotis Danglis
 3
Panagiotis Danglis was a Hellenic Army general and politician. He is particularly notable for his invention of the Schneider-Danglis mountain gun, his service as chief of staff in the Balkan Wars and...
3
Panagiotis Danglis was a Hellenic Army general and politician. He is particularly notable for his invention of the Schneider-Danglis mountain gun, his service as chief of staff in the Balkan Wars and...
Ioannis Velissariou
 3
Ioannis Velissariou was a Hellenic Army officer and hero of the Balkan Wars. He is considered to be one of the most important figures in the military history of modern Greece. He had a decisive role...
3
Ioannis Velissariou was a Hellenic Army officer and hero of the Balkan Wars. He is considered to be one of the most important figures in the military history of modern Greece. He had a decisive role...
Epaminondas
 3
Epaminondas was a Greek general and statesman of the 4th century BC who transformed the Ancient Greek city-state of Thebes, leading it out of Spartan subjugation into a pre-eminent position in Greek...
3
Epaminondas was a Greek general and statesman of the 4th century BC who transformed the Ancient Greek city-state of Thebes, leading it out of Spartan subjugation into a pre-eminent position in Greek...
Sappho
 3
Sappho was an Archaic Greek poet from Eresos or Mytilene on the island of Lesbos. Sappho is known for her lyric poetry, written to be sung while accompanied by music. In ancient times, Sappho was...
3
Sappho was an Archaic Greek poet from Eresos or Mytilene on the island of Lesbos. Sappho is known for her lyric poetry, written to be sung while accompanied by music. In ancient times, Sappho was...
Idomeneus of Crete
 3
In Greek mythology, Idomeneus was a Cretan king and commander who led the Cretan armies to the Trojan War, in eighty black ships. He was also one of the suitors of Helen, as well as a comrade of the...
3
In Greek mythology, Idomeneus was a Cretan king and commander who led the Cretan armies to the Trojan War, in eighty black ships. He was also one of the suitors of Helen, as well as a comrade of the...
Three Holy Hierarchs
 3
The Three Hierarchs of Eastern Christianity refers to Basil the Great, Gregory the Theologian and John Chrysostom. They were highly influential bishops of the early church who played pivotal roles in...
3
The Three Hierarchs of Eastern Christianity refers to Basil the Great, Gregory the Theologian and John Chrysostom. They were highly influential bishops of the early church who played pivotal roles in...
Andromache
 3
In Greek mythology, Andromache was the wife of Hector, daughter of Eetion, and sister to Podes. She was born and raised in the city of Cilician Thebe, over which her father ruled. The name means 'man...
3
In Greek mythology, Andromache was the wife of Hector, daughter of Eetion, and sister to Podes. She was born and raised in the city of Cilician Thebe, over which her father ruled. The name means 'man...
Pisistratus
 3
Pisistratus was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular peninsula of Greece...
3
Pisistratus was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular peninsula of Greece...
Ιωάννης Γρυπάρης (λογοτέχνης)
Aris Velouchiotis
 3
Athanasios Klaras, better known by the nom de guerre Aris Velouchiotis, was a Greek journalist, politician, member of the Communist Party of Greece, the most prominent leader and chief instigator of...
3
Athanasios Klaras, better known by the nom de guerre Aris Velouchiotis, was a Greek journalist, politician, member of the Communist Party of Greece, the most prominent leader and chief instigator of...
Eleutherius and Antia
 3
Eleutherius, also written as Eleutherus, Eleuterus and Eleftherios; sometimes called Liberalis or Liberator, the former transliterations and the latter translations of his and his mother Antia are...
3
Eleutherius, also written as Eleutherus, Eleuterus and Eleftherios; sometimes called Liberalis or Liberator, the former transliterations and the latter translations of his and his mother Antia are...
Makarios III
 3
Makarios III was a Greek Cypriot archbishop, primate, statesman and politician, who served as the first President of Cyprus between 1960 and 1977. He was also the Archbishop of the autocephalous...
3
Makarios III was a Greek Cypriot archbishop, primate, statesman and politician, who served as the first President of Cyprus between 1960 and 1977. He was also the Archbishop of the autocephalous...
Marcus Junius Brutus
 3
Marcus Junius Brutus was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Servilius Caepio Brutus, which...
3
Marcus Junius Brutus was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Servilius Caepio Brutus, which...
Κιθαιρών (μυθολογία)
 3
Στην ελληνική μυθολογία ο Κιθαιρών (Κιθαιρώνας) ήταν ένας βασιλιάς των Πλαταιών, από τον οποίο κατά την μυθολογία πήρε το όνομά του, το γειτονικό ομώνυμο βουνό Κιθαιρώνας. Ο Κιθαιρών βασίλευσε πριν...
3
Στην ελληνική μυθολογία ο Κιθαιρών (Κιθαιρώνας) ήταν ένας βασιλιάς των Πλαταιών, από τον οποίο κατά την μυθολογία πήρε το όνομά του, το γειτονικό ομώνυμο βουνό Κιθαιρώνας. Ο Κιθαιρών βασίλευσε πριν...
Andreas Laskaratos
 3
Andreas Laskaratos was a satirical poet and writer from the Ionian island of Cefalonia, representative of the Heptanese School (literature). He was excommunicated by the Greek Orthodox Church because...
3
Andreas Laskaratos was a satirical poet and writer from the Ionian island of Cefalonia, representative of the Heptanese School (literature). He was excommunicated by the Greek Orthodox Church because...
Demetrios I of Constantinople
 3
Demetrios I, also Dimitrios I or Demetrius I, born Demetrios Papadopoulos, was the 269th Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from July 16, 1972, to October 2, 1991, serving as the spiritual leader...
3
Demetrios I, also Dimitrios I or Demetrius I, born Demetrios Papadopoulos, was the 269th Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from July 16, 1972, to October 2, 1991, serving as the spiritual leader...
Anthimos Gazis
 3
Anthimos Gazis or Gazes was a Greek scholar, revolutionary and politician. He was born in Milies (Thessaly) in Ottoman Greece in 1758 into a family of modest means. In 1774 he became an Eastern...
3
Anthimos Gazis or Gazes was a Greek scholar, revolutionary and politician. He was born in Milies (Thessaly) in Ottoman Greece in 1758 into a family of modest means. In 1774 he became an Eastern...
Constantine P. Cavafy
 3
Konstantinos Petrou Kavafis, known, especially in English, as Constantine P. Cavafy and often published as C. P. Cavafy, was a Greek poet, journalist, and civil servant from Alexandria. A major...
3
Konstantinos Petrou Kavafis, known, especially in English, as Constantine P. Cavafy and often published as C. P. Cavafy, was a Greek poet, journalist, and civil servant from Alexandria. A major...
Georgios Vizyinos
Ιωάννης Κονδυλάκης
 3
Ο Ιωάννης Κονδυλάκης (1861−1920) ήταν Έλληνας λογοτέχνης, διηγηματογράφος, δημοσιογράφος και χρονογράφος. Ήταν ο πρώτος πρόεδρος της ΕΣΗΕΑ και από τα γνωστότερα έργα του είναι ο Πατούχας και "Όταν...
3
Ο Ιωάννης Κονδυλάκης (1861−1920) ήταν Έλληνας λογοτέχνης, διηγηματογράφος, δημοσιογράφος και χρονογράφος. Ήταν ο πρώτος πρόεδρος της ΕΣΗΕΑ και από τα γνωστότερα έργα του είναι ο Πατούχας και "Όταν...
Seleucus I Nicator
 3
Seleucus I Nicator was a Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the eponymous Seleucid Empire, led by the Seleucid dynasty. Initially a secondary...
3
Seleucus I Nicator was a Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the eponymous Seleucid Empire, led by the Seleucid dynasty. Initially a secondary...
Elijah
 3
Elijah was, according to the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible, a prophet and a miracle worker who lived in the northern kingdom of Israel during the reign of King Ahab.
3
Elijah was, according to the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible, a prophet and a miracle worker who lived in the northern kingdom of Israel during the reign of King Ahab.
Andreas Kalvos
 3
Andreas Kalvos was a Greek poet of the Romantic school. He published five volumes of poetry and drama - Canzone... (1811), Le Danaidi (1818), Elpis patridos (1818), Lyra (1824) and New odes (1826)....
3
Andreas Kalvos was a Greek poet of the Romantic school. He published five volumes of poetry and drama - Canzone... (1811), Le Danaidi (1818), Elpis patridos (1818), Lyra (1824) and New odes (1826)....
Iro Konstantopoulou
 3
Iro Konstantopoulou was a member of the Greek resistance during World War II. She worked with the resistance in Greece to oppose the Axis occupation of the country for three years before being...
3
Iro Konstantopoulou was a member of the Greek resistance during World War II. She worked with the resistance in Greece to oppose the Axis occupation of the country for three years before being...
Margaret the Virgin
 3
Margaret, known as Margaret of Antioch in the West, and as Saint Marina the Great Martyr in the East, is celebrated as a saint on 20 July in Western Christianity, on 30th of July by the Eastern...
3
Margaret, known as Margaret of Antioch in the West, and as Saint Marina the Great Martyr in the East, is celebrated as a saint on 20 July in Western Christianity, on 30th of July by the Eastern...